[Swift]LeetCode218. 天际线问题 | The Skyline Problem
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(shanqingyongzhi)
➤博客园地址:山青咏芝(https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/)
➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode
➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/p/10198037.html
➤如果链接不是山青咏芝的博客园地址,则可能是爬取作者的文章。
➤原文已修改更新!强烈建议点击原文地址阅读!支持作者!支持原创!
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
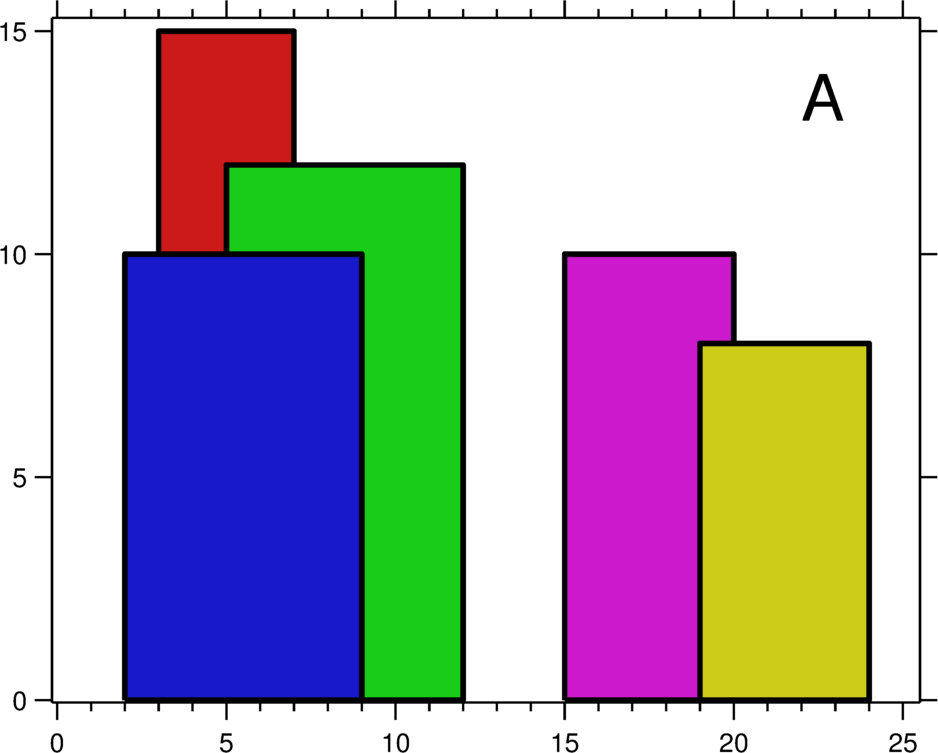
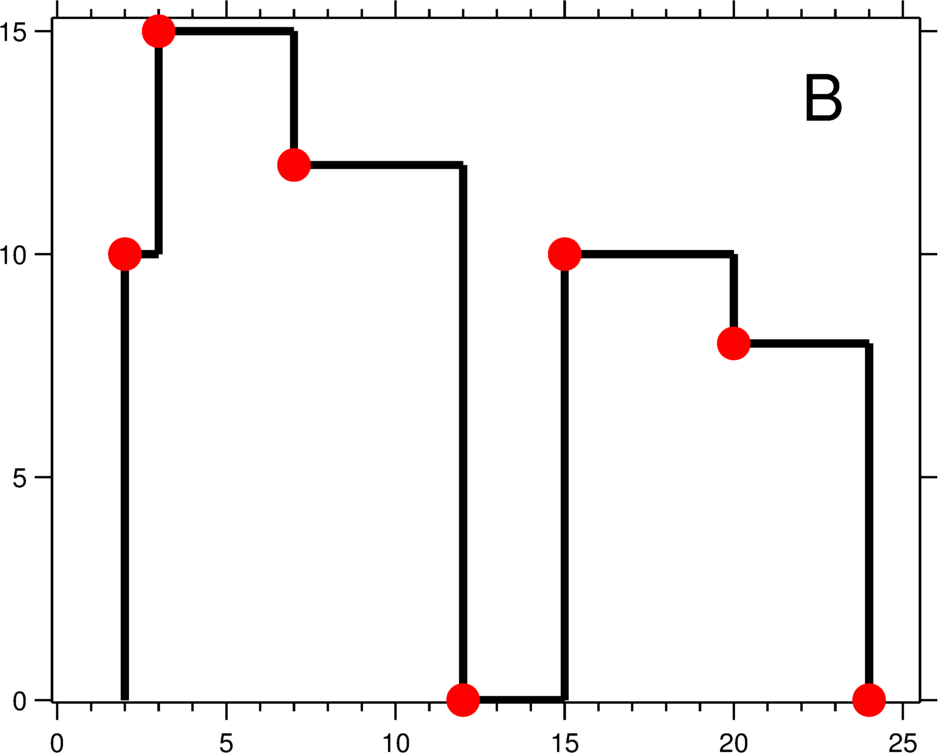
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Now suppose you are given the locations and height of all the buildings as shown on a cityscape photo (Figure A), write a program to output the skylineformed by these buildings collectively (Figure B).
The geometric information of each building is represented by a triplet of integers [Li, Ri, Hi], where Li and Ri are the x coordinates of the left and right edge of the ith building, respectively, and Hi is its height. It is guaranteed that 0 ≤ Li, Ri ≤ INT_MAX, 0 < Hi ≤ INT_MAX, and Ri - Li > 0. You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
For instance, the dimensions of all buildings in Figure A are recorded as: [ [2 9 10], [3 7 15], [5 12 12], [15 20 10], [19 24 8] ] .
The output is a list of "key points" (red dots in Figure B) in the format of [ [x1,y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], ... ] that uniquely defines a skyline. A key point is the left endpoint of a horizontal line segment. Note that the last key point, where the rightmost building ends, is merely used to mark the termination of the skyline, and always has zero height. Also, the ground in between any two adjacent buildings should be considered part of the skyline contour.
For instance, the skyline in Figure B should be represented as:[ [2 10], [3 15], [7 12], [12 0], [15 10], [20 8], [24, 0] ].
Notes:
- The number of buildings in any input list is guaranteed to be in the range
[0, 10000]. - The input list is already sorted in ascending order by the left x position
Li. - The output list must be sorted by the x position.
- There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance,
[...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...]is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
城市的天际线是从远处观看该城市中所有建筑物形成的轮廓的外部轮廓。现在,假设您获得了城市风光照片(图A)上显示的所有建筑物的位置和高度,请编写一个程序以输出由这些建筑物形成的天际线(图B)。
每个建筑物的几何信息用三元组 [Li,Ri,Hi] 表示,其中 Li 和 Ri分别是第 i 座建筑物左右边缘的 x 坐标,Hi 是其高度。可以保证 0 ≤ Li, Ri ≤ INT_MAX, 0 < Hi ≤ INT_MAX 和 Ri - Li > 0。您可以假设所有建筑物都是在绝对平坦且高度为 0 的表面上的完美矩形。
例如,图A中所有建筑物的尺寸记录为:[ [2 9 10], [3 7 15], [5 12 12], [15 20 10], [19 24 8] ] 。
输出是以 [ [x1,y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], ... ] 格式的“关键点”(图B中的红点)的列表,它们唯一地定义了天际线。关键点是水平线段的左端点。请注意,最右侧建筑物的最后一个关键点仅用于标记天际线的终点,并始终为零高度。此外,任何两个相邻建筑物之间的地面都应被视为天际线轮廓的一部分。
例如,图B中的天际线应该表示为:[ [2 10], [3 15], [7 12], [12 0], [15 10], [20 8], [24, 0] ]。
说明:
- 任何输入列表中的建筑物数量保证在
[0, 10000]范围内。 - 输入列表已经按升序排列在左边的 x 位置
Li。 - 输出列表必须按 x 位排序。
- 输出天际线中不得有连续的相同高度的水平线。例如
[...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...]是不正确的答案;三条高度为 5 的线应该在最终输出中合并为一个:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
264ms
1 class Solution { 2 func getSkyline(_ buildings: [[Int]]) -> [[Int]] { 3 var queue = [[Int]]() 4 for building in buildings { 5 let begin = [building[0],building[2]] 6 let end = [building[1], -building[2]] 7 queue.append(begin) 8 queue.append(end) 9 } 10 11 queue.sort { (nums1, nums2) -> Bool in 12 if nums1[0] == nums2[0] { 13 return nums1[1] > nums2[1] 14 } 15 16 return nums1[0] < nums2[0] 17 } 18 19 20 var res = [[Int]]() 21 var heights = Heap(array: [Int](), sort: >) 22 var removes = Heap(array: [Int](), sort: >) 23 var pHeight = 0 24 for line in queue { 25 let h = line[1] 26 27 if h > 0 { 28 if h > pHeight { 29 res.append([line[0],h]) 30 } 31 heights.insert(h) 32 pHeight = heights.peek()! 33 }else { 34 removes.insert(-h) 35 while !heights.isEmpty && !removes.isEmpty && heights.peek()! == removes.peek()! { 36 heights.remove() 37 removes.remove() 38 } 39 pHeight = heights.peek() ?? 0 40 if -h > pHeight { 41 res.append([line[0],pHeight]) 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 return res 46 } 47 48 public struct Heap<T> { 49 var nodes = [T]() 50 51 private var orderCriteria:(T,T) -> Bool 52 53 public init(sort:@escaping (T,T) -> Bool) { 54 self.orderCriteria = sort 55 } 56 57 public init(array:[T],sort:@escaping(T, T) -> Bool) { 58 self.orderCriteria = sort 59 configureHeap(from:array) 60 } 61 62 private mutating func configureHeap(from array:[T]) { 63 nodes = array 64 for i in stride(from: (nodes.count - 1) / 2, through: 0, by: -1) { 65 shiftDown(i) 66 } 67 } 68 69 public var isEmpty:Bool { 70 return nodes.isEmpty 71 } 72 73 public var count : Int { 74 return nodes.count 75 } 76 77 @inline(__always) internal func parentIndex(ofIndex i : Int) -> Int { 78 return (i - 1) / 2 79 } 80 81 @inline(__always) internal func leftChildIndex(ofIndex i : Int) -> Int { 82 return 2 * i + 1 83 } 84 85 @inline(__always) internal func rightChildIndex(ofIndex i : Int) -> Int { 86 return 2 * i + 2 87 } 88 89 public func peek() -> T? { 90 return nodes.first 91 } 92 93 public mutating func insert(_ value: T) { 94 nodes.append(value) 95 shiftUp(nodes.count - 1) 96 } 97 98 public mutating func insert<S:Sequence>(_ sequence: S) where S.Iterator.Element == T { 99 for value in sequence { 100 insert(value) 101 } 102 } 103 104 @discardableResult public mutating func remove() -> T? { 105 guard !isEmpty else {return nil} 106 if nodes.count == 1 { 107 return nodes.removeFirst() 108 }else { 109 let value = nodes[0] 110 nodes[0] = nodes.removeLast() 111 shiftDown(0) 112 return value 113 } 114 } 115 116 117 @discardableResult public mutating func remove(at index: Int) -> T? { 118 guard index < count else {return nil} 119 120 let size = nodes.count - 1 121 if index != count { 122 nodes.swapAt(index, size) 123 shiftDown(form: index, until: size) 124 shiftUp(index) 125 } 126 127 return nodes.removeLast() 128 129 } 130 131 internal mutating func shiftUp(_ index : Int) { 132 var childIndex = index 133 let child = nodes[childIndex] 134 var parentIndex = self.parentIndex(ofIndex: childIndex) 135 136 while childIndex > 0 && orderCriteria(child, nodes[parentIndex]) { 137 nodes[childIndex] = nodes[parentIndex] 138 childIndex = parentIndex 139 parentIndex = self.parentIndex(ofIndex: childIndex) 140 } 141 nodes[childIndex] = child 142 } 143 144 internal mutating func shiftDown(form index: Int, until endIndex: Int) { 145 let leftChildIndex = self.leftChildIndex(ofIndex: index) 146 let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1 147 var first = index 148 if leftChildIndex < endIndex && orderCriteria(nodes[leftChildIndex], nodes[first]) { 149 first = leftChildIndex 150 } 151 152 if rightChildIndex < endIndex && orderCriteria(nodes[rightChildIndex], nodes[first]) { 153 first = rightChildIndex 154 } 155 if first == index {return} 156 nodes.swapAt(index, first) 157 shiftDown(form: first, until: endIndex) 158 } 159 160 internal mutating func shiftDown(_ index:Int) { 161 162 shiftDown(form: index, until: nodes.count) 163 } 164 165 } 166 }
676ms
1 class Solution { 2 func getSkyline(_ buildings: [[Int]]) -> [[Int]] { 3 var points: [Int] = [] 4 for building in buildings { 5 points.append(building[0]) 6 points.append(building[1]) 7 } 8 points.sort() 9 10 var segs = [Int](repeating: 0, count: points.count) 11 12 var pos = 0 13 for building in buildings { 14 // find start point 15 while points[pos] < building[0] { pos += 1 } 16 // go to end 17 var i = pos 18 19 while points[i] < building[1] { 20 if segs[i] < building[2] { 21 segs[i] = building[2] 22 } 23 i += 1 24 } 25 } 26 27 var result: [[Int]] = [] 28 var currHeight = 0 29 for (index, h) in segs.enumerated() { 30 if currHeight != h { 31 result.append([points[index], h]) 32 currHeight = h 33 } 34 } 35 36 return result 37 } 38 }
1660ms
1 class Solution { 2 public struct PriorityQueue<T: Comparable> { 3 4 fileprivate var heap = [T]() 5 private let ordered: (T, T) -> Bool 6 7 public init(ascending: Bool = false, startingValues: [T] = []) { 8 self.init(order: ascending ? { $0 > $1 } : { $0 < $1 }, startingValues: startingValues) 9 } 10 11 /// Creates a new PriorityQueue with the given ordering. 12 /// 13 /// - parameter order: A function that specifies whether its first argument should 14 /// come after the second argument in the PriorityQueue. 15 /// - parameter startingValues: An array of elements to initialize the PriorityQueue with. 16 public init(order: @escaping (T, T) -> Bool, startingValues: [T] = []) { 17 ordered = order 18 19 // Based on "Heap construction" from Sedgewick p 323 20 heap = startingValues 21 var i = heap.count/2 - 1 22 while i >= 0 { 23 sink(i) 24 i -= 1 25 } 26 } 27 28 /// How many elements the Priority Queue stores 29 public var count: Int { return heap.count } 30 31 /// true if and only if the Priority Queue is empty 32 public var isEmpty: Bool { return heap.isEmpty } 33 34 /// Add a new element onto the Priority Queue. O(lg n) 35 /// 36 /// - parameter element: The element to be inserted into the Priority Queue. 37 public mutating func push(_ element: T) { 38 heap.append(element) 39 swim(heap.count - 1) 40 } 41 42 /// Remove and return the element with the highest priority (or lowest if ascending). O(lg n) 43 /// 44 /// - returns: The element with the highest priority in the Priority Queue, or nil if the PriorityQueue is empty. 45 public mutating func pop() -> T? { 46 47 if heap.isEmpty { return nil } 48 if heap.count == 1 { return heap.removeFirst() } // added for Swift 2 compatibility 49 // so as not to call swap() with two instances of the same location 50 heap.swapAt(0, heap.count - 1) 51 let temp = heap.removeLast() 52 sink(0) 53 54 return temp 55 } 56 57 58 /// Removes the first occurence of a particular item. Finds it by value comparison using ==. O(n) 59 /// Silently exits if no occurrence found. 60 /// 61 /// - parameter item: The item to remove the first occurrence of. 62 public mutating func remove(_ item: T) { 63 if let index = heap.index(of: item) { 64 heap.swapAt(index, heap.count - 1) 65 heap.removeLast() 66 if index < heap.count { // if we removed the last item, nothing to swim 67 swim(index) 68 sink(index) 69 } 70 } 71 } 72 73 /// Removes all occurences of a particular item. Finds it by value comparison using ==. O(n) 74 /// Silently exits if no occurrence found. 75 /// 76 /// - parameter item: The item to remove. 77 public mutating func removeAll(_ item: T) { 78 var lastCount = heap.count 79 remove(item) 80 while (heap.count < lastCount) { 81 lastCount = heap.count 82 remove(item) 83 } 84 } 85 86 /// Get a look at the current highest priority item, without removing it. O(1) 87 /// 88 /// - returns: The element with the highest priority in the PriorityQueue, or nil if the PriorityQueue is empty. 89 public func peek() -> T? { 90 return heap.first 91 } 92 93 /// Eliminate all of the elements from the Priority Queue. 94 public mutating func clear() { 95 heap.removeAll(keepingCapacity: false) 96 } 97 98 // Based on example from Sedgewick p 316 99 private mutating func sink(_ index: Int) { 100 var index = index 101 while 2 * index + 1 < heap.count { 102 103 var j = 2 * index + 1 104 105 if j < (heap.count - 1) && ordered(heap[j], heap[j + 1]) { j += 1 } 106 if !ordered(heap[index], heap[j]) { break } 107 108 heap.swapAt(index, j) 109 index = j 110 } 111 } 112 113 // Based on example from Sedgewick p 316 114 private mutating func swim(_ index: Int) { 115 var index = index 116 while index > 0 && ordered(heap[(index - 1) / 2], heap[index]) { 117 heap.swapAt((index - 1) / 2, index) 118 index = (index - 1) / 2 119 } 120 } 121 } 122 123 func getSkyline(_ buildings: [[Int]]) -> [[Int]] { 124 var heights: [(pos: Int, h: Int)] = [] 125 for building in buildings { 126 heights.append((building[0], -building[2])) 127 heights.append((building[1], building[2])) 128 } 129 heights.sort { (a, b) in 130 if (a.pos == b.pos) { 131 return a.h < b.h 132 } else { 133 return a.pos < b.pos 134 } 135 } 136 137 var heap = PriorityQueue<Int>() 138 var result: [[Int]] = [] 139 var prev = 0 140 141 heap.push(0) 142 for h in heights { 143 if (h.h < 0) { 144 heap.push(-h.h) 145 } else { 146 heap.remove(h.h) 147 } 148 if let curr = heap.peek(), prev != curr { 149 result.append([h.pos, curr]) 150 prev = curr 151 } 152 } 153 154 return result 155 } 156 }
1712ms
1 class PriorityQueue<T> { 2 private var heap: [T] = [T]() 3 private let ordered: (T, T) -> Bool 4 5 init(order: @escaping (T, T) -> Bool) { 6 self.ordered = order 7 } 8 9 var isEmpty: Bool { 10 return heap.isEmpty 11 } 12 var count: Int { 13 return heap.count 14 } 15 16 func push(_ element: T) { 17 heap.append(element) 18 swim(heap.count - 1) 19 } 20 21 func pop() -> T? { 22 if self.isEmpty { 23 return nil 24 } 25 26 if self.heap.count == 1 { 27 return heap.remove(at: 0) 28 } 29 30 heap.swapAt(0, heap.count - 1) 31 let temp = heap.removeLast() 32 sink(0) 33 return temp 34 } 35 36 func peek() -> T? { 37 if self.isEmpty { 38 return nil 39 } 40 41 return self.heap[0] 42 } 43 44 private func sink(_ index: Int) { 45 var index = index 46 while 2 * index + 1 < heap.count { 47 let leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1 48 49 var first = index 50 if leftChildIndex < heap.count && ordered(heap[leftChildIndex], heap[first]) { 51 first = leftChildIndex 52 } 53 54 let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1 55 if rightChildIndex < heap.count && ordered(heap[rightChildIndex], heap[first]) { 56 first = rightChildIndex 57 } 58 59 if index == first { 60 break 61 } 62 63 heap.swapAt(index, first) 64 index = first 65 } 66 } 67 68 private func swim(_ index: Int) { 69 var index = index 70 while index > 0 && ordered(heap[index], heap[(index - 1) / 2]) { 71 heap.swapAt((index - 1) / 2, index) 72 index = (index - 1) / 2 73 } 74 } 75 } 76 77 extension PriorityQueue where T: Comparable { 78 func remove(_ element: T) { 79 if let index = heap.index(of: element) { 80 heap.swapAt(index, heap.count - 1) 81 heap.removeLast() 82 if index < heap.count { 83 swim(index) 84 sink(index) 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 } 89 90 class Solution { 91 class Point { 92 var pos: Int 93 var height: Int 94 var isStart: Bool 95 96 init(_ pos: Int, _ height: Int, _ isStart: Bool) { 97 self.pos = pos 98 self.height = height 99 self.isStart = isStart 100 } 101 } 102 103 func getSkyline(_ buildings: [[Int]]) -> [[Int]] { 104 guard buildings.count > 0 && buildings[0].count > 0 else { 105 return [] 106 } 107 108 var positions = Array(repeating: Point(0, 0, false), count: buildings.count * 2) 109 for idx in 0 ..< buildings.count { 110 let start = Point(buildings[idx][0], buildings[idx][2], true) 111 positions[idx * 2] = start 112 113 let end = Point(buildings[idx][1], buildings[idx][2], false) 114 positions[idx * 2 + 1] = end 115 } 116 117 positions.sort { pt1, pt2 in 118 if pt1.pos != pt2.pos { 119 return pt1.pos < pt2.pos 120 } 121 122 if pt1.isStart && pt2.isStart { 123 return pt1.height > pt2.height 124 } 125 126 if !pt1.isStart && !pt2.isStart { 127 return pt1.height < pt2.height 128 } 129 130 return pt1.isStart 131 } 132 133 let queue = PriorityQueue<Int>(order: >) 134 queue.push(0) 135 136 var result: [[Int]] = [] 137 var preMaxVal = 0 138 for point in positions { 139 if point.isStart { 140 queue.push(point.height) 141 let curMaxVal = queue.peek()! 142 if curMaxVal > preMaxVal { 143 result.append([point.pos, point.height]) 144 preMaxVal = curMaxVal 145 } 146 } else { 147 queue.remove(point.height) 148 let curMaxVal = queue.peek()! 149 if curMaxVal < preMaxVal { 150 result.append([point.pos, curMaxVal]) 151 preMaxVal = curMaxVal 152 } 153 } 154 } 155 156 return result 157 } 158 }
1916ms
1 class Solution { 2 func getSkyline(_ buildings: [[Int]]) -> [[Int]] { 3 if buildings.count == 0 { 4 return [] 5 } 6 if buildings.count == 1 { 7 let b = buildings[0] 8 let x1 = b[0]; let x2 = b[1]; let y = b[2] 9 return [[x1, y], [x2, 0]] 10 } 11 var bsplit: [(Int, Int, Bool)] = [] 12 for b in buildings { 13 let x1 = b[0]; let x2 = b[1]; let y = b[2] 14 bsplit.append((x1, y, false)) 15 bsplit.append((x2, y, true)) 16 } 17 // TODO replace h with priority queue 18 var h: [(Int, Int)] = [] 19 let s1: ((Int, Int), (Int, Int)) -> Bool = { 20 $0.1 > $1.1 21 || ($0.1 == $1.1 && $0.0 > $0.1) 22 } 23 let so: ((Int, Int, Bool), (Int, Int, Bool)) -> Bool = { 24 $0.0 < $1.0 25 || ($0.0 == $1.0 && $0.2 == false && $1.2 == true) 26 || ($0.0 == $1.0 && $0.1 > $1.1) 27 } 28 let buildingsSorted = bsplit.sorted(by: so) 29 // print("buildingsSorted \(buildingsSorted)") 30 var ans: [[Int]] = [] 31 for i in 0..<buildingsSorted.count { 32 let b = buildingsSorted[i] 33 let bx = b.0; let by = b.1; let close = b.2 == true 34 // print("b \(b) h \(h)") 35 if h.count == 0 { 36 h.append((bx, by)) 37 ans.append([bx, by]) 38 continue 39 } 40 if close { 41 if let index = h.firstIndex(where: {$0.1 == by}) { 42 h.remove(at: index) 43 if h.count == 0 { ans.append([bx, 0]) } 44 if let l = h.first { 45 if l.1 < by { ans.append([bx, l.1]) } 46 } 47 } 48 continue 49 } 50 // print("b \(b) h \(h)") 51 if let l = h.first { 52 if l.1 < by { ans.append([bx, by]) } 53 // print("l.1 \(l.1) by \(by) x3 ans \(ans)") 54 } 55 if let index = h.firstIndex(where: { $0.1 < by }) { 56 h.insert((bx, by), at:index) 57 } else { 58 h.append((bx, by)) 59 } 60 /* 61 h.append((bx, by)) 62 h.sort(by: s1) // need to optimize??? 63 */ 64 // print("hx \(h)") 65 } 66 // print("ans \(ans)") 67 var i = 1 68 while i < ans.count { 69 // print("i \(i) ans \(ans)") 70 if ans[i][0] == ans[i-1][0] { 71 ans.remove(at: i - 1) 72 continue 73 } 74 i += 1 75 } 76 return ans 77 } 78 }







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了