Java反射机制
反射 Reflection
反射机制允许程序在执行期间借助 Reflection API 取得任何类的内部信息, 并能直接操作任意对象的内部属性以及方法
加载完类之后,在堆内存的方法区中就产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个类只有一个Class对象),这个对象就包含了完整的类的结构信息.我们可以通过这个对象看到类的结构.这个对象就像一面镜子,透过镜子看类的结构,所以形象的称之为:反射

反射机制提供的功能
- 在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
- 在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
- 在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
- 在运行时获取泛型信息
- 在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员变量和方法
- 在运行时处理注解
- 生成动态代理
反射相关的API
- java.lang.Class : 代表一个类
- java.lang.reflect.Method: 代表类的方法
- java.lang.reflect.Field : 代表类的成员变量
- java.lang.reflect.Constructor : 代表类的构造器
package com.guanxing.reflection;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//通过反射获取类的class对象
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("com.guanxing.reflection.User");
Class<?> c2 = Class.forName("com.guanxing.reflection.User");
Class<?> c3 = Class.forName("com.guanxing.reflection.User");
//一个类在内存中只有一个Class对象
//一个类被加载后,类的整个结构都会被封装在Class对象中
System.out.println(c1); //class com.guanxing.reflection.User
System.out.println(c1.hashCode()); //460141958
System.out.println(c2.hashCode()); //460141958
System.out.println(c3.hashCode()); //460141958
}
}
//定义一个实体类 : pojo entity
class User{
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
Class 类
- Class 本身也是一个类
- Class 对象只能由系统创建
- 一个加载的类在 JVM 中只会有一个 Class 实例
- 一个 Class 对象对应的是一个加载到 JVM 中的一个 class 文件
- 每个类的实例都会记得自己是由哪个 Class 实例所生成 (反射)
- 通过 Class 可以完整地得到一个类中的所有被加载的结构
- Class 是反射的根源, 针对任何你想动态加载, 运行的类, 唯有先获得相应的 Class 对象
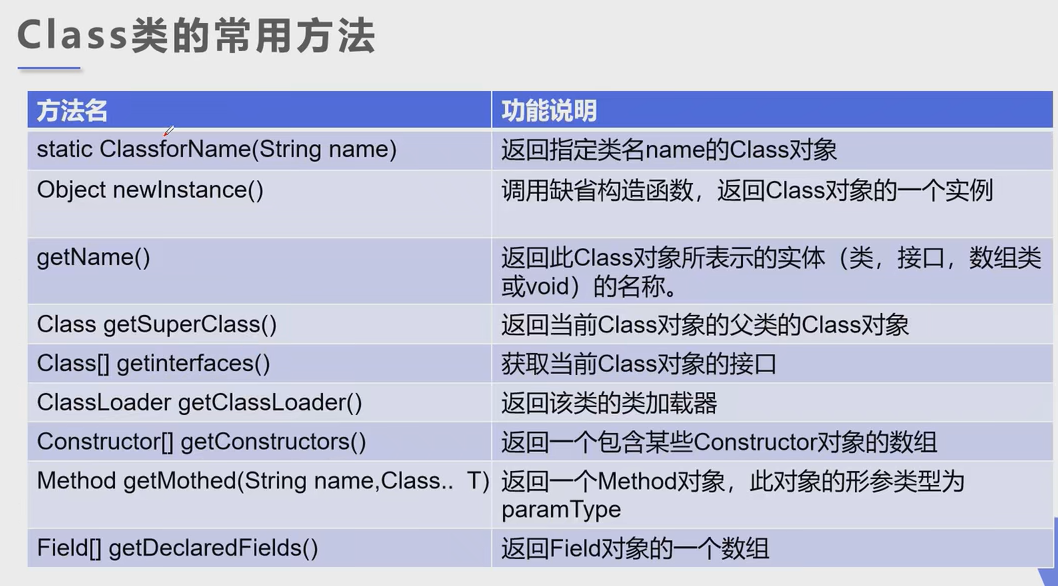
获取 Class 类的实例 ( 对象 )
package com.guanxing.reflection;
//测试class对象的生成方式
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//实例化一个对象
Person p1 = new Student();
System.out.println("这个人是"+p1.name);
//1.通过对象获取
Class<? extends Person> c1 = p1.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//2.通过forName包路径获取
Class<?> c2 = Class.forName("com.guanxing.reflection.Student");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
//3.通过类名获取
Class<Student> c3 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
//4.内置类特有
Class<Integer> c4 = Integer.TYPE;
System.out.println(c4); //int
//5.获得父类的类型
Class<?> c5 = c1.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(c5); //class com.guanxing.reflection.Person
}
}
//定义一个超类Person
class Person{
public String name;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
//定义一个Student类
class Student extends Person{
public Student(){
this.name = "学生";
}
}
//定义一个Teacher类
class Teacher extends Person{
public Teacher(){
this.name = "老师";
}
}
哪些类型有 Class 对象
- Class : 外部类, 成员(成员内部类, 静态内部类), 局部内部类, 匿名内部类
- interface : 接口
- [] : 数组
- enum : 枚举
- annotation : 注解
- primitive type : 基本数据类型
- void
内存相关
分析类的初始化
测试类什么时候会初始化
package com.guanxing.reflection;
public class Test04 {
static {
System.out.println("main类被加载");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1.主动引用 (main-->父类-->子类)
//Son son = new Son();
//2.反射也会产生主动引用
//Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("com.guanxing.reflection.Son");
//3.被动引用
//如:通过子类调用父类的静态变量,不会导致子类初始化
//main --> 父类初始化 --> 200
//System.out.println(Son.b);
//通过子类调用常量 main --> 1
//父类和子类都没有初始化!
//链接阶段,常量就加载到常量池了
System.out.println(Son.M);
}
}
class Father{
static int b = 200;
static {
System.out.println("父类被加载");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
static {
System.out.println("子类被加载");
m = 300;
}
static int m = 100;
static final int M = 1;
}
类加载器的作用
将 class 文件字节码内容加载到内存中, 并将这些静态数据转换成方法区的运行时数据结构, 然后在堆中生成一个代表这个类的 java.lang.Class 对象, 作为方法区中类数据的访问入口
类缓存 : 标准的 JavaSE 类加载器可以按要求查找类, 但一旦某个类被加载到类加载器中, 它将维持加载 (缓存) 一段时间, 不过 JVM 垃圾回收机制可以回收这些 Class 对象
源程序(.java文件) --> Java编译器 --> 字节码(.class文件) --> 类加载器 --> 字节码校验器 --> 解释器 --> 操作系统
package com.guanxing.reflection;
//看看类加载器
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//获取系统类的加载器
ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println(systemClassLoader); //sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
//获取系统类加载器的父类加载器 --> 扩展类加载器
ClassLoader parent = systemClassLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(parent); //sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@1b6d3586
//获取扩展类加载器的父类加载器 --> 根加载器(c/c++)
ClassLoader oldParent = parent.getParent();
System.out.println(oldParent); //null(无法直接获取)
//测试当前类是哪个类加载器加载的
//系统类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = Class.forName("com.guanxing.reflection.Test05").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader); //sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
//测试jdk内置类是哪个类加载器加载
//根加载器
ClassLoader classLoader2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader2); //null
//如何获得系统类加载器可以加载的路径
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.class.path"));
//双亲委派机制
//确保安全性,会检测是否已经存在
}
}
获取类运行时的结构
package com.guanxing.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//获取类的运行时数据结构
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("com.guanxing.reflection.User");
//1.获取类的名字 / 简单名字
System.out.println(c1.getName()); //com.guanxing.reflection.User
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName()); //User
System.out.println("===================");
//2.获取类的属性
Field[] fields = c1.getFields(); //只能找到public属性
Field[] declaredFields = c1.getDeclaredFields(); //可以找到全部属性
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(declaredField);
}
/*
private int com.guanxing.reflection.User.id
private java.lang.String com.guanxing.reflection.User.name
private int com.guanxing.reflection.User.age
*/
//3.获得指定属性
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name); //private java.lang.String com.guanxing.reflection.User.name
System.out.println("===================");
//4.获得类的方法
Method[] methods = c1.getMethods(); //获得本类及其父类的全部public方法
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("正常的:"+method);
}
methods = c1.getDeclaredMethods(); //获得本类(不含父类)的全部方法(包括私有的)
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("getDeclaredMethods:"+method);
}
System.out.println("------------------");
//5.获得指定方法,需要提供参数类型
//重载
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null);
Method setName = c1.getMethod("setName", String.class);
System.out.println(getName);
System.out.println(setName);
/*
public java.lang.String com.guanxing.reflection.User.getName()
public void com.guanxing.reflection.User.setName(java.lang.String)
*/
System.out.println("===================");
//6.获得指定的构造器
Constructor<?>[] constructors = c1.getConstructors(); //public
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
constructors = c1.getDeclaredConstructors(); //全部
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
/*
public com.guanxing.reflection.User()
public com.guanxing.reflection.User(int,java.lang.String,int)
public com.guanxing.reflection.User()
public com.guanxing.reflection.User(int,java.lang.String,int)
*/
//7.获取指定构造器(注意参数类型的顺序!)
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class, int.class);
System.out.println("指定构造器"+declaredConstructor);
//指定构造器public com.guanxing.reflection.User(int,java.lang.String,int)
}
}
动态创建对象
package com.guanxing.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//通过反射,动态创建对象
public class Test07 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
//获得Class对象
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.guanxing.reflection.User");
//构造一个对象
//User user1 = (User) c1.newInstance(); //本质是调用了类的无参构造器
//System.out.println(user1); //User{id=0, name='null', age=0}
//通过构造器创建对象
//Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class, int.class);
//User user2 = (User) constructor.newInstance(007, "John", 18);
//System.out.println(user2); //User{id=7, name='John', age=18}
//通过反射调用普通方法
User user3 = (User)c1.newInstance();
//通过反射获取一个方法
Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
//invoke: 激活的意思
// (对象, "方法的值")
setName.invoke(user3, "Jack");
System.out.println(user3.getName()); //Jack
//user3.setName("jack");
//System.out.println(user3.getName()); //jack
//通过反射操作属性
User user4 = (User)c1.newInstance();
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
//关闭安全检测(是否允许访问), 属性/方法/构造器都有这个方法
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(user4, "harris");
System.out.println(user4.getName()); //直接访问会报错, "private" 无权限
}
}
通过反射获取注解
package com.guanxing.reflection;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
//练习反射操作注解
public class Test08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
//获取Class对象
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("com.guanxing.reflection.Student2");
//通过反射获取类的注解
Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation); //@com.guanxing.reflection.Table(value=db_student)
}
//获得类的注解的value的值
// Annotation annotation = c1.getAnnotation(Table.class);
Table table = (Table)c1.getAnnotation(Table.class);
String value = table.value();
int size = table.size();
System.out.println(value+" "+size); //db_student 10
//获得类指定属性的注解
//先获得属性
Field field_name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
Field_annotation name_annotation = field_name.getAnnotation(Field_annotation.class);
System.out.println(name_annotation.columnName()); //db_name
System.out.println(name_annotation.type()); //varchar
System.out.println(name_annotation.length()); //5
}
}
@Table(value = "db_student", size = 10)
class Student2{
@Field_annotation(columnName = "db_id", type = "int", length = 10)
private int id;
@Field_annotation(columnName = "db_age", type = "int", length = 10)
private int age;
@Field_annotation(columnName = "db_name", type = "varchar", length = 5)
private String name;
public Student2() {
}
public Student2(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student2{" +
"id=" + id +
", age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
//定义一个类的注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Table{
String value();
int size();
}
//属性的注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Field_annotation{
String columnName();
String type();
int length();
}
回忆知识点
-
注解
- 什么是注解?
- 内置注解
- 自定义注解
- 元注解
-
反射
- 什么是反射? 反射机制提供的功能?
- 反射相关的API
- Class 类以及实例
- Class 类的常用方法
- Java 的内存分析, 类如何加载?
- 类加载器
- 创建运行时的类对象
- 通过反射调用指定的方法, 操作泛型, 获取注解




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号