前端面试
前端跳槽面试必备技巧
一面
页面布局类 / CSS盒模型
DOM事件类 / HTTP协议类
面向对象类 / 原型链类
通信类 / 安全类 / 算法类
二面
渲染机制 / 异步线程
页面性能 / 错误监控
MVVM框架 (vue) 解析
工作原理 / 生命周期
双向绑定 / 项目特色
面试是一个考试。是经过精心设计的。
(1) Javascript的算法包含哪些?
去重,数组排序,交叉
(2) 前端性能优化
(3) 数组的操作
(4) CSS,以及CSS3新增的属性
(5) JS的面向对象
(6) Vue的生命周期,以及工作原理
(7) 在Vue开发的过程中遇到过哪些问题
(8) ES6的继承类
程序员的第三年,是一到坎,基础知识掌握不扎实,学高阶知识,根本没用。
所以,基础知识,加ES6,加Vue,基本就行了。
有一个要注意的一点就是,如果你学的东西,未来用不上。那么你就是在浪费时间。
(1)
页面布局 / CSS盒模型
DOM事件 / HTTP协议
面向对象 / 原型链
通信 / 安全 / 算法
(1) 页面布局
题目:假设高度已知,请写出三栏布局,其中左栏、右栏宽度各为300px,中间自适应。
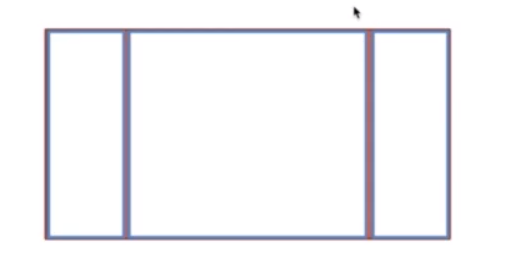
至少不下于3种解决方案:
(1)浮动
(2)绝对定位
(3) flex-box
(4) 表格布局(table-box)
(5)grid 网格布局
(1)浮动解决方案
<section class="layout float"> <article class="left-right-center"> <div class="left"></div> <div class="right"></div> <div class="center"> <h1>浮动解决方案</h1> 1.这是三栏布局中间部分 2.这是三栏布局中间部分 </div> </article> </section>
(2) 绝对定位
// VSCode 快捷写法
// 然后回车
div.left+div.center+div.right
不断的收集面试题,以及刷面试题。
最高端的还有北邮的计算机研究生,可以去了解一下。怎么会没有事情做?
<style>
* {
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.layout article div {
min-height: 100px;
}
.layout.absolute .left-center-right > div {
position: absolute;
}
.layout.absolute .left {
left: 0;
width: 300px;
background: red;
}
.layout.absolute .center {
left: 300px;
right: 300px;
background: yellow;
}
.layout.absolute .right {
right:0;
width: 300px;
background: blue;
}
</style>
<section class="layout absolute">
<article class="left-center-right">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="center">
<h2>绝对定位解决方案</h2>
1.这是三栏布局绝对定位中间部分。
</div>
<div class="right"></div>
</article>
</section>
(3) flexbox解决方案
<style>
* {
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.layout article div {
min-height: 100px;
}
.layout.flexbox .left-center-right {
display: flex;
}
.layout.flexbox .left {
width: 300px;
background: red;
}
.layout.flexbox .center {
flex:1;
background: yellow;
}
.layout.flexbox .right {
width: 300px;
background: blue;
}
</style>
<section class="layout flexbox">
<article class="left-center-right">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="center">
<h2>flexbox解决方案</h2>
1.这是三栏布局flexbox中间部分
2.这是三栏布局flexbox中间部分
</div>
<div class="right"></div>
</article>
</section>
(4) 表格布局
<style>
* {
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.layout article div {
min-height: 100px;
}
.layout.table .left-center-right {
width: 100%;
display: table;
height: 100px;
}
.layout.table .left-center-right > div {
display: table-cell;
}
.layout.table .left {
width: 300px;
background: red;
}
.layout.table .center {
background: yellow;
}
.layout.table .right {
width: 300px;
background: blue;
}
</style>
<section class="layout table">
<article class="left-center-right">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="center">
<h2>表格布局解决方案</h2>
1.这是三栏布局表格布局中间部分
2.这是三栏布局表格布局中间部分
</div>
<div class="right"></div>
</article>
</section>
(5) 网格布局
<style>
* {
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.layout.grid .left-center-right {
display: grid; /** 父容器声明为网格布局 **/
width: 100%;
grid-template-rows: 100px;
grid-template-columns: 300px auto 300px;
}
.layout.grid .left {
background: red;
}
.layout.grid .center {
background: yellow;
}
.layout.grid .right {
background: blue;
}
</style>
<section class="layout grid">
<article class="left-center-right">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="center">
<h2>网格布局解决方案</h2>
1.这是三栏布局网格布局中间部分
2.这是三栏布局网格布局中间部分
</div>
<div class="right"></div>
</article>
</section>
这道题目怎么延申?
(1) 这5种解决方案各自有什么优缺点?
浮动解决方案的兼容性比较好,只要把清除浮动给做好的话。
绝对定位解决方案,好处是快捷,缺点是布局已经脱离文档流了,那意味着下面所有的子元素也必须脱离文档流。
那么就导致了这个方案的有效性,也就是可使用性是比较差的。
flexbox布局,是CSS3中新出现的一种布局方式,flexbox布局,是比较完美的一个,现在的移动端,基本上
都是基于flexbox布局。
表格布局,在很多场景中,还是比较适用的。表格布局的兼容性是非常好的。因为IE8不兼容flexbox,所以,在
低版本的浏览器中可以使用表格布局。
网格布局,是新出的技术。
(2) 还有,如果高度未知,中间的高度被撑开了,需要左边和右边也跟着被撑开。那么刚才写的5种方案,
哪个还可以被适用?哪个已经不可以用了?
如果高度未知,哪一种解决方案不再适用?
浮动解决方案不能用。
绝对定位解决方案不能用。
flexbox解决方案可以用。
表格布局可以用。
网格布局不能用。
(3) 这5种方案的兼容性(浏览器)如何?真正到业务中去使用,哪一个最实用?
(4) 为什么浮动解决方案,中间的超出部分为什么会这样显示?

原理就是内容向左浮动的时候,当内容超出以后,左边的宽度是固定的,中间的文字,没有了遮挡物,
所以,内容就会向左。
(5) 如何让浮动解决方案的中间超出部分,不要跑到左边去?
这个时候,应该怎么做?
答案是创建BFC。
什么是BFC,在盒模型中有这个概念。
页面布局的变通
三栏布局:
- 左右宽度固定,中间自适应
- 上下宽度固定,中间自适应
两栏布局:
- 左宽度固定,右自适应
- 右宽度固定,左自适应
- 上高度固定,下自适应
- 下高度固定,上自适应
还有一个布局面试题,比较常见,"居中"。
题目:1、请写出css样式实现一个不定宽高的弹出框上下左右居中(至少两种)
就是弹层高度宽度不确定,始终上下左右居中(css方法)
(1) translate定位解决方案
CSS3的属性,IE8不支持。
这是css3的transform的属性,可以将宽高度设为百分比,IE8不支持,在移动端使用较好。
<style>
* {
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.translateCenter {
width: 40%;
height: 20%;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
background: blue;
}
</style>
<div class="translateCenter">我是translate居中定位</div>
(2) margin居中定位解决方案
不需要确定div的宽度和高度,让top,bottom,left,right都为0,再加个margin: auto。 IE7不支持。
<style>
* {
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.marginCenter {
width: 40%;
height: 20%;
position: absolute;
left:0;
top:0;
right:0;
bottom:0;
margin: auto;
background: yellow;
}
</style>
<div class="marginCenter">我是margin居中定位</div>
(3) 另一种简单的margin居中布局解决方案。
不需要确定div的宽度和高度。原理类似于translate。
<style>
* {
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.marginCenter {
width: 40%;
height: 20%;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
margin-left: -20%;
margin-top: -10%;
background: blue;
}
</style>
<div class="marginCenter">我是margin居中定位</div>
(4) 使用flexbox布局解决方案
纯css实现不定宽度提示框水平垂直页面居中。
一些提示框里的文字字数是不一定的,宽度不能写死。
运用flexbox布局。
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
控制 .text 在页面水平垂直居中。
提示框不需要设置宽度和高度,只需要控制父容器。
<style>
* {
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.wrapper {
position: fixed;
top:0;
bottom:0;
z-index:99;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
background: red;
}
.text {
background: rgba(0,0,0,.6);
padding: 10px;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="text">我是flexbox居中定位</div>
</div>
总结:
有四个解决方案:
(1) 通过translate实现不定宽高元素水平垂直居中
.demo1 {
position: absolue;
top: 50%;
left:50%;
-webkit-transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
简单分析:
先把元素设定为绝对定位。
绝对定位指的就是 position: absolute;
position:relative; 指的是相对定位。
然后通过top 和 left把元素的最左点和最上点移动到屏幕的中间。
最后通过 translate属性,根据元素自身大小,相对向左和向上移动自身宽高的50%。
从而实现了不定宽高元素的水平垂直居中。
(2) 通过margin居中定位实现不定宽高元素水平垂直居中。
(3) 另一种简单的margin居中定位解决方案,原理类似于translate属性。
(4) 通过flexbox布局解决方案。
.wrapper1 {
display: -webkit-flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
简单分析:
设置父级元素 display 为flex;
justify-content 设定子元素水平居中。
align-items 设定子元素垂直居中。
延申:
使用flexbox布局解决方案的时候,要注意兼容性写法。
.container{ display: -webkit-box; /* Chrome 4+, Safari 3.1, iOS Safari 3.2+ */ display: -moz-box; /* Firefox 17- */ display: -webkit-flex; /* Chrome 21+, Safari 6.1+, iOS Safari 7+, Opera 15/16 */ display: -moz-flex; /* Firefox 18+ */ display: -ms-flexbox; /* IE 10 */ display: flex; /* Chrome 29+, Firefox 22+, IE 11+, Opera 12.1/17/18, Android 4.4+ */ }
(2) CSS盒模型
题目:谈谈你对CSS盒模型的认识
关联知识非常多。
(1) 基本概念:标准模型+IE模型

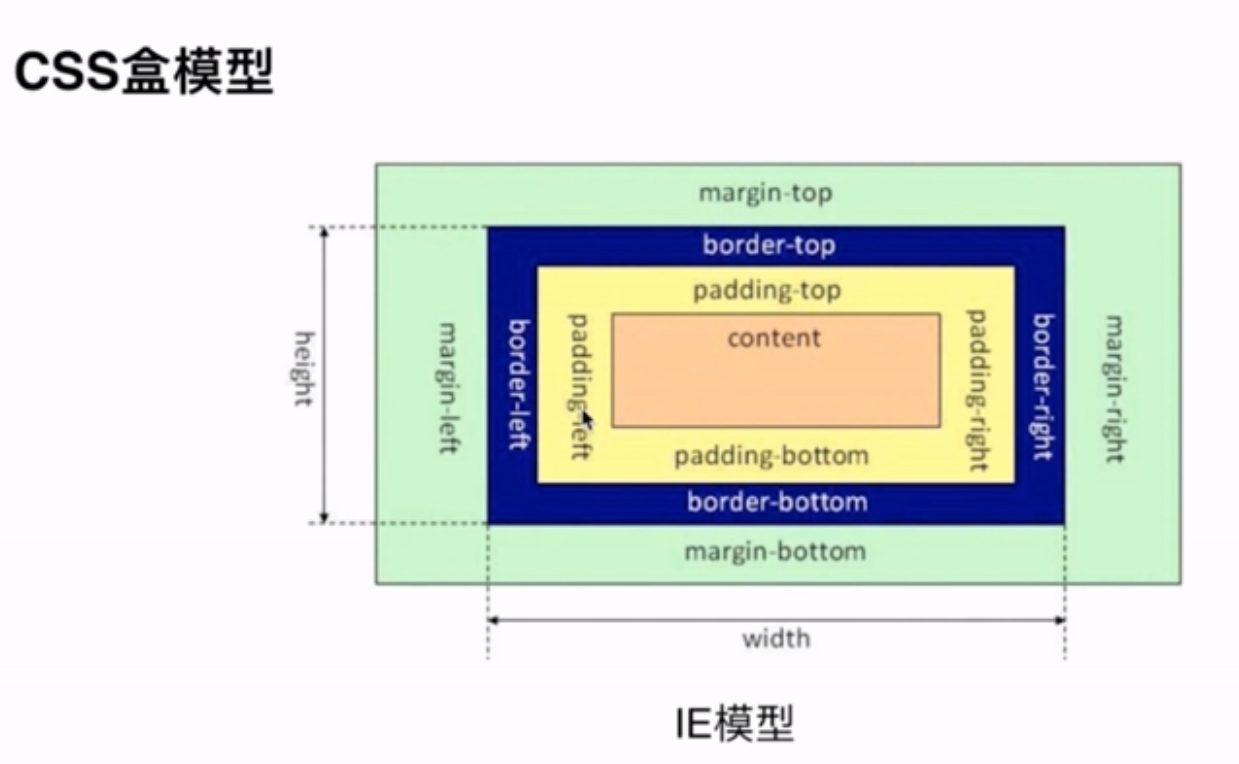
(2) 标准模型和IE模型区别
标准模型和IE模型的区别,就是宽度和高度的计算方式不同。
标准模型,的宽度指的就是content的宽度。
不包含padding和border。
IE模型,的宽度包含padding 和 border。
比如:宽度是200px,那么content的宽度只有180px。
高度也是类似的。
(3) CSS如何设置这两种模型
box-sizing 是CSS3的一个属性。
box-sizing: content-box;
或者
box-sizing: border-box;
(4) JS如何设置获取盒模型对应的宽和高
dom.style.width或者 dom.style.height
dom.currentStyle.width 或者 dom.currentStyle.height ,这个属性只有IE支持。
window.getComputedStyle(dom).width 或者 window.getComputedStyle(dom).height ,这个属性所有浏览器都支持。
dom.getBoundingClientRect().width 或者 dom.getBoundingClientRect().height ,这个API适用于获取绝对位置。
(5) 实例题(根据盒模型解释边距重叠)

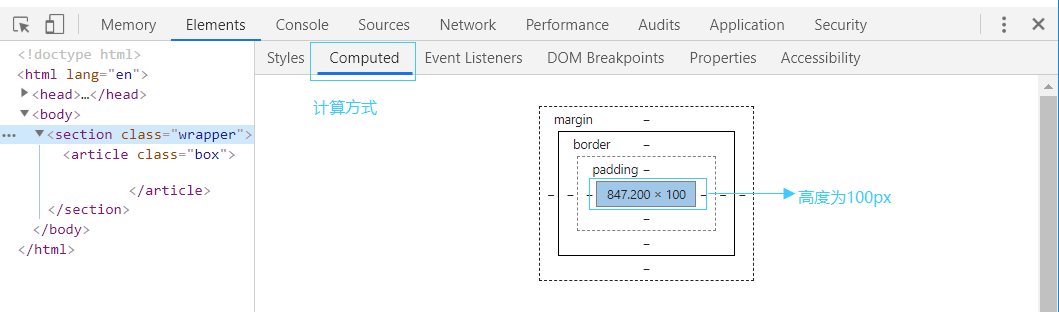
给 .wrapper 加上 overflow: hidden; 之后, .wrapper的高度变为 110px。
(6) BFC(边距重叠解决方案)
BFC是用来解决边距重叠的方案的。
BFC的基本概念:就是块级格式化上下文。
跟BFC并列的另一个叫IFC,叫内联格式化上下文。
BFC的原理:
- 在BFC垂直方向的,边距会发生重叠。
- BFC的区域,不会与浮动元素的box重叠。
- BFC在页面上是一个独立的容器,外面的元素不会影响它里面的元素。反过来,里面的元素也不会影响外面的元素。
- 计算BFC高度的时候,浮动元素也会参与计算。
如何创建BFC?
- 通过给父元素加上 overflow:hidden;
- float不为none;
- position的值是absolute或者fixed。
- display 设置为inline-box 或者 table 以及 table-xxx相关的。
(7) BFC的使用场景
CSS的基石就是盒模型
(3) DOM事件
(4) 通信 (跨域)
(5) CSRF / XSS 安全
(6) 算法
去重,迭代



