Install and Manage Windows Updates with PowerShell (PSWindowsUpdate)
Install and Manage Windows Updates with PowerShell (PSWindowsUpdate)
You can use the PSWindowsUpdate PowerShell module to manage Windows Updates from the command line. PSWindowsUpdate module is available for download from the PowerShell Gallery and allows administrators to scan, download, install, remove, or hide Windows updates on local or remote workstations and servers.
- Installing the PSWindowsUpdate Module
- Scan and Download Windows Updates with PowerShell
- Installing Windows Updates with PowerShell
- Check Windows Update History Using PowerShell
- Uninstalling Windows Updates with PowerShell
- How to Hide or Show Windows Updates Using PowerShell
- Install Windows Updates on Remote Computers with PowerShell
Installing the PSWindowsUpdate Module
You can install the PSWindowsUpdate module on Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2022/2019/2016 from the online repository (PSGallery) using the command:
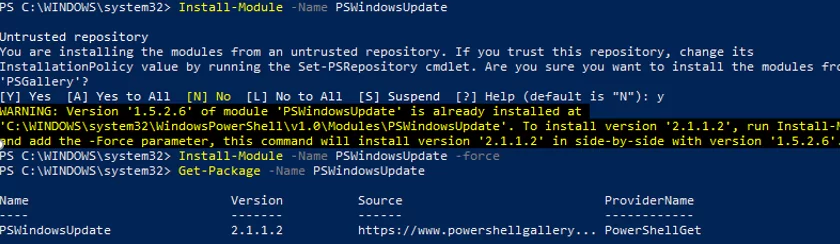
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate -Force
Confirm adding repositories by pressing Y. Check that the update management module is installed on Windows:
Get-Package -Name PSWindowsUpdate
- In an isolated environment, the PSWindowsUpdate module can be installed offline;
- To use the module on older versions of Windows, you must update the version of PowerShell.
You can remotely install the PSWindowsUpdate module on other computers on the network. The following command will copy the module files to the specified computers (WinRM is used to access remote computers).
$Targets = "lon-fs02.woshub.loc", "lon-db01.woshub.loc"
Update-WUModule -ComputerName $Targets –Local
The default PowerShell script execution policy in Windows blocks the third-party cmdlets (including PSWindowsUpdate commands) from running,
Set-ExecutionPolicy –ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -force
Or, you can allow module commands to run only in the current PowerShell session:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process
Import the module into your PowerShell session:
Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate
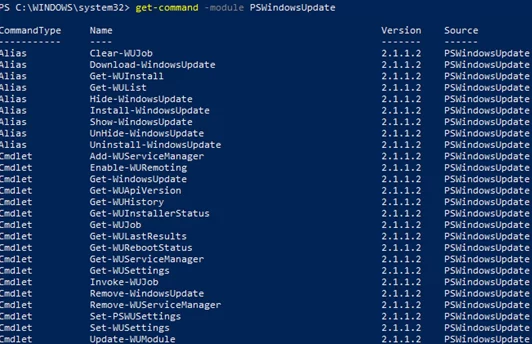
List available cmdlets in the PSWindowsUpdate module
Get-Command -module PSWindowsUpdate
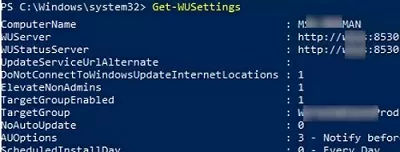
Check the current Windows Update client settings:
Get-WUSettings
ComputerName : WKS5S2N39S2 WUServer : http://MN-WSUS:8530 WUStatusServer : http://MN-WSUS:8530 AcceptTrustedPublisherCerts : 1 ElevateNonAdmins : 1 DoNotConnectToWindowsUpdateInternetLocations : 1 TargetGroupEnabled : 1 TargetGroup : ServersProd NoAutoUpdate : 0 AUOptions : 3 - Notify before installation ScheduledInstallDay : 0 - Every Day ScheduledInstallTime : 3 UseWUServer : 1 AutoInstallMinorUpdates : 0 AlwaysAutoRebootAtScheduledTime : 0 DetectionFrequencyEnabled : 1 DetectionFrequency : 4
In this example, the Windows Update client on the computer is configured by GPO to receive updates from the local WSUS update server.
Scan and Download Windows Updates with PowerShell
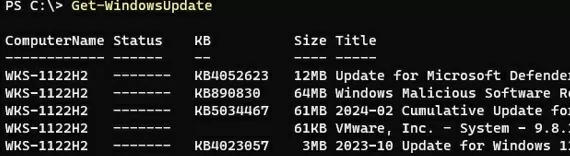
To scan your computer against an update server and get the updates it needs, run the command:
Get-WindowsUpdate
Or:
Get-WUList
The command lists the updates that need to be installed on your computer.
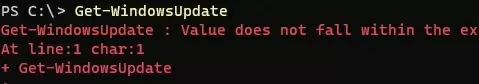
Value does not fall within the expected range.
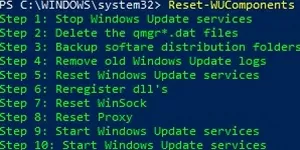
To fix the error, you must reset the Windows Update agent settings, re-register the libraries, and restore the wususerv service to its default state by using the command:
Reset-WUComponents -Verbose
To check the source of Windows Update on your computer (is it the Windows Update servers on the Internet or is it the local WSUS), run the following command:
Get-WUServiceManager
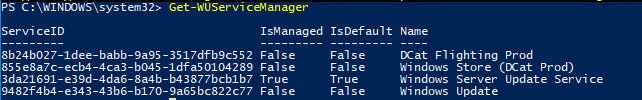
In this example, the computer is configured to receive updates from the local WSUS server (Windows Server Update Service = True). In this case, you should see a list of updates that have been approved for your computer.
To scan your computer against Microsoft Update servers on the Internet (these servers contain updates for Office and other products in addition to Windows updates), run this command:
Get-WUlist -MicrosoftUpdate
You will get this warning:
Get-WUlist : Service Windows Update was not found on computer. Use Get-WUServiceManager to get registered service.
To allow scanning on Microsoft Update, run this command:
Add-WUServiceManager -ServiceID "7971f918-a847-4430-9279-4a52d1efe18d" -AddServiceFlag 7
If you want to remove specific products or specific KBs from the list of updates that your computer receives, you can exclude them by:
- Category (
-NotCategory); - Title (
-NotCategory); - Update number (
-NotKBArticleID).
For example, to exclude driver updates, OneDrive, and a specific KB from the update list:
Get-WUlist -NotCategory "Drivers" -NotTitle "OneDrive" -NotKBArticleID KB4489873
You can download all available updates to your computer (update files are downloaded to the local update cache in the C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download).
Get-WindowsUpdate -Download -AcceptAll
Windows will download any available updates (MSU and CAB files) from the update server to the local update directory, but it will not install them automatically.
Installing Windows Updates with PowerShell
To automatically download and install all available updates for your Windows device from Windows Update servers (instead of local WSUS), run the command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -MicrosoftUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
The AcceptAll option accepts the installation of all update packages, and AutoReboot allows Windows to automatically restart after the updates are installed.
You can also use the following options:
- IgnoreReboot – disable automatic computer reboot;
- ScheduleReboot – Schedule the exact time of the computer’s reboot.
You can write the update installation history to a log file (you can use it instead of the WindowsUpdate.log file).
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -Install -AutoReboot | Out-File "c:\logs\$(get-date -f yyyy-MM-dd)-WindowsUpdate.log" -force
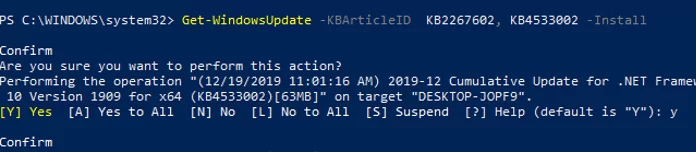
You can only install the specific updates by their KB numbers:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602, KB4533002 -Install
If you want to skip some updates during installation, run this command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -NotCategory "Drivers" -NotTitle OneDrive -NotKBArticleID KB4011670 -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot
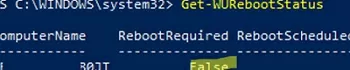
Check whether you need to restart your computer after installing the update (pending reboot):
Get-WURebootStatus | select RebootRequired, RebootScheduled
Check Windows Update History Using PowerShell
The Get-WUHistory cmdlet is used to get the list of updates that have previously been automatically or manually installed on your computer.
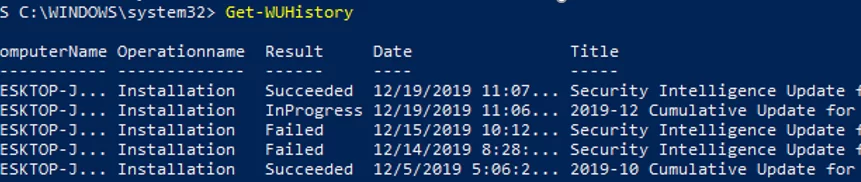
Check the date when the specific update was installed on the computer:
Get-WUHistory| Where-Object {$_.Title -match "KB4517389"} | Select-Object *|ft
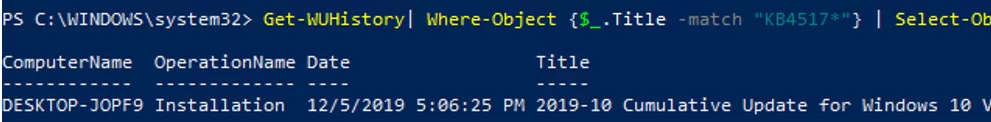
Find out when your computer was last scanned and when the update was installed:
Get-WULastResults |select LastSearchSuccessDate, LastInstallationSuccessDate
Uninstalling Windows Updates with PowerShell
Use the Remove-WindowsUpdate cmdlet to uninstall Windows updates on a computer. Simply specify the KB number as the argument of the KBArticleID parameter:
Remove-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB4489873 -NoRestart
How to Hide or Show Windows Updates Using PowerShell
You can hide certain updates to prevent the Windows Update service from installing them (most often you need to hide the driver updates). For example, to hide the KB4489873 and KB4489243 updates, run these commands:
$HideList = "KB4489873", "KB4489243"
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList –Hide
Or use an alias:
Hide-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -Verbose
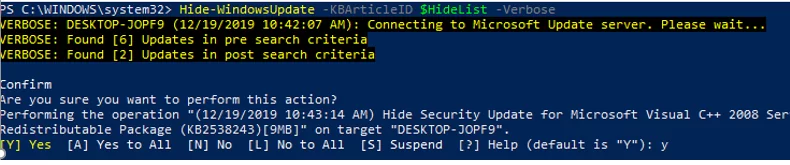
Hidden updates will not appear in the list of available updates the next time you use the Get-WindowsUpdate command to check for updates.
List hidden updates:
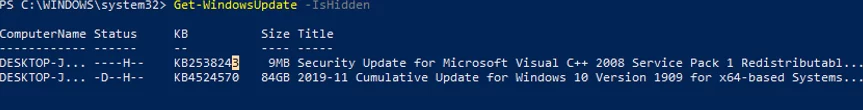
Get-WindowsUpdate –IsHidden
Notice that the H (Hidden) attribute has appeared in the Status column for hidden updates.
To unhide updates on the computer:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -WithHidden -Hide:$false
or:
Show-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList
Install Windows Updates on Remote Computers with PowerShell
Almost all PSWindowsUpdate cmdlets allow you to manage updates on remote computers. Use the –Computername parameter for that. WinRM must be enabled and configured (manually or via GPO) on remote computers. The PSWindowsUpdate module can be used to remotely manage Windows Updates both on computers in an AD domain and a workgroup (requires PowerShell Remoting configuration for workgroup environment).
To manage updates on remote computers, you must add hostnames to your WinRM trusted hosts list or configure PowerShell Remoting (WinRM) via HTTPS.
winrm set winrm/config/client '@{TrustedHosts="server1,server2,…"}'
Or with PowerShell:Set-Item wsman:\localhost\client\TrustedHosts -Value server1 -Force
You can use the Invoke-Command command to enable the PSWindowsUpdate module on the remote computers and open the required ports in the Windows Defender firewall (Enable-WURemoting command):
$Targets = "lon-fs02", "lon-db01"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $Target -ScriptBlock {Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -force }
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $Target -ScriptBlock {Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate; Enable-WURemoting}
Check the list of available updates on the remote computer:
Get-WUList –ComputerName server2
Download and install all available updates on several remote Windows hosts:
$ServerNames = "server1, server2, server3"
Invoke-WUJob -ComputerName $ServerNames -Script {ipmo PSWindowsUpdate; Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll | Out-File C:\Windows\PSWindowsUpdate.log } -RunNow -Confirm:$false -Verbose -ErrorAction Ignore
The Invoke-WUJob cmdlet creates a Scheduler task on the remote computer that runs under a local SYSTEM account.
You can set the exact time you want Windows updates to be installed:
Invoke-WUJob -ComputerName $ServerNames -Script {ipmo PSWindowsUpdate; Install-WindowsUpdate –AcceptAll -AutoReboot | Out-File C:\Windows\PSWindowsUpdate.log } -Confirm:$false -TriggerDate (Get-Date -Hour 22 -Minute 0 -Second 0)
Check the status of the update installation task:
Get-WUJob -ComputerName $ServerNames
If the command returns an empty list, the update installation task is complete on all computers.
Check multiple remote hosts for the specific update:
"server1","server2" | Get-WUHistory| Where-Object {$_.Title -match "KB4011634"} | Select-Object *|ft
To get the latest update installation date on all domain computers, use the Get-ADComputer cmdlet (from the Active Directory for PowerShell module):
$Computers=Get-ADComputer -Filter {enabled -eq "true" -and OperatingSystem -Like '*Windows*' }
Foreach ($Computer in $Computers)
{
Get-WULastResults -ComputerName $Computer.Name|select ComputerName, LastSearchSuccessDate, LastInstallationSuccessDate
}
The PSWindowsUpdate PowerShell module provides a convenient way to download and install Windows updates from the command prompt. This is a useful option for installing updates on hosts without a GUI: Windows Server Core or Hyper-V Server. This module is also essential if you need to install and track update installation on multiple Windows servers/workstations at the same time.





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 25岁的心里话
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现