2020软件工程作业04
- 寻找数组中第K大是数 考察算法:排序算法
手动实现
- 解题思路
获取用户键盘输入对应的值,手写快速排序排序,最后输出结果。
- 解题代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt(); //序列长度
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i =0; i<n; i++){
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt(); // 接受给定序列
}
int m = scanner.nextInt(); // 询问次数
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int l = scanner.nextInt();
int r = scanner.nextInt();
int k = scanner.nextInt();
//序列元素索引从1开始, l 到 r 中的 第 k 大小的数输出 :1 5 2 / 2 3 2
int[] arr2 = new int[r-l+1];
for(int z=0; z< r-l+1; z++){
arr2[z] = arr[l-1+z];
}
//Arrays.sort(arr2); //底层快速排序
quickShort(arr2,0,arr2.length-1);
arrayList.add(arr2[r-l-k+1]);//第K大的数输出
}
for (Integer integer : arrayList) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
}
// 快速排序
public static void quickShort(int[] arr, int left, int right){
int l = left;
int r = left;
int pivot = arr[(left+right)/2];
int temp = 0;
while (l < r){
while(arr[l] < pivot){
l += 1;
}
while(arr[r] > pivot){
l -= 1;
}
if (l >= r){
break;
}
temp = arr[l];
arr[l] = arr[r];
arr[r] = temp;
if (arr[l]==pivot){
r-=1;
}
if (arr[l]==pivot){
r+=1;
}
}
if(l == r){
l += 1;
r -= 1;
}
if (left < r){
quickShort(arr,left,r);
}
if(right > l){
quickShort(arr,l,right);
}
}
}

- 二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历 考察算法:dfs + bfs搜索算法
- 解题思路
利用递归的方式实现先、中、后序遍历
先序:先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树
中序:先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树
后序:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点
- 解题代码
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
作业要求:叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
自己实现四个方法,main方法中调用,将结果打印到控制台
*/
/* 二叉树的结构
A
/ \
T 6
/
D
/ \
N 5
/ \ /
B 4 1
\
9
*/
Node root = into();
// 先序遍历
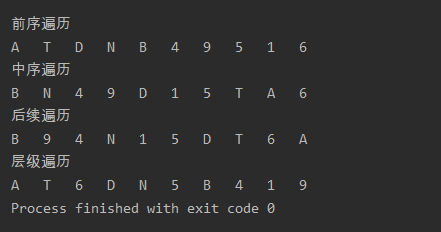
System.out.println("\n"+"前序遍历");
A(root);
// 中序遍历
System.out.println("\n"+"中序遍历");
B(root);
// 后续遍历
System.out.println("\n"+"后续遍历");
C(root);
// 层级遍历
System.out.println("\n"+"层级遍历");
D(root);
}
private static void A(Node node) {
// TODO 先序遍历
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
if(node.l != null){
A(node.l);
}
if(node.r != null){
A(node.r);
}
}
private static void B(Node node) {
// TODO 中序遍历
if(node.l != null){
B(node.l);
}
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
if(node.r != null){
B(node.r);
}
}
private static void C(Node node) {
// TODO 后续遍历
if(node.l != null){
C(node.l);
}
if(node.r != null){
C(node.r);
}
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
}
private static void D(Node node) {
// TODO 层级遍历
if(node == null) {
return ;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Node current = null;
queue.offer(node);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
current = queue.poll();//出队队头元素并访问
System.out.print(current.data+ "\t");
if(current.l != null) { //如果当前节点的左节点不为空入队
queue.offer(current.l);
}
if(current.r != null) {//如果当前节点的右节点不为空,把右节点入队
queue.offer(current.r);
}
}
}
// 构建一颗树,返回根节点
private static Node into(){
Node root = new Node("A");
Node node1 = new Node("T");
Node node2 = new Node("D");
Node node3 = new Node("N");
Node node4 = new Node("B");
Node node5 = new Node("6");
Node node6 = new Node("5");
Node node7 = new Node("4");
Node node8 = new Node("9");
Node node9 = new Node("1");
root.l = node1;
node1.l = node2;
node2.l = node3;
node2.r = node6;
node3.r = node7;
node7.r = node8;
node6.l = node9;
node3.l = node4;
root.r = node5;
return root;
}
// 节点
static class Node{
// 数据
Object data;
// 左孩子
Node l;
// 右孩子
Node r;
public Node(){}
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
this.l = null;
this.r = null;
}
public Node(Object data, Node l, Node r) {
this.data = data;
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
}
}