shiro源码分析-认证过程
一。shiro的认证过程源码分析
1.程序登录入口,页面传递地参数userName,password ,loginType3个参数,用 LoginUser 对象接收。loginType 为登录方式,因为我这里有多种登录方式,因此用这个字段来区分。不同的登录方式,采用不同的token封装登录信息。登录的过程就是调用Subject 的login方法,参数为封装登录信息的token。shiro用抛异常的方式来反馈登录结果,不同的异常代表不同的反馈结果。

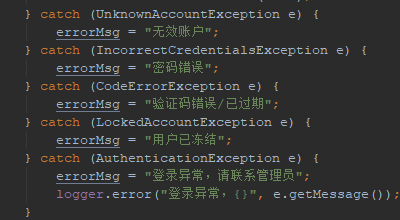
public ResultBean login(LoginUser loginUser) { String userName = loginUser.getUserName(); String password = loginUser.getPassword(); String loginType = loginUser.getLoginType(); if (StringUtils.isAnyBlank(userName, password, loginType)) { return ResultBean.paramsError(); } Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); AuthenticationToken token = null; if (PASSWORD_LOGIN.equals(loginType)) { token = new UsernamePasswordToken(userName, password); } else if (CODE_LOGIN.equals(loginType)) { token = new PhoneCodeToken(userName, password); } else { return ResultBean.failure("不支持的登录方式"); } String errorMsg = ""; try { subject.login(token);return ResultBean.success(user); } catch (UnknownAccountException e) { errorMsg = "无效账户"; } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { errorMsg = "密码错误"; } catch (CodeErrorException e) { errorMsg = "验证码错误/已过期"; } catch (LockedAccountException e) { errorMsg = "用户已冻结"; } catch (AuthenticationException e) { errorMsg = "登录异常,请联系管理员"; logger.error("登录异常,{}", e.getMessage()); } return ResultBean.failure(errorMsg); }
2.重点看subject.login(token)方法。跟踪进去,看到DelegatingSubject类的login()方法。DelegatingSubject为subject接口的实现类。可以看到,在login()方法里面,调用SecurityManager的login()方法。
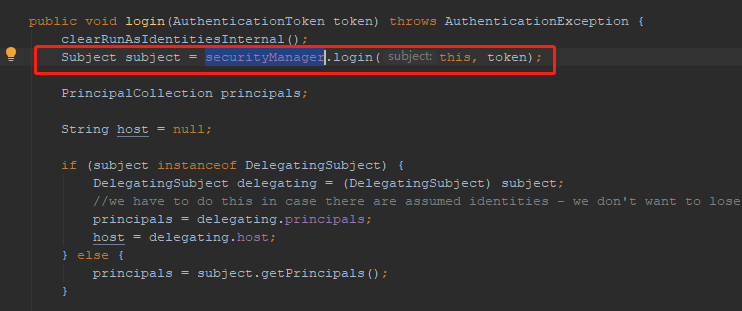
3.跟踪进去,到了DefaultSecurityManager的login()方法。此方法中调用父类AuthenticatingSecurityManager的authenticate(token)方法。返回AuthenticationInfo对象,这个对象包涵认证信息。
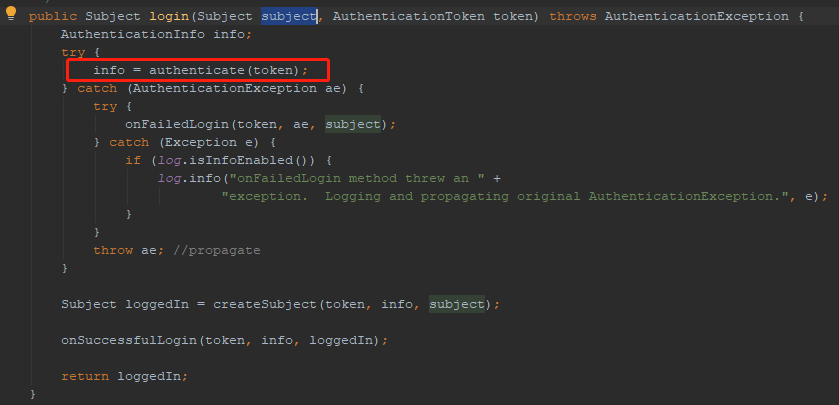
4.进到AuthenticatingSecurityManager的authenticate(token)方法。this.authenticator对象就是shiro的认证器,它是个接口,默认实现是ModularRealmAuthenticator。
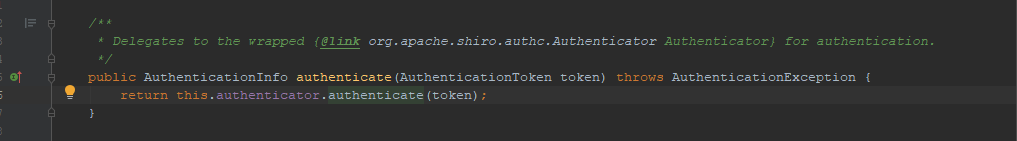
5.继续跟进。进入到AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate(token)方法,此类是ModularRealmAuthenticator的父类。方法中继续调用doAuthenticate(token)方法。

6.继续跟进。就到了ModularRealmAuthenticator。这个类就是shiro认证器的默认实现。看doAuthenticate(token)方法。shiro的realm部分,是用户自定义实现部分,一般有几种登录方式,就写几个realm。shiro中一个realm和多个realm的认证策略是不一样,因此这里一个条件判断,判断realm的个数。简单点,我们看doSingleRealmAuthentication()方法。
多个realm中,就有认证策略的问题。AuthenticationStrategy这个接口,就是认证策略的接口。后面再讲。
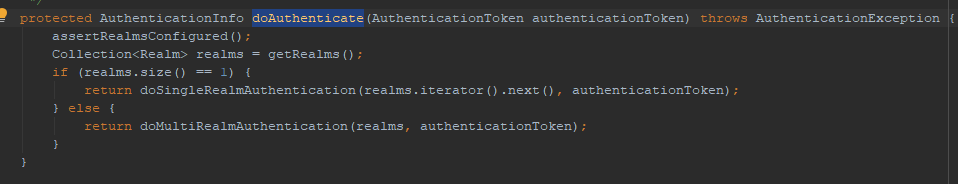
7.看ModularRealmAuthenticator的doSingleRealmAuthentication(realm,token)方法。这里面就调用realm的getAuthenticationInfo(token)方法。这里的realm就是我们自己实现的realm.

8.继续跟进。 进入到AuthenticatingRealm的getAuthenticationInfo(token)方法。AuthenticatingRealm也就是我们自己实现的realm的父类。该方法中首先从缓存中取认证信息,如果没有就调用我们定义的realm的doGetAuthenticationInfo(token)方法。
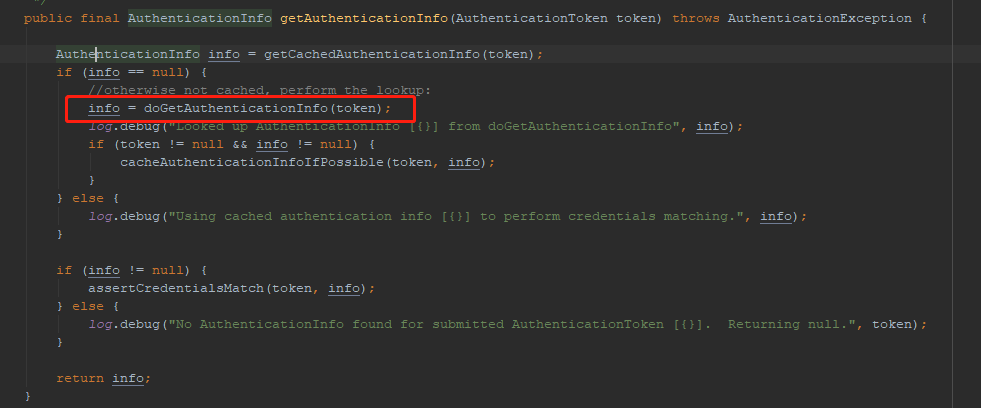
9.此时就可以到我们自己实现的realm了。在自定义的doGetAuthenticationInfo(token)中,我们调用服务层,获取用户信息。然后构建SimpleAuthenticationInfo对象返回。该对象中第一个参数,就是主体信息,可以是user对象,也可以是一个用户名。后面我们用subject.getPrincipal(),返回值就是这个值。第二个参数就是密码,第三个参数就是散列散发的盐。第四个参数就是当前Realm的名字,可以用通过方法getName()获取。

@Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token; String username = usernamePasswordToken.getUsername(); UserVO user = userService.fetchOneByUserName(username); if (user == null) { throw new UnknownAccountException(); } //帐号被锁定 if ("0".equals(user.getState())) { throw new LockedAccountException(); } return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo( user, user.getPassword(), ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getCredentialsSalt()), getName() ); }
10.然后一路返回AuthenticationInfo对象。里面就包涵,密码,盐等认证信息。返回到AuthenticatingRealm的getAuthenticationInfo(token)方法。下一步就是调用密码匹配器验证密码了。
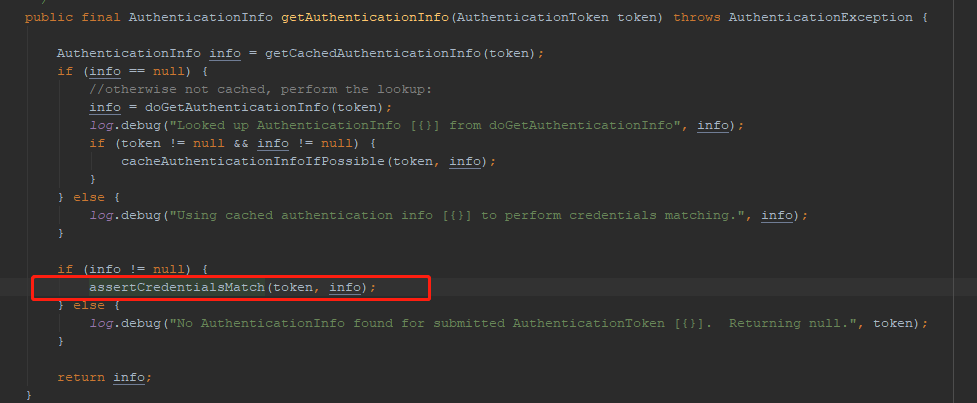
11.进入到assertCredentialsMatch(token, info)。第一个参数就是登录信息,第二个参数就是realm返回的认证信息。然后就调用密码匹配器去匹配。因为shiro是根据抛出异常来反馈匹配结果,所以没有返回值。如果匹配正确,登录过程就完成了,如果匹配错误,就会抛出具体的异常。

12.这里列举了几个具体的异常。CodeErrorException是我自己添加的,用来抛出验证码登录时,验证码错误的异常。
posted on 2020-07-15 12:39 ajax取个名字真难 阅读(191) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报






【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步