TensorFlow学习笔记2(创建Tensor)
创建Tensor
从numpy上转换得到,或者通过list
通过`tf.convert_to_tensor()'将一个numpy的array或者list转化为tensor
tf.convert_to_tensor(np.ones([2,3])) #将int型转化为float64,需要再次将float64转化为float32
tf.convert_to_tensor(np.zeros([2,3])) #将int型转化为float64
直接传入list
tf.convert_to_tensor([1,2]) #转化为int32
tf.convert_to_tensor([1,2.]) #转化为float32
tf.convert_to_tensor([[1],[2.]])
新建一个全为0或全为1的tensor(zeros, ones)
tf.zeros([]) #接受一个shape,新建一个标量0
tf.zeros([1]) #新建一个[0.]
tf.zeros_like 便捷功能,新建一个与传入tensor相同大小,元素全部为0的新的tensor
a=tf.zeros([2,3,3])
tf.zeros_like(a)
等同于tf.zeros(a.shape)
tf.ones 接受一个shape
tf.ones(1) #[1.]
tf.ones([]) #1.0
tf.ones([2]) #[1.,1.]
tf.ones([2,3])
tf.ones_like(a)
应用:通常将\(wx+b\)中的\(b\)初始化为0,\(w\)初始化全为1或者一些随机数
新建一个任意数字构成的tensor(fill)
将全部填充为相同的数
tf.fill([2,2],0) #填充为2行2列,元素全部为0的tensor
tf.fill([2,2],1)
tf.fill([2,2],9)
随机化初始
可以采用某种分布来随机初始化数据
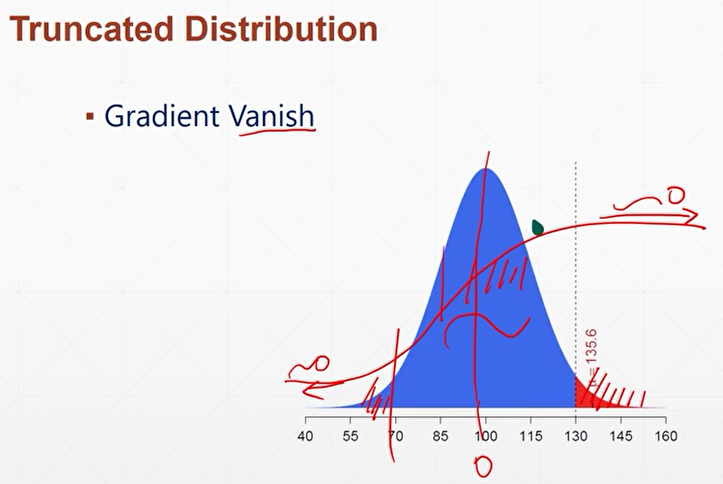
从正态分布/截断正态分布中进行抽样
tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=1,stddev=1)
tf.random.truncated_normal([2,2],mean=0,stddev=1)
为了解决梯度消失问题,从truncated normal中抽样的数据进行初始化
从均匀分布随机抽样
tf.random.uniform([2,2],minval=0, maxval=1)
随机打散
idx = tf.range(10)
idx = tf.random.shuffle(idx)
a = tf.gather(a, idx)
b = tf.gather(b, idx)
通过constant方式,与第一种相似
tf.constant(1)
tf.constant([1])
tf.constant([1,2.])
典型应用
Scalar: Loss, Accuracy
Vector: Bias
Matrix: input, weight
Dim=3 Tensor: 自然语言x: [b, seq_len, word_dim], b个句子中,每个句子的长度seq_len(单词数), 每个单词可以编码为长度为word_dim的向量
Dim=4 Tensor: 图片保存方式 Image [b, h, w, 3]
Dime=5 Tensor: single task: [b, h, w, 3],
meta-learning: [task_b, b, h, w, 3]

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号