在update_engine-DownloadAction(一)中对DownloadAction介绍到了DeltaPerformer的Write方法。下面开始介绍Write方法。
src/system/update_engine/payload_consumer/delta_performer.cc
1 bool DeltaPerformer::Write(const void* bytes, size_t count, ErrorCode *error) {
2 *error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
3
4 const char* c_bytes = reinterpret_cast<const char*>(bytes);
5
6 // Update the total byte downloaded count and the progress logs.
7 total_bytes_received_ += count;
8 UpdateOverallProgress(false, "Completed "); //更新进度包括了已经应用的操作数,下载的数据量,以及总的进度
9
10 while (!manifest_valid_) { //manifest_valid_的初始值为false
11 // Read data up to the needed limit; this is either maximium payload header
12 // size, or the full metadata size (once it becomes known).
13 const bool do_read_header = !IsHeaderParsed(); //是否解析过Header
14 CopyDataToBuffer(&c_bytes, &count, //将数据拷贝到缓存区server中
15 (do_read_header ? kMaxPayloadHeaderSize :
16 metadata_size_ + metadata_signature_size_));
17
18 MetadataParseResult result = ParsePayloadMetadata(buffer_, error); //解析元数据
19 if (result == kMetadataParseError)
20 return false;
21 if (result == kMetadataParseInsufficientData) {
22 // If we just processed the header, make an attempt on the manifest.
23 if (do_read_header && IsHeaderParsed())
24 continue;
25
26 return true;
27 }
28
29 // Checks the integrity of the payload manifest.
30 if ((*error = ValidateManifest()) != ErrorCode::kSuccess) //验证Manifest
31 return false;
32 manifest_valid_ = true;
33
34 // Clear the download buffer.
35 DiscardBuffer(false, metadata_size_); //清除缓存区
36
37 // This populates |partitions_| and the |install_plan.partitions| with the
38 // list of partitions from the manifest.
39 if (!ParseManifestPartitions(error)) //解析Manifest中的Partitions的信息
40 return false;
41
42 // |install_plan.partitions| was filled in, nothing need to be done here if
43 // the payload was already applied, returns false to terminate http fetcher,
44 // but keep |error| as ErrorCode::kSuccess.
45 if (payload_->already_applied) //检查当前payload_是否已经被应用
46 return false;
47
48 num_total_operations_ = 0;
49 for (const auto& partition : partitions_) {
50 num_total_operations_ += partition.operations_size(); //计算总的操作数
51 acc_num_operations_.push_back(num_total_operations_); //将每次计算的操作数放入到集合中,这样做的意义有能够根据操作数来判断是哪个
52 } //分区要进行操作,以及是该分区的第几个操作
53
54 LOG_IF(WARNING, !prefs_->SetInt64(kPrefsManifestMetadataSize,
55 metadata_size_))
56 << "Unable to save the manifest metadata size.";
57 LOG_IF(WARNING, !prefs_->SetInt64(kPrefsManifestSignatureSize,
58 metadata_signature_size_))
59 << "Unable to save the manifest signature size.";
60
61 if (!PrimeUpdateState()) { /更新主要的状态,包含了block_size_,next_operation_num等
62 *error = ErrorCode::kDownloadStateInitializationError;
63 LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to prime the update state.";
64 return false;
65 }
66
67 if (!OpenCurrentPartition()) { //打开当前的分区,包括source_slot和target_slot的,为升级做准备
68 *error = ErrorCode::kInstallDeviceOpenError;
69 return false;
70 }
71
72 if (next_operation_num_ > 0)
73 UpdateOverallProgress(true, "Resuming after ");
74 LOG(INFO) << "Starting to apply update payload operations";
75 }
76
77 while (next_operation_num_ < num_total_operations_) { //开始进行更新
78 // Check if we should cancel the current attempt for any reason.
79 // In this case, *error will have already been populated with the reason
80 // why we're canceling.
81 if (download_delegate_ && download_delegate_->ShouldCancel(error)) //目前什么都没做,直接返回了false
82 return false;
83
84 // We know there are more operations to perform because we didn't reach the
85 // |num_total_operations_| limit yet.
86 while (next_operation_num_ >= acc_num_operations_[current_partition_]) { //说明了当前分区已经更新完成,需要更新下一个分区
87 CloseCurrentPartition(); //关闭当前分区
88 current_partition_++; //切换到下一个分区
89 if (!OpenCurrentPartition()) { //打开
90 *error = ErrorCode::kInstallDeviceOpenError;
91 return false;
92 }
93 }
94 const size_t partition_operation_num = next_operation_num_ - (
95 current_partition_ ? acc_num_operations_[current_partition_ - 1] : 0); //计算出当前分区将要应用的操作数
96
97 const InstallOperation& op =
98 partitions_[current_partition_].operations(partition_operation_num); //获取到操作的类型
99
100 CopyDataToBuffer(&c_bytes, &count, op.data_length()); //将该操作对应的数据放到缓存区中
101
102 // Check whether we received all of the next operation's data payload.
103 if (!CanPerformInstallOperation(op)) //验证该操作是否能够进行,主要就是看该操作对应的数据是否已经全部都下载完了
104 return true;
105
106 // Validate the operation only if the metadata signature is present.
107 // Otherwise, keep the old behavior. This serves as a knob to disable
108 // the validation logic in case we find some regression after rollout.
109 // NOTE: If hash checks are mandatory and if metadata_signature is empty,
110 // we would have already failed in ParsePayloadMetadata method and thus not
111 // even be here. So no need to handle that case again here.
112 if (!payload_->metadata_signature.empty()) {
113 // Note: Validate must be called only if CanPerformInstallOperation is
114 // called. Otherwise, we might be failing operations before even if there
115 // isn't sufficient data to compute the proper hash.
116 *error = ValidateOperationHash(op); //校验操作对应数据的hash值是否正确
117 if (*error != ErrorCode::kSuccess) {
118 if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) {
119 LOG(ERROR) << "Mandatory operation hash check failed";
120 return false;
121 }
122
123 // For non-mandatory cases, just send a UMA stat.
124 LOG(WARNING) << "Ignoring operation validation errors";
125 *error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
126 }
127 }
128
129 // Makes sure we unblock exit when this operation completes.
130 ScopedTerminatorExitUnblocker exit_unblocker =
131 ScopedTerminatorExitUnblocker(); // Avoids a compiler unused var bug.
132
133 bool op_result;
134 switch (op.type()) { //根据操作的类型执行对应的操作
135 case InstallOperation::REPLACE:
136 case InstallOperation::REPLACE_BZ:
137 case InstallOperation::REPLACE_XZ:
138 op_result = PerformReplaceOperation(op);
139 break;
140 case InstallOperation::ZERO:
141 case InstallOperation::DISCARD:
142 op_result = PerformZeroOrDiscardOperation(op);
143 break;
144 case InstallOperation::MOVE:
145 op_result = PerformMoveOperation(op);
146 break;
147 case InstallOperation::BSDIFF:
148 op_result = PerformBsdiffOperation(op);
149 break;
150 case InstallOperation::SOURCE_COPY:
151 op_result = PerformSourceCopyOperation(op, error);
152 break;
153 case InstallOperation::SOURCE_BSDIFF:
154 op_result = PerformSourceBsdiffOperation(op, error);
155 break;
156 case InstallOperation::IMGDIFF:
157 // TODO(deymo): Replace with PUFFIN operation.
158 op_result = false;
159 break;
160 default:
161 op_result = false;
162 }
163 if (!HandleOpResult(op_result, InstallOperationTypeName(op.type()), error)) //对处理结果进行打印
164 return false;
165
166 next_operation_num_++;
167 UpdateOverallProgress(false, "Completed ");
168 CheckpointUpdateProgress(); //保存更新进度,类似于断点能够进行保存
169 }
170
171 // In major version 2, we don't add dummy operation to the payload.
172 // If we already extracted the signature we should skip this step.
173 if (major_payload_version_ == kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion &&
174 manifest_.has_signatures_offset() && manifest_.has_signatures_size() &&
175 signatures_message_data_.empty()) {
176 if (manifest_.signatures_offset() != buffer_offset_) {
177 LOG(ERROR) << "Payload signatures offset points to blob offset "
178 << manifest_.signatures_offset()
179 << " but signatures are expected at offset "
180 << buffer_offset_;
181 *error = ErrorCode::kDownloadPayloadVerificationError;
182 return false;
183 }
184 CopyDataToBuffer(&c_bytes, &count, manifest_.signatures_size());
185 // Needs more data to cover entire signature.
186 if (buffer_.size() < manifest_.signatures_size())
187 return true;
188 if (!ExtractSignatureMessage()) { //获取升级文件中数据区域的签名
189 LOG(ERROR) << "Extract payload signature failed.";
190 *error = ErrorCode::kDownloadPayloadVerificationError;
191 return false;
192 }
193 DiscardBuffer(true, 0);
194 // Since we extracted the SignatureMessage we need to advance the
195 // checkpoint, otherwise we would reload the signature and try to extract
196 // it again.
197 CheckpointUpdateProgress();
198 }
199
200 return true;
201 }
这个方法乍一看上去内容特别的多,而且如果对升级文件没有一个了解的情况下分析这段代码会有一点点困难,但是当跨过这个困难的时候就会对升级文件的结构有一个了解。要想了解升级文件的结构可以直接分析升级文件,但是在android引入A/B升级之后,升级文件是纯二进制的文件,而且还被加了密。分析起来难度也比较大,当然我们也可以分析代码中是如何解析的,根据解析我们就能够获取到升级文件的结构。另外在A/B升级中,它应用更新的流程就是下载->解析->验证->应用。这里的下载指的就是将数据加载到内存中,并且是边下载边更新,更新完之后就会把数据从内存中移除。下面是分析代码所得到升级文件的结构。
升级文件的结构
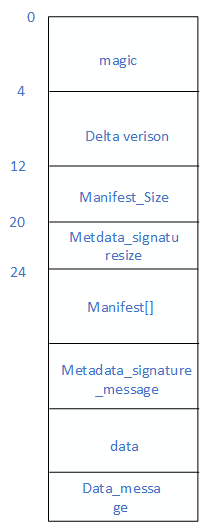
magic:是用于校验数据在内存中的地址偏移量是否正确。假设我们预期从地址0到3存放A,B,C,D可是当计算存在问题时,应该得到0的时候我们得到的是1,那么就会在1到4存放A,B,C,D,而我们再从0开始访问就会有问题。如果在内存的开始部分加入一个magic,当我们从0开始访问的时候,就先根据定义好的magic判断数据在内存中是否发生偏移错误。也就存放数据的时候我们存放magic,A,B,C,D正确的结果是0到4,但是却放到了1到5,这个时候我们依然去用0开始访问,但是我们首先会检验在0上的magic和预期的一样,如果一样则说明没有发生偏移错误,可以继续访问,如果不一样则说明偏移错误,之后可以进行相应的处理。
delta version:是差分版本,也就是update_engine的版本号
manifest_size: 代表manifest的大小,manifest意为清单文件,系统如何升级也是根据manifest来做的。
metadata_signaturesize:代表了元数据签名的大小。可以将magic,dleta version,manifest_size,metadata_signaturesize以及manifest[]称为元数据。
manifest[]: 主要的清单文件,记录了各个分区的更新的操作,以及数据信息等
metadata_signaturesize_message : 元数据的签名,而且也是经过加密的
data: 用于更新的数据
data_messgage:为data的签名信息。在kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion 这个版本中才会有。在A/B更新出现后,一共出现了两个版本一个kChromeOSMajorPayloadVersion一个kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion,kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion这个版本为新版本,也是Android8.0中使用的。
当有了这些了解后再来分析Write方法是就会简单很多。在Write中主要做的事情为:
1. ParsePayloadMetadata解析元数据。来看一下是如何解析的。
1 DeltaPerformer::MetadataParseResult DeltaPerformer::ParsePayloadMetadata(
2 const brillo::Blob& payload, ErrorCode* error) {
3 *error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
4 uint64_t manifest_offset;
5
6 if (!IsHeaderParsed()) { //没有解析过
7 // Ensure we have data to cover the major payload version.
8 if (payload.size() < kDeltaManifestSizeOffset) //kDeltaManifestSizeOffset=kDeltaVersionOffset + kDeltaVersionSize
9 return kMetadataParseInsufficientData; //没有将magic和delta version加载完
10
11 // Validate the magic string.
12 if (memcmp(payload.data(), kDeltaMagic, sizeof(kDeltaMagic)) != 0) { //校验magic,
13 LOG(ERROR) << "Bad payload format -- invalid delta magic.";
14 *error = ErrorCode::kDownloadInvalidMetadataMagicString;
15 return kMetadataParseError;
16 }
17
18 // Extract the payload version from the metadata.
19 static_assert(sizeof(major_payload_version_) == kDeltaVersionSize,
20 "Major payload version size mismatch");
21 memcpy(&major_payload_version_,
22 &payload[kDeltaVersionOffset], //保存DeltaVesion
23 kDeltaVersionSize);
24 // switch big endian to host
25 major_payload_version_ = be64toh(major_payload_version_); //转换为主机字节序
26
27 if (major_payload_version_ != supported_major_version_ && //判断版本号是否正确
28 major_payload_version_ != kChromeOSMajorPayloadVersion) {
29 LOG(ERROR) << "Bad payload format -- unsupported payload version: "
30 << major_payload_version_;
31 *error = ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMajorPayloadVersion;
32 return kMetadataParseError;
33 }
34
35 // Get the manifest offset now that we have payload version.
36 if (!GetManifestOffset(&manifest_offset)) { //获取指向manifest的地址偏移量
37 *error = ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMajorPayloadVersion;
38 return kMetadataParseError;
39 }
40 // Check again with the manifest offset.
41 if (payload.size() < manifest_offset) //判断manifset之前的数据是否都已经加载到了内存中
42 return kMetadataParseInsufficientData;
43
44 // Next, parse the manifest size.
45 static_assert(sizeof(manifest_size_) == kDeltaManifestSizeSize,
46 "manifest_size size mismatch");
47 memcpy(&manifest_size_, //保存manifest的大小
48 &payload[kDeltaManifestSizeOffset],
49 kDeltaManifestSizeSize);
50 manifest_size_ = be64toh(manifest_size_); // 转换为主机字节序
51
52 if (GetMajorVersion() == kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion) { //如果是新版本
53 // Parse the metadata signature size.
54 static_assert(sizeof(metadata_signature_size_) ==
55 kDeltaMetadataSignatureSizeSize,
56 "metadata_signature_size size mismatch");
57 uint64_t metadata_signature_size_offset;
58 if (!GetMetadataSignatureSizeOffset(&metadata_signature_size_offset)) { //获取metadata_signature_size数据的偏移量
59 *error = ErrorCode::kError;
60 return kMetadataParseError;
61 }
62 memcpy(&metadata_signature_size_, //保存元数据的大小
63 &payload[metadata_signature_size_offset],
64 kDeltaMetadataSignatureSizeSize);
65 metadata_signature_size_ = be32toh(metadata_signature_size_); //转换为主机字节序
66 }
67
68 // If the metadata size is present in install plan, check for it immediately
69 // even before waiting for that many number of bytes to be downloaded in the
70 // payload. This will prevent any attack which relies on us downloading data
71 // beyond the expected metadata size.
72 metadata_size_ = manifest_offset + manifest_size_; //计算元数据的大小
73 if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) { //进行强制性检查,增加安全性
74 if (payload_->metadata_size != metadata_size_) {
75 LOG(ERROR) << "Mandatory metadata size in Omaha response ("
76 << payload_->metadata_size
77 << ") is missing/incorrect, actual = " << metadata_size_;
78 *error = ErrorCode::kDownloadInvalidMetadataSize;
79 return kMetadataParseError;
80 }
81 }
82 }
83
84 // Now that we have validated the metadata size, we should wait for the full
85 // metadata and its signature (if exist) to be read in before we can parse it.
86 if (payload.size() < metadata_size_ + metadata_signature_size_) //检查metadata_signature_message是否已经加载到了内存
87 return kMetadataParseInsufficientData;
88
89 // Log whether we validated the size or simply trusting what's in the payload
90 // here. This is logged here (after we received the full metadata data) so
91 // that we just log once (instead of logging n times) if it takes n
92 // DeltaPerformer::Write calls to download the full manifest.
93 if (payload_->metadata_size == metadata_size_) { //payload_中也保存了metadata_size,进行比对一下
94 LOG(INFO) << "Manifest size in payload matches expected value from Omaha";
95 } else {
96 // For mandatory-cases, we'd have already returned a kMetadataParseError
97 // above. We'll be here only for non-mandatory cases. Just send a UMA stat.
98 LOG(WARNING) << "Ignoring missing/incorrect metadata size ("
99 << payload_->metadata_size
100 << ") in Omaha response as validation is not mandatory. "
101 << "Trusting metadata size in payload = " << metadata_size_;
102 }
103
104 // We have the full metadata in |payload|. Verify its integrity
105 // and authenticity based on the information we have in Omaha response.
106 *error = ValidateMetadataSignature(payload); //验证元数据的签名
107 if (*error != ErrorCode::kSuccess) {
108 if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) {
109 // The autoupdate_CatchBadSignatures test checks for this string
110 // in log-files. Keep in sync.
111 LOG(ERROR) << "Mandatory metadata signature validation failed";
112 return kMetadataParseError;
113 }
114
115 // For non-mandatory cases, just send a UMA stat.
116 LOG(WARNING) << "Ignoring metadata signature validation failures";
117 *error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
118 }
119
120 if (!GetManifestOffset(&manifest_offset)) { //获取manifest_offset
121 *error = ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMajorPayloadVersion;
122 return kMetadataParseError;
123 }
124 // The payload metadata is deemed valid, it's safe to parse the protobuf.
125 if (!manifest_.ParseFromArray(&payload[manifest_offset], manifest_size_)) { //解析manifest
126 LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to parse manifest in update file.";
127 *error = ErrorCode::kDownloadManifestParseError;
128 return kMetadataParseError;
129 }
130
131 manifest_parsed_ = true;
132 return kMetadataParseSuccess;
133 }
可以看到整个解析的过程也比较简单了。接下来着重看一下ValidateMetadataSignature的实现
1 ErrorCode DeltaPerformer::ValidateMetadataSignature(
2 const brillo::Blob& payload) {
3 if (payload.size() < metadata_size_ + metadata_signature_size_)
4 return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureError; //判断签名是否已经加载到了内存中
5
6 brillo::Blob metadata_signature_blob, metadata_signature_protobuf_blob;
7 if (!payload_->metadata_signature.empty()) { //payload_中已经保存了metadata_signature
8 // Convert base64-encoded signature to raw bytes.
9 if (!brillo::data_encoding::Base64Decode(payload_->metadata_signature,
10 &metadata_signature_blob)) { //先对签名进行Base64的简码
11 LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to decode base64 metadata signature: "
12 << payload_->metadata_signature;
13 return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureError;
14 }
15 } else if (major_payload_version_ == kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion) {
16 metadata_signature_protobuf_blob.assign( //没有保存就从内存中加载
17 payload.begin() + metadata_size_,
18 payload.begin() + metadata_size_ + metadata_signature_size_);
19 }
20
21 if (metadata_signature_blob.empty() &&
22 metadata_signature_protobuf_blob.empty()) { //没有metadata_signature
23 if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) {
24 LOG(ERROR) << "Missing mandatory metadata signature in both Omaha "
25 << "response and payload.";
26 return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureMissingError;
27 }
28
29 LOG(WARNING) << "Cannot validate metadata as the signature is empty";
30 return ErrorCode::kSuccess;
31 }
32
33 // See if we should use the public RSA key in the Omaha response.
34 base::FilePath path_to_public_key(public_key_path_);
35 base::FilePath tmp_key;
36 if (GetPublicKeyFromResponse(&tmp_key)) //检查install_plan_中是否已经带了公钥
37 path_to_public_key = tmp_key;
38 ScopedPathUnlinker tmp_key_remover(tmp_key.value());
39 if (tmp_key.empty())
40 tmp_key_remover.set_should_remove(false);
41
42 LOG(INFO) << "Verifying metadata hash signature using public key: "
43 << path_to_public_key.value();
44
45 brillo::Blob calculated_metadata_hash;
46 if (!HashCalculator::RawHashOfBytes( //根据元数据计算一个hash
47 payload.data(), metadata_size_, &calculated_metadata_hash)) {
48 LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to compute actual hash of manifest";
49 return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureVerificationError;
50 }
51
52 PayloadVerifier::PadRSA2048SHA256Hash(&calculated_metadata_hash); //对hash进行填充
53 if (calculated_metadata_hash.empty()) {
54 LOG(ERROR) << "Computed actual hash of metadata is empty.";
55 return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureVerificationError;
56 }
57
58 if (!metadata_signature_blob.empty()) { //payload_中已经保存了签名
59 brillo::Blob expected_metadata_hash;
60 if (!PayloadVerifier::GetRawHashFromSignature(metadata_signature_blob, //使用公钥对其进行解密
61 path_to_public_key.value(),
62 &expected_metadata_hash)) {
63 LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to compute expected hash from metadata signature";
64 return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureError;
65 }
66 if (calculated_metadata_hash != expected_metadata_hash) { //判断保存的和自己算出来的签名是否相同
67 LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest hash verification failed. Expected hash = ";
68 utils::HexDumpVector(expected_metadata_hash);
69 LOG(ERROR) << "Calculated hash = ";
70 utils::HexDumpVector(calculated_metadata_hash);
71 return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureMismatch;
72 }
73 } else { //在升级数据中含有签名信息时,对签名的校验
74 if (!PayloadVerifier::VerifySignature(metadata_signature_protobuf_blob,
75 path_to_public_key.value(),
76 calculated_metadata_hash)) {
77 LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest hash verification failed.";
78 return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureMismatch;
79 }
80 }
81
82 // The autoupdate_CatchBadSignatures test checks for this string in
83 // log-files. Keep in sync.
84 LOG(INFO) << "Metadata hash signature matches value in Omaha response.";
85 return ErrorCode::kSuccess;
86 }
这个方法主要说明了metadata_signature签名的验证机制,其中有一个payload_,是在DeltaPerformer构造函数中赋的值。接下来在分析manifest_.ParseFromArray(&payload[manifest_offset], manifest_size_),在初看到这行代码的时候,花了很长时间也没有找到ParseFromArray的实现。DeltaArchiveManifest类也没有找到对应的C++类,但是却找到了update_metadata_pb2.py和update_metadata.proto。update_metadata.proto的内容如下
src/system/update_engine/update_metadata.proto
1 message Extent {
2 optional uint64 start_block = 1;
3 optional uint64 num_blocks = 2;
4 }
5
6 message Signatures {
7 message Signature {
8 optional uint32 version = 1;
9 optional bytes data = 2;
10 }
11 repeated Signature signatures = 1;
12 }
13
14 message PartitionInfo {
15 optional uint64 size = 1;
16 optional bytes hash = 2;
17 }
18
19 // Describe an image we are based on in a human friendly way.
20 // Examples:
21 // dev-channel, x86-alex, 1.2.3, mp-v3
22 // nplusone-channel, x86-alex, 1.2.4, mp-v3, dev-channel, 1.2.3
23 //
24 // All fields will be set, if this message is present.
25 message ImageInfo {
26 optional string board = 1;
27 optional string key = 2;
28 optional string channel = 3;
29 optional string version = 4;
30
31 // If these values aren't present, they should be assumed to match
32 // the equivalent value above. They are normally only different for
33 // special image types such as nplusone images.
34 optional string build_channel = 5;
35 optional string build_version = 6;
36 }
37
38 message InstallOperation {
39 enum Type {
40 REPLACE = 0; // Replace destination extents w/ attached data
41 REPLACE_BZ = 1; // Replace destination extents w/ attached bzipped data
42 MOVE = 2; // Move source extents to destination extents
43 BSDIFF = 3; // The data is a bsdiff binary diff
44
45 // On minor version 2 or newer, these operations are supported:
46 SOURCE_COPY = 4; // Copy from source to target partition
47 SOURCE_BSDIFF = 5; // Like BSDIFF, but read from source partition
48
49 // On minor version 3 or newer and on major version 2 or newer, these
50 // operations are supported:
51 ZERO = 6; // Write zeros in the destination.
52 DISCARD = 7; // Discard the destination blocks, reading as undefined.
53 REPLACE_XZ = 8; // Replace destination extents w/ attached xz data.
54
55 // On minor version 4 or newer, these operations are supported:
56 IMGDIFF = 9; // The data is in imgdiff format.
57 }
58 required Type type = 1;
59 // The offset into the delta file (after the protobuf)
60 // where the data (if any) is stored
61 optional uint32 data_offset = 2;
62 // The length of the data in the delta file
63 optional uint32 data_length = 3;
64
65 // Ordered list of extents that are read from (if any) and written to.
66 repeated Extent src_extents = 4;
67 // Byte length of src, equal to the number of blocks in src_extents *
68 // block_size. It is used for BSDIFF, because we need to pass that
69 // external program the number of bytes to read from the blocks we pass it.
70 // This is not used in any other operation.
71 optional uint64 src_length = 5;
72
73 repeated Extent dst_extents = 6;
74 // Byte length of dst, equal to the number of blocks in dst_extents *
75 // block_size. Used for BSDIFF, but not in any other operation.
76 optional uint64 dst_length = 7;
77
78 // Optional SHA 256 hash of the blob associated with this operation.
79 // This is used as a primary validation for http-based downloads and
80 // as a defense-in-depth validation for https-based downloads. If
81 // the operation doesn't refer to any blob, this field will have
82 // zero bytes.
83 optional bytes data_sha256_hash = 8;
84
85 // Indicates the SHA 256 hash of the source data referenced in src_extents at
86 // the time of applying the operation. If present, the update_engine daemon
87 // MUST read and verify the source data before applying the operation.
88 optional bytes src_sha256_hash = 9;
89 }
90
91 // Describes the update to apply to a single partition.
92 message PartitionUpdate {
93 // A platform-specific name to identify the partition set being updated. For
94 // example, in Chrome OS this could be "ROOT" or "KERNEL".
95 required string partition_name = 1;
96
97 // Whether this partition carries a filesystem with post-install program that
98 // must be run to finalize the update process. See also |postinstall_path| and
99 // |filesystem_type|.
100 optional bool run_postinstall = 2;
101
102 // The path of the executable program to run during the post-install step,
103 // relative to the root of this filesystem. If not set, the default "postinst"
104 // will be used. This setting is only used when |run_postinstall| is set and
105 // true.
106 optional string postinstall_path = 3;
107
108 // The filesystem type as passed to the mount(2) syscall when mounting the new
109 // filesystem to run the post-install program. If not set, a fixed list of
110 // filesystems will be attempted. This setting is only used if
111 // |run_postinstall| is set and true.
112 optional string filesystem_type = 4;
113
114 // If present, a list of signatures of the new_partition_info.hash signed with
115 // different keys. If the update_engine daemon requires vendor-signed images
116 // and has its public key installed, one of the signatures should be valid
117 // for /postinstall to run.
118 repeated Signatures.Signature new_partition_signature = 5;
119
120 optional PartitionInfo old_partition_info = 6;
121 optional PartitionInfo new_partition_info = 7;
122
123 // The list of operations to be performed to apply this PartitionUpdate. The
124 // associated operation blobs (in operations[i].data_offset, data_length)
125 // should be stored contiguously and in the same order.
126 repeated InstallOperation operations = 8;
127
128 // Whether a failure in the postinstall step for this partition should be
129 // ignored.
130 optional bool postinstall_optional = 9;
131 }
132
133 message DeltaArchiveManifest {
134 // Only present in major version = 1. List of install operations for the
135 // kernel and rootfs partitions. For major version = 2 see the |partitions|
136 // field.
137 repeated InstallOperation install_operations = 1;
138 repeated InstallOperation kernel_install_operations = 2;
139
140 // (At time of writing) usually 4096
141 optional uint32 block_size = 3 [default = 4096];
142
143 // If signatures are present, the offset into the blobs, generally
144 // tacked onto the end of the file, and the length. We use an offset
145 // rather than a bool to allow for more flexibility in future file formats.
146 // If either is absent, it means signatures aren't supported in this
147 // file.
148 optional uint64 signatures_offset = 4;
149 optional uint64 signatures_size = 5;
150
151 // Only present in major version = 1. Partition metadata used to validate the
152 // update. For major version = 2 see the |partitions| field.
153 optional PartitionInfo old_kernel_info = 6;
154 optional PartitionInfo new_kernel_info = 7;
155 optional PartitionInfo old_rootfs_info = 8;
156 optional PartitionInfo new_rootfs_info = 9;
157
158 // old_image_info will only be present for delta images.
159 optional ImageInfo old_image_info = 10;
160
161 optional ImageInfo new_image_info = 11;
162
163 // The minor version, also referred as "delta version", of the payload.
164 optional uint32 minor_version = 12 [default = 0];
165
166 // Only present in major version >= 2. List of partitions that will be
167 // updated, in the order they will be updated. This field replaces the
168 // |install_operations|, |kernel_install_operations| and the
169 // |{old,new}_{kernel,rootfs}_info| fields used in major version = 1. This
170 // array can have more than two partitions if needed, and they are identified
171 // by the partition name.
172 repeated PartitionUpdate partitions = 13;
173
174 // The maximum timestamp of the OS allowed to apply this payload.
175 // Can be used to prevent downgrading the OS.
176 optional int64 max_timestamp = 14;
177 }
可以看出它应该就是由update_metadata_pb2.py这个脚本解析的manifest的数据格式。后来了解到这是Protobuf数据格式,是比xml和json更加高效的数据格式,采用了二进制的存储。那么其实根据DeltaArchiveManifest我们就能大体推断出Manifest中所包含的数据类型。主要就是安装更新操作的类型,数据的签名,新旧内核,rootfs,ImageInfo,分区更新等。到此ParsePayloadMetadata这个方法就算是分析完了。回到Write中继续分析,当解析完成了Manifest之后,就调用了ValidateManifest()来验证manifest。
2.ValidateManifest()来验证manifest
1 ErrorCode DeltaPerformer::ValidateManifest() {
2 // Perform assorted checks to sanity check the manifest, make sure it
3 // matches data from other sources, and that it is a supported version.
4
5 bool has_old_fields =
6 (manifest_.has_old_kernel_info() || manifest_.has_old_rootfs_info());
7 for (const PartitionUpdate& partition : manifest_.partitions()) {
8 has_old_fields = has_old_fields || partition.has_old_partition_info();
9 }
10
11 // The presence of an old partition hash is the sole indicator for a delta
12 // update.
13 InstallPayloadType actual_payload_type =
14 has_old_fields ? InstallPayloadType::kDelta : InstallPayloadType::kFull; //获取升级的类型
15
16 if (payload_->type == InstallPayloadType::kUnknown) { //payload_->type的默认值是KUnknown
17 LOG(INFO) << "Detected a '"
18 << InstallPayloadTypeToString(actual_payload_type)
19 << "' payload.";
20 payload_->type = actual_payload_type;
21 } else if (payload_->type != actual_payload_type) {
22 LOG(ERROR) << "InstallPlan expected a '"
23 << InstallPayloadTypeToString(payload_->type)
24 << "' payload but the downloaded manifest contains a '"
25 << InstallPayloadTypeToString(actual_payload_type)
26 << "' payload.";
27 return ErrorCode::kPayloadMismatchedType;
28 }
29
30 // Check that the minor version is compatible.
31 if (actual_payload_type == InstallPayloadType::kFull) { //进行更加安全性检测
32 if (manifest_.minor_version() != kFullPayloadMinorVersion) {
33 LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest contains minor version "
34 << manifest_.minor_version()
35 << ", but all full payloads should have version "
36 << kFullPayloadMinorVersion << ".";
37 return ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMinorPayloadVersion;
38 }
39 } else {
40 if (manifest_.minor_version() != supported_minor_version_) {
41 LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest contains minor version "
42 << manifest_.minor_version()
43 << " not the supported "
44 << supported_minor_version_;
45 return ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMinorPayloadVersion;
46 }
47 }
48
49 if (major_payload_version_ != kChromeOSMajorPayloadVersion) {
50 if (manifest_.has_old_rootfs_info() || //这些字段只应该在kChromeOSMajorPayloadVersion中有
51 manifest_.has_new_rootfs_info() ||
52 manifest_.has_old_kernel_info() ||
53 manifest_.has_new_kernel_info() ||
54 manifest_.install_operations_size() != 0 ||
55 manifest_.kernel_install_operations_size() != 0) {
56 LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest contains deprecated field only supported in "
57 << "major payload version 1, but the payload major version is "
58 << major_payload_version_;
59 return ErrorCode::kPayloadMismatchedType;
60 }
61 }
62
63 if (manifest_.max_timestamp() < hardware_->GetBuildTimestamp()) { //对时间戳的检测
64 LOG(ERROR) << "The current OS build timestamp ("
65 << hardware_->GetBuildTimestamp()
66 << ") is newer than the maximum timestamp in the manifest ("
67 << manifest_.max_timestamp() << ")";
68 return ErrorCode::kPayloadTimestampError;
69 }
70
71 // TODO(garnold) we should be adding more and more manifest checks, such as
72 // partition boundaries etc (see chromium-os:37661).
73
74 return ErrorCode::kSuccess;
75 }
这个方法主要验证的了升级的类型,已经升级程序版本的正确性,最后对时间戳进行了一次校验,理论上升级包中新版本的时间戳应该比系统中当前版本的时间戳更新一些,才允许升级。对manifest进行了校验之后,在Write方法中标记manifest_valid_为true,清空缓存区后,开始对分区信息进行解析。
3.解析Manifest中的Partitions的信息
1 bool DeltaPerformer::ParseManifestPartitions(ErrorCode* error) {
2 if (major_payload_version_ == kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion) {
3 partitions_.clear();
4 for (const PartitionUpdate& partition : manifest_.partitions()) {
5 partitions_.push_back(partition); //将partitons的信息保存到partitions中
6 }
7 manifest_.clear_partitions(); //将manifest_中的分区信息进行删除
8 } else if (major_payload_version_ == kChromeOSMajorPayloadVersion) {
9 LOG(INFO) << "Converting update information from old format.";
10 //这部分是老版本的在使用,就先不进行分析了
11 }
12
13 // Fill in the InstallPlan::partitions based on the partitions from the
14 // payload.
15 for (const auto& partition : partitions_) {
16 InstallPlan::Partition install_part;
17 install_part.name = partition.partition_name(); //分区的name
18 install_part.run_postinstall = //postinstall
19 partition.has_run_postinstall() && partition.run_postinstall();
20 if (install_part.run_postinstall) {
21 install_part.postinstall_path =
22 (partition.has_postinstall_path() ? partition.postinstall_path()
23 : kPostinstallDefaultScript);
24 install_part.filesystem_type = partition.filesystem_type();
25 install_part.postinstall_optional = partition.postinstall_optional();
26 }
27
28 if (partition.has_old_partition_info()) { //获取old 分区中的信息
29 const PartitionInfo& info = partition.old_partition_info();
30 install_part.source_size = info.size();
31 install_part.source_hash.assign(info.hash().begin(), info.hash().end());
32 }
33
34 if (!partition.has_new_partition_info()) {
35 LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to get new partition hash info on partition "
36 << install_part.name << ".";
37 *error = ErrorCode::kDownloadNewPartitionInfoError;
38 return false;
39 }
40 const PartitionInfo& info = partition.new_partition_info();
41 install_part.target_size = info.size(); //新分区的信息
42 install_part.target_hash.assign(info.hash().begin(), info.hash().end());
43
44 install_plan_->partitions.push_back(install_part); //保存到install_plan_
45 }
46
47 if (!install_plan_->LoadPartitionsFromSlots(boot_control_)) { //根据分区name,slot,获取分区的路径
48 LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to determine all the partition devices.";
49 *error = ErrorCode::kInstallDeviceOpenError;
50 return false;
51 }
52 LogPartitionInfo(partitions_); //打印分区信息
53 return true;
54 }
其实解析分区主要就是将分区信息从manifest_中转移到install_plan_。在Write中最后做的就是获取操作数,获取操作类型,根据操作类型执行对应的操作,验证payload中数据的签名。其中需要注意的是关于操作数的计算和更新数据的校验。
4.关于操作数的计算,可以看下面相关的部分
1 num_total_operations_ = 0;
2 for (const auto& partition : partitions_) {
3 num_total_operations_ += partition.operations_size();
4 acc_num_operations_.push_back(num_total_operations_);
5 }
6
7 while (next_operation_num_ >= acc_num_operations_[current_partition_]) {
8 CloseCurrentPartition();
9 current_partition_++;
10 if (!OpenCurrentPartition()) {
11 *error = ErrorCode::kInstallDeviceOpenError;
12 return false;
13 }
14 }
15
16 const size_t partition_operation_num = next_operation_num_ - (
17 current_partition_ ? acc_num_operations_[current_partition_ - 1] : 0);
假设有分区A,B,C对应的操作数为2,4,6。那么num_total_operations_ =12,acc_num_operations_.中存放的元素为2,6,12,此时执行到了第2个操作,next_operation_num_ =2,而2是等于acc_num_operations_[0]的,而存放操作的数组是从0开始的,也就是说,当next_operation_num_等于acc_num_operations_时也就是说当前分区的操作已经执行完了,应该切换到下一个分区了,最后根据next_operation_num_和acc_num_operations_计算出操作类型的索引,获取对应的操作类型。最后对于更新数据的校验是指每当应用所下载的数据的时候,都会对其进行校验,首先是保存了数据的hash值之后再根据所下载的数据计算一个hash指,进行比对,验证数据是否正确。
到这里DownloadAction的核心部分已经分析完成,下面一篇文章会分析FilesystemVerifierAction,PostinstallRunnerAction。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号