在update_engine-整体结构(二)中分析到了Action,那么我们接着继续分析.
首先来看一下BuildUpdateActons(...)这个方法。
src/system/update_engine/update_attempter_android.cc
1 void UpdateAttempterAndroid::BuildUpdateActions(const string& url) {
2 CHECK(!processor_->IsRunning());
3 processor_->set_delegate(this);
4
5 // Actions:
6 shared_ptr<InstallPlanAction> install_plan_action(
7 new InstallPlanAction(install_plan_));
8
9 HttpFetcher* download_fetcher = nullptr;
10 if (FileFetcher::SupportedUrl(url)) {
11 DLOG(INFO) << "Using FileFetcher for file URL.";
12 download_fetcher = new FileFetcher();
13 } else {
14 #ifdef _UE_SIDELOAD
15 LOG(FATAL) << "Unsupported sideload URI: " << url;
16 #else
17 LibcurlHttpFetcher* libcurl_fetcher =
18 new LibcurlHttpFetcher(&proxy_resolver_, hardware_);
19 libcurl_fetcher->set_server_to_check(ServerToCheck::kDownload);
20 download_fetcher = libcurl_fetcher;
21 #endif // _UE_SIDELOAD
22 }
23 shared_ptr<DownloadAction> download_action(
24 new DownloadAction(prefs_,
25 boot_control_,
26 hardware_,
27 nullptr, // system_state, not used.
28 download_fetcher)); // passes ownership
29 shared_ptr<FilesystemVerifierAction> filesystem_verifier_action(
30 new FilesystemVerifierAction());
31
32 shared_ptr<PostinstallRunnerAction> postinstall_runner_action(
33 new PostinstallRunnerAction(boot_control_, hardware_));
34
35 download_action->set_delegate(this);
36 download_action->set_base_offset(base_offset_);
37 download_action_ = download_action;
38 postinstall_runner_action->set_delegate(this);
39
40 actions_.push_back(shared_ptr<AbstractAction>(install_plan_action));
41 actions_.push_back(shared_ptr<AbstractAction>(download_action));
42 actions_.push_back(shared_ptr<AbstractAction>(filesystem_verifier_action));
43 actions_.push_back(shared_ptr<AbstractAction>(postinstall_runner_action));
44
45 // Bond them together. We have to use the leaf-types when calling
46 // BondActions().
47 BondActions(install_plan_action.get(), download_action.get());
48 BondActions(download_action.get(), filesystem_verifier_action.get());
49 BondActions(filesystem_verifier_action.get(),
50 postinstall_runner_action.get());
51
52 // Enqueue the actions.
53 for (const shared_ptr<AbstractAction>& action : actions_)
54 processor_->EnqueueAction(action.get());
55 }
我们会发现processor_,InstallPlanAction,DownloadAction,FilesystemVerifierAction,PostinstallRunnerAction。首先分析processor_,它是在UpdateAttempterAndroid的构造方法中被赋值
1 UpdateAttempterAndroid::UpdateAttempterAndroid(
2 DaemonStateInterface* daemon_state,
3 PrefsInterface* prefs,
4 BootControlInterface* boot_control,
5 HardwareInterface* hardware)
6 : daemon_state_(daemon_state),
7 prefs_(prefs),
8 boot_control_(boot_control),
9 hardware_(hardware),
10 processor_(new ActionProcessor()) {
11 network_selector_ = network::CreateNetworkSelector();
12 }
ActionProcessor的数据结构为:
1 // An ActionProcessor keeps a queue of Actions and processes them in order.
2
3 namespace chromeos_update_engine {
4
5 class AbstractAction;
6 class ActionProcessorDelegate;
7
8 class ActionProcessor {
9 public:
10 ActionProcessor() = default;
11
12 virtual ~ActionProcessor();
13
14 // Starts processing the first Action in the queue. If there's a delegate,
15 // when all processing is complete, ProcessingDone() will be called on the
16 // delegate.
17 virtual void StartProcessing();
18
19 // Aborts processing. If an Action is running, it will have
20 // TerminateProcessing() called on it. The Action that was running and all the
21 // remaining actions will be lost and must be re-enqueued if this Processor is
22 // to use it.
23 void StopProcessing();
24
25 // Suspend the processing. If an Action is running, it will have the
26 // SuspendProcessing() called on it, and it should suspend operations until
27 // ResumeProcessing() is called on this class to continue. While suspended,
28 // no new actions will be started. Calling SuspendProcessing while the
29 // processing is suspended or not running this method performs no action.
30 void SuspendProcessing();
31
32 // Resume the suspended processing. If the ActionProcessor is not suspended
33 // or not running in the first place this method performs no action.
34 void ResumeProcessing();
35
36 // Returns true iff the processing was started but not yet completed nor
37 // stopped.
38 bool IsRunning() const { return current_action_ != nullptr || suspended_; }
39
40 // Adds another Action to the end of the queue.
41 virtual void EnqueueAction(AbstractAction* action);
42
43 // Sets/gets the current delegate. Set to null to remove a delegate.
44 ActionProcessorDelegate* delegate() const { return delegate_; }
45 void set_delegate(ActionProcessorDelegate *delegate) {
46 delegate_ = delegate;
47 }
48
49 // Returns a pointer to the current Action that's processing.
50 AbstractAction* current_action() const {
51 return current_action_;
52 }
53
54 // Called by an action to notify processor that it's done. Caller passes self.
55 void ActionComplete(AbstractAction* actionptr, ErrorCode code);
56
57 private:
58 // Continue processing actions (if any) after the last action terminated with
59 // the passed error code. If there are no more actions to process, the
60 // processing will terminate.
61 void StartNextActionOrFinish(ErrorCode code);
62
63 // Actions that have not yet begun processing, in the order in which
64 // they'll be processed.
65 std::deque<AbstractAction*> actions_;
66
67 // A pointer to the currently processing Action, if any.
68 AbstractAction* current_action_{nullptr};
69
70 // The ErrorCode reported by an action that was suspended but finished while
71 // being suspended. This error code is stored here to be reported back to the
72 // delegate once the processor is resumed.
73 ErrorCode suspended_error_code_{ErrorCode::kSuccess};
74
75 // Whether the action processor is or should be suspended.
76 bool suspended_{false};
77
78 // A pointer to the delegate, or null if none.
79 ActionProcessorDelegate* delegate_{nullptr};
80
81 DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(ActionProcessor);
82 };
83
84 // A delegate object can be used to be notified of events that happen
85 // in an ActionProcessor. An instance of this class can be passed to an
86 // ActionProcessor to register itself.
87 class ActionProcessorDelegate {
88 public:
89 virtual ~ActionProcessorDelegate() = default;
90
91 // Called when all processing in an ActionProcessor has completed. A pointer
92 // to the ActionProcessor is passed. |code| is set to the exit code of the
93 // last completed action.
94 virtual void ProcessingDone(const ActionProcessor* processor,
95 ErrorCode code) {}
96
97 // Called when processing has stopped. Does not mean that all Actions have
98 // completed. If/when all Actions complete, ProcessingDone() will be called.
99 virtual void ProcessingStopped(const ActionProcessor* processor) {}
100
101 // Called whenever an action has finished processing, either successfully
102 // or otherwise.
103 virtual void ActionCompleted(ActionProcessor* processor,
104 AbstractAction* action,
105 ErrorCode code) {}
106 };
107
108 }
从中可以看到ActionProcessor其实就是用来管理Action的,它的方法都比较简单,根据注释我们大体就能够明白每个方法的意思,在遇到的时候某一个方法再具体分析。接下来再看Action它所存在的继承关系如下
Aciton继承关系

FilesystemVerifierAction,PostinstallRunnerAction,DownloadAction都继承了InstallPlanAction,根据继承关系可以看出他们都会有PerformAction,ActionCompleted等方法。PerformAction()是在Action开始执行前进行调用,而ActionCompleted是在执行完成后进行调用。先来看看InstallPlanAction中的内容
src/system/update_engine/payload_consumer/install_plan.h
1 class InstallPlanAction : public Action<InstallPlanAction> {
2 public:
3 InstallPlanAction() {}
4 explicit InstallPlanAction(const InstallPlan& install_plan):
5 install_plan_(install_plan) {}
6
7 void PerformAction() override {
8 if (HasOutputPipe()) {
9 SetOutputObject(install_plan_);
10 }
11 processor_->ActionComplete(this, ErrorCode::kSuccess);
12 }
13
14 InstallPlan* install_plan() { return &install_plan_; }
15
16 static std::string StaticType() { return "InstallPlanAction"; }
17 std::string Type() const override { return StaticType(); }
18
19 typedef ActionTraits<InstallPlanAction>::InputObjectType InputObjectType;
20 typedef ActionTraits<InstallPlanAction>::OutputObjectType OutputObjectType;
21
22 private:
23 InstallPlan install_plan_;
24
25 DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(InstallPlanAction);
26 };
可以看到InstallAction比较简单,仅仅是将install_plan_设置为了输出对象,传递给了下一个Action,这是Action之间的一个通信方式,这个方式可以称之为pipe方式,下面来分析一下这种通信方式。先来看在Action这个类里面提到的ActionPipe
src/system/update_engine/common/action_pipe.h
1 namespace chromeos_update_engine {
2
3 // Used by Actions an InputObjectType or OutputObjectType to specify that
4 // for that type, no object is taken/given.
5 class NoneType {};
6
7 template<typename T>
8 class Action;
9
10 template<typename ObjectType>
11 class ActionPipe {
12 public:
13 virtual ~ActionPipe() {}
14
15 // This should be called by an Action on its input pipe.
16 // Returns a reference to the stored object.
17 const ObjectType& contents() const { return contents_; } //获取管道中的内容
18
19 // This should be called by an Action on its output pipe.
20 // Stores a copy of the passed object in this pipe.
21 void set_contents(const ObjectType& contents) { contents_ = contents; } //设置管道中的内容
22
23 // Bonds two Actions together with a new ActionPipe. The ActionPipe is
24 // jointly owned by the two Actions and will be automatically destroyed
25 // when the last Action is destroyed.
26 template<typename FromAction, typename ToAction>
27 static void Bond(FromAction* from, ToAction* to) { //将两个Action连接通过pipe连接在一起
28 std::shared_ptr<ActionPipe<ObjectType>> pipe(new ActionPipe<ObjectType>);
29 from->set_out_pipe(pipe);
30
31 to->set_in_pipe(pipe); // If you get an error on this line, then
32 // it most likely means that the From object's OutputObjectType is
33 // different from the To object's InputObjectType.
34 }
35
36 private:
37 ObjectType contents_;
38
39 // The ctor is private. This is because this class should construct itself
40 // via the static Bond() method.
41 ActionPipe() {}
42 DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(ActionPipe);
43 };
44
45 // Utility function
46 template<typename FromAction, typename ToAction>
47 void BondActions(FromAction* from, ToAction* to) {
48 static_assert(
49 std::is_same<typename FromAction::OutputObjectType,
50 typename ToAction::InputObjectType>::value,
51 "FromAction::OutputObjectType doesn't match ToAction::InputObjectType");
52 ActionPipe<typename FromAction::OutputObjectType>::Bond(from, to);
53 }
54
55 }
可以看到ActionPipe主要就是将两个Action连接在一起。为什么说就会连接在一起呢?再来看Action中相关的方法
src/system/update_engine/common/action.h
1 template<typename SubClass>
2 class Action : public AbstractAction {
3 public:
4 ~Action() override {}
5
6 // Attaches an input pipe to this Action. This is optional; an Action
7 // doesn't need to have an input pipe. The input pipe must be of the type
8 // of object that this class expects.
9 // This is generally called by ActionPipe::Bond()
10 void set_in_pipe( //设置输入管道
11 // this type is a fancy way of saying: a shared_ptr to an
12 // ActionPipe<InputObjectType>.
13 const std::shared_ptr<ActionPipe<
14 typename ActionTraits<SubClass>::InputObjectType>>& in_pipe) {
15 in_pipe_ = in_pipe;
16 }
17
18 // Attaches an output pipe to this Action. This is optional; an Action
19 // doesn't need to have an output pipe. The output pipe must be of the type
20 // of object that this class expects.
21 // This is generally called by ActionPipe::Bond()
22 void set_out_pipe( //设置输出管道
23 // this type is a fancy way of saying: a shared_ptr to an
24 // ActionPipe<OutputObjectType>.
25 const std::shared_ptr<ActionPipe<
26 typename ActionTraits<SubClass>::OutputObjectType>>& out_pipe) {
27 out_pipe_ = out_pipe;
28 }
29
30 // Returns true iff there is an associated input pipe. If there's an input
31 // pipe, there's an input object, but it may have been constructed with the
32 // default ctor if the previous action didn't call SetOutputObject().
33 bool HasInputObject() const { return in_pipe_.get(); } //是否有输入管道
34
35 // returns a const reference to the object in the input pipe.
36 const typename ActionTraits<SubClass>::InputObjectType& GetInputObject() //获取输入的内容
37 const {
38 CHECK(HasInputObject());
39 return in_pipe_->contents();
40 }
41
42 // Returns true iff there's an output pipe.
43 bool HasOutputPipe() const { //是否有输出管道
44 return out_pipe_.get();
45 }
46
47 // Copies the object passed into the output pipe. It will be accessible to
48 // the next Action via that action's input pipe (which is the same as this
49 // Action's output pipe).
50 void SetOutputObject( //设置输出的内容
51 const typename ActionTraits<SubClass>::OutputObjectType& out_obj) {
52 CHECK(HasOutputPipe());
53 out_pipe_->set_contents(out_obj);
54 }
55
56 // Returns a reference to the object sitting in the output pipe.
57 const typename ActionTraits<SubClass>::OutputObjectType& GetOutputObject() { //获取输出的内容
58 CHECK(HasOutputPipe());
59 return out_pipe_->contents();
60 }
61
62 protected:
63 // We use a shared_ptr to the pipe. shared_ptr objects destroy what they
64 // point to when the last such shared_ptr object dies. We consider the
65 // Actions on either end of a pipe to "own" the pipe. When the last Action
66 // of the two dies, the ActionPipe will die, too.
67 std::shared_ptr<ActionPipe<typename ActionTraits<SubClass>::InputObjectType>>
68 in_pipe_;
69 std::shared_ptr<ActionPipe<typename ActionTraits<SubClass>::OutputObjectType>>
70 out_pipe_;
71 };
从这里我们就能够看出每个Action其实有两个ActionPipe,一个是输入ActionPipe,一个是输出ActionPipe,输入ActionPipe和前一个Action的输出ActionPipe其实是一个ActionPipe,输出Actionpipe和下一个Action的输出ActionPipe是一个ActionPipe.
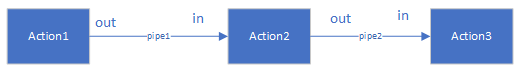
ActionTraits在这个类里仅仅是为InstallPlan这个类型定义了一个新的类型
src/system/update_engine/payload_consumer/install_plan.h
1 template<>
2 class ActionTraits<InstallPlanAction> {
3 public:
4 // Takes the install plan as input
5 typedef InstallPlan InputObjectType;
6 // Passes the install plan as output
7 typedef InstallPlan OutputObjectType;
8 };
到这里Action机制也分析的差不多了,我们可以回到BuildUpdateActions中继续进行分析了。

1 void UpdateAttempterAndroid::BuildUpdateActions(const string& url) { 2 CHECK(!processor_->IsRunning()); 3 processor_->set_delegate(this); 4 5 // Actions: 6 shared_ptr<InstallPlanAction> install_plan_action( 7 new InstallPlanAction(install_plan_)); 8 9 HttpFetcher* download_fetcher = nullptr; 10 if (FileFetcher::SupportedUrl(url)) { 11 DLOG(INFO) << "Using FileFetcher for file URL."; 12 download_fetcher = new FileFetcher(); 13 } else { 14 #ifdef _UE_SIDELOAD 15 LOG(FATAL) << "Unsupported sideload URI: " << url; 16 #else 17 LibcurlHttpFetcher* libcurl_fetcher = 18 new LibcurlHttpFetcher(&proxy_resolver_, hardware_); 19 libcurl_fetcher->set_server_to_check(ServerToCheck::kDownload); 20 download_fetcher = libcurl_fetcher; 21 #endif // _UE_SIDELOAD 22 } 23 shared_ptr<DownloadAction> download_action( 24 new DownloadAction(prefs_, 25 boot_control_, 26 hardware_, 27 nullptr, // system_state, not used. 28 download_fetcher)); // passes ownership 29 shared_ptr<FilesystemVerifierAction> filesystem_verifier_action( 30 new FilesystemVerifierAction()); 31 32 shared_ptr<PostinstallRunnerAction> postinstall_runner_action( 33 new PostinstallRunnerAction(boot_control_, hardware_)); 34 35 download_action->set_delegate(this); 36 download_action->set_base_offset(base_offset_); 37 download_action_ = download_action; 38 postinstall_runner_action->set_delegate(this); 39 40 actions_.push_back(shared_ptr<AbstractAction>(install_plan_action)); 41 actions_.push_back(shared_ptr<AbstractAction>(download_action)); 42 actions_.push_back(shared_ptr<AbstractAction>(filesystem_verifier_action)); 43 actions_.push_back(shared_ptr<AbstractAction>(postinstall_runner_action)); 44 45 // Bond them together. We have to use the leaf-types when calling 46 // BondActions(). 47 BondActions(install_plan_action.get(), download_action.get()); 48 BondActions(download_action.get(), filesystem_verifier_action.get()); 49 BondActions(filesystem_verifier_action.get(), 50 postinstall_runner_action.get()); 51 52 // Enqueue the actions. 53 for (const shared_ptr<AbstractAction>& action : actions_) 54 processor_->EnqueueAction(action.get()); 55 }
在这个方法里主要做了:
1.为processor_设置delegate,其实也就是注册了回调方法,UpdateAttempterAndroid实现了ActionProcessDelegate中的方法.
2. 创建了InstallPlanAction
3.创建了download_fetcher,我们这里假定用的是本地的文件既使用file:///协议,所以download_fetcher即为FileFetcher,从这一部分的代码可以看HtppFetcher,FileFetcher,LibcurlHttpFetcher之间具有继承或实现的关系。
4.创建DownloadAction,注意在创建的时候传入了download_fetcher为FileFetcher类型
5.创建FilesystemVerifierAction,PostinstallRunnerAction.从这里可以看出升级流程的精华应该就是这三个Action了
6.为download_action设置delegate,设置开始下载的offfset等,因为代码中设置delegate的操作比较多,如果不注意很有可能记混乱了。
7.为postinstall_runner_action设置delegate
8.将Action加入到Action的集合中
9.使用BondActions方法为Action之间建立管道。
10.将action遍历放入到processor_的队列中,并且设置action的管理者为processor_。
在分析完这个方法所干的事情之后,再分析一下HtppFetcher,FileFetcher,LibcurlHttpFetcher这三者之间的关系
HtppFetcher,FileFetcher,LibcurlHttpFetcher这三者之间的关系


现在继续分析ApplyPayload中的最后一个方法UpdateBootFlags()
1 void UpdateAttempterAndroid::UpdateBootFlags() {
2 if (updated_boot_flags_) {
3 LOG(INFO) << "Already updated boot flags. Skipping.";
4 CompleteUpdateBootFlags(true);
5 return;
6 }
7 // This is purely best effort.
8 LOG(INFO) << "Marking booted slot as good.";
9 if (!boot_control_->MarkBootSuccessfulAsync(
10 Bind(&UpdateAttempterAndroid::CompleteUpdateBootFlags,
11 base::Unretained(this)))) {
12 LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to mark current boot as successful.";
13 CompleteUpdateBootFlags(false);
14 }
15 }
首先检查当前运行的slot是否已经被标记为successful状态,如果是则调用CompleteUpdateBootFlags方法,否则的就调用MarkBootSuccessfulAsync将当前的slot标记为successful。标记完成后调用CompleteUpdateBootFlags方法
1 void UpdateAttempterAndroid::CompleteUpdateBootFlags(bool successful) {
2 updated_boot_flags_ = true;
3 ScheduleProcessingStart();
4 }
从这里看出即使标记失败了仍然调用 ScheduleProcessingStart(),这个方法主要就是开始执行Action
1 void UpdateAttempterAndroid::ScheduleProcessingStart() {
2 LOG(INFO) << "Scheduling an action processor start.";
3 brillo::MessageLoop::current()->PostTask(
4 FROM_HERE,
5 Bind([](ActionProcessor* processor) { processor->StartProcessing(); },
6 base::Unretained(processor_.get())));
7 }
在来看看StartProcessing()方法的实现,首先是获取对列中的第一个action,打印action的类型,之后将action移出队列,并且调用PerformAction。
src/system/update_engine/common/action_processor.cc
1 void ActionProcessor::StartProcessing() {
2 CHECK(!IsRunning());
3 if (!actions_.empty()) {
4 current_action_ = actions_.front();
5 LOG(INFO) << "ActionProcessor: starting " << current_action_->Type();
6 actions_.pop_front();
7 current_action_->PerformAction();
8 }
9 }
分析到了这里就对整体的update_engine有了一定的了解,接下来只需要对各个Action逐个击破就好了。在之前已经看过了InstallPlanAction,它的内容很简单,仅仅是在输出管道中设置了install_plan_,接下来就调用了processor_->ActionComplete(this, ErrorCode::kSuccess),看一下ActionComplete的内容,它是如何让下一个action开始执行的。
1 void ActionProcessor::ActionComplete(AbstractAction* actionptr,
2 ErrorCode code) {
3 CHECK_EQ(actionptr, current_action_);
4 if (delegate_)
5 delegate_->ActionCompleted(this, actionptr, code);
6 string old_type = current_action_->Type();
7 current_action_->ActionCompleted(code);
8 current_action_->SetProcessor(nullptr);
9 current_action_ = nullptr;
10 LOG(INFO) << "ActionProcessor: finished "
11 << (actions_.empty() ? "last action " : "") << old_type
12 << (suspended_ ? " while suspended" : "")
13 << " with code " << utils::ErrorCodeToString(code);
14 if (!actions_.empty() && code != ErrorCode::kSuccess) {
15 LOG(INFO) << "ActionProcessor: Aborting processing due to failure.";
16 actions_.clear();
17 }
18 if (suspended_) {
19 // If an action finished while suspended we don't start the next action (or
20 // terminate the processing) until the processor is resumed. This condition
21 // will be flagged by a nullptr current_action_ while suspended_ is true.
22 suspended_error_code_ = code;
23 return;
24 }
25 StartNextActionOrFinish(code);
26 }
其实这个方法中也就进行了善后和开始下一个Action的工作。包括:
1.判断是否注册了回调方法。这里的delegate_的类型为UpdateAttempterAndroid。如果注册了就回调ActionCompleted方法,在UpdateAttempterAndroid中它的内容为
1 void UpdateAttempterAndroid::ActionCompleted(ActionProcessor* processor,
2 AbstractAction* action,
3 ErrorCode code) {
4 // Reset download progress regardless of whether or not the download
5 // action succeeded.
6 const string type = action->Type();
7 if (type == DownloadAction::StaticType()) {
8 download_progress_ = 0;
9 }
10 if (code != ErrorCode::kSuccess) {
11 // If an action failed, the ActionProcessor will cancel the whole thing.
12 return;
13 }
14 if (type == DownloadAction::StaticType()) {
15 SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus::FINALIZING);
16 }
17 }
可以看到这个方法主要就是为重置下载的进度。
2.调用当前的Action的ActionCompleted,将Processor和当前Action置空等。
3.如果执行到某人Action的时候出了错,则停止执行其他的Action
4. processor如果被挂起,则暂停执行下一个Action
5.执行下一个Action或者是否完成了所有的Action,StartNextActionOrFinish(code),该方法比较简单,就不进行分析了。
到这里整体的Action的执行流程也就通了,下一篇开始会分析其他三个Action
.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号