在update_engine-整体结构(一)中分析UpdateEngineDaemon::OnInit()的整体情况。下面先分析在该方法中涉及的DaemonStateAndroid和BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService。
DaemonStateAndroid
它的继承关系为
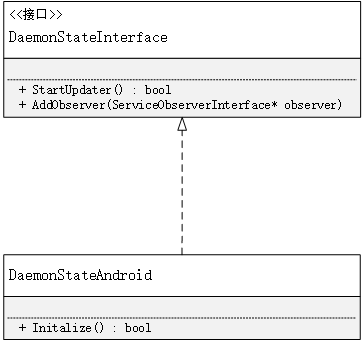
aemonStateInterface中的成员函数都是纯虚函数,在这种情况中可以认为和java中的接口一样,所以在这里使用的是实现的关系,同时也只列出了较为重要的方法。UpdateEngineDaemon的OnInit()方法中调用了DaemonStateAndroid的Initialize()方法,那么这个方法都干了些什么呢?
src/system/update_engine/daemon_state_android.cc
1 bool DaemonStateAndroid::Initialize() {
2 boot_control_ = boot_control::CreateBootControl(); //创建BootControl
3 if (!boot_control_) {
4 LOG(WARNING) << "Unable to create BootControl instance, using stub "
5 << "instead. All update attempts will fail.";
6 boot_control_.reset(new BootControlStub());
7 }
8
9 hardware_ = hardware::CreateHardware(); //创建hardware
10 if (!hardware_) {
11 LOG(ERROR) << "Error intializing the HardwareInterface.";
12 return false;
13 }
14
15 LOG_IF(INFO, !hardware_->IsNormalBootMode()) << "Booted in dev mode.";
16 LOG_IF(INFO, !hardware_->IsOfficialBuild()) << "Booted non-official build.";
17
18 // Initialize prefs.
19 base::FilePath non_volatile_path;
20 // TODO(deymo): Fall back to in-memory prefs if there's no physical directory
21 // available.
22 if (!hardware_->GetNonVolatileDirectory(&non_volatile_path)) {
23 LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to get a non-volatile directory.";
24 return false;
25 }
26 Prefs* prefs = new Prefs(); //创建Prefs
27 prefs_.reset(prefs);
28 if (!prefs->Init(non_volatile_path.Append(kPrefsSubDirectory))) {
29 LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to initialize preferences.";
30 return false;
31 }
32
33 // The CertificateChecker singleton is used by the update attempter.
34 certificate_checker_.reset(
35 new CertificateChecker(prefs_.get(), &openssl_wrapper_)); //设置certificateChecker
36 certificate_checker_->Init();
37
38 // Initialize the UpdateAttempter before the UpdateManager.
39 update_attempter_.reset(new UpdateAttempterAndroid( //设置UpdateAttempterAndroid
40 this, prefs_.get(), boot_control_.get(), hardware_.get()));
41
42 return true;
43 }
可以看到初始化了boot_control_,hardware_,ceritficate_checker_,update_attempter_。boot_control_,hardware_,主要实现对slot等底层的操作(在A/B升级中,会存在双系统A和B,可以将A和B称为slot)而update_attempter_其实是A/B升级的核心操作。在UpdateEngineDaemon的OnInit()中的daemon_state->StartUpdater(),最终调用的其实是update_attempter_->Init()
1 bool DaemonStateAndroid::StartUpdater() {
2 // The DaemonState in Android is a passive daemon. It will only start applying
3 // an update when instructed to do so from the exposed binder API.
4 update_attempter_->Init();
5 return true;
6 }
其实DaemonStateAndroid只进行了一个初始化的工作后,就把其他的工作交给了UpdateAttempterAndroid。DaemonStateAndroid到此就算分析完成了。下面认识UpdateAttempterAndroid。
UpdateAttempterAndroid
它的继承关系为
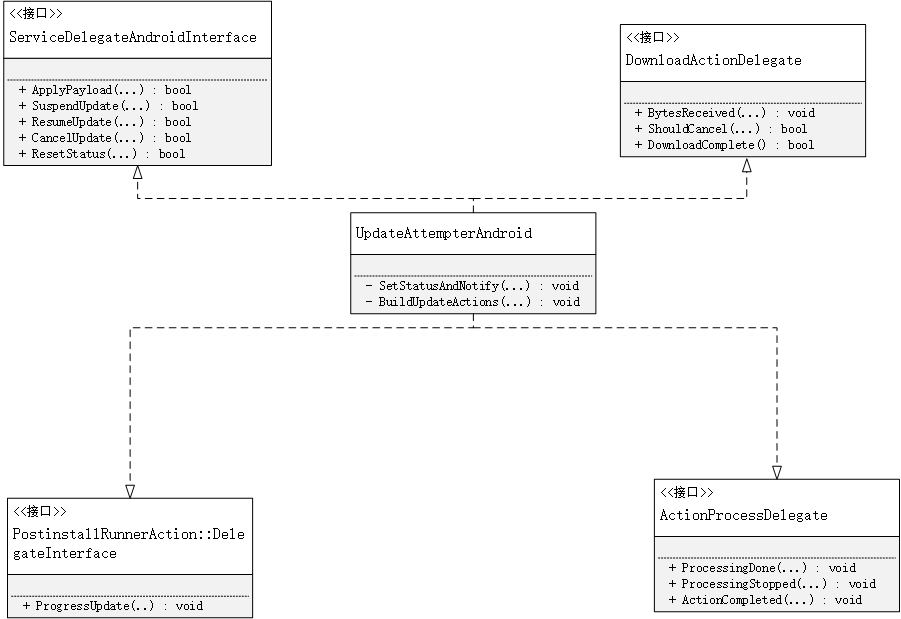

从它的结构就可以看出这个类的重要性了,在画类图的时候省略了函数的参数,已经成员函数只是部分出现。这个类图只是为了帮助理清类的结构。其实这几个接口都是回调接口,他们的函数都是在程序的运行过程中充当回调的角色。UpdateAttempterAndroid通过Init()来开始接管升级的主要流程,内容为:
src/system/update_engine/update_attempter_android.cc
1 void UpdateAttempterAndroid::Init() {
2 // In case of update_engine restart without a reboot we need to restore the
3 // reboot needed state.
4 if (UpdateCompletedOnThisBoot())
5 SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus::UPDATED_NEED_REBOOT);
6 else
7 SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus::IDLE);
8 }
在这个方法中首先判断是否已经升级完成了但是没有重启,如果是那么就会发出重启的消息,否则就会发出空闲的请求。在来看SetStatusAndNotify这个方法
SetStatusAndNotify
1 void UpdateAttempterAndroid::SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus status) {
2 status_ = status;
3 size_t payload_size =
4 install_plan_.payloads.empty() ? 0 : install_plan_.payloads[0].size;
5 for (auto observer : daemon_state_->service_observers()) {
6 observer->SendStatusUpdate(
7 0, download_progress_, status_, "", payload_size);
8 }
9 last_notify_time_ = TimeTicks::Now();
10 }
在这个方法中首先会获取payload(升级包中的payload.bin文件)的大小,之后遍历binder观察者的集合,将更新的情况发送出去,从而通知客户端(使用update_engine服务的)。最后更新通知时间。关于install_plan是一个比较重要的结构体,在后面的叙述中会对其进行描述,现在只需知道它是代表升级包的一个数据结构便可。再看来BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService。
BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService
它的继承结构为
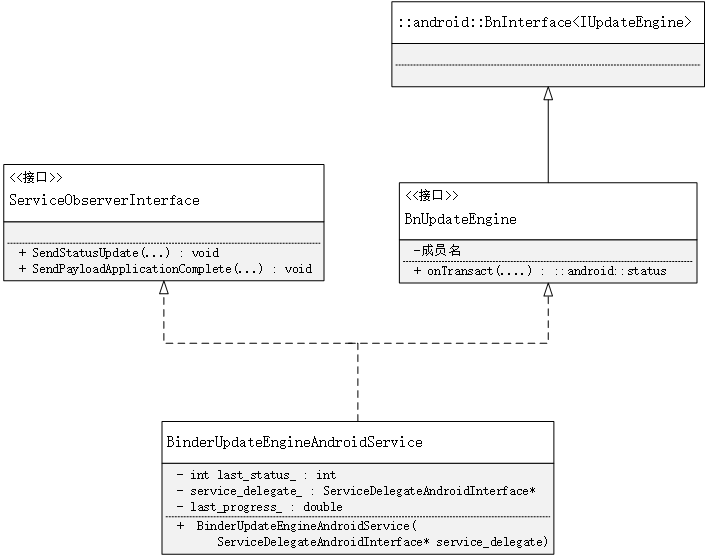
BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService代表了服务端的binder(BnBinder)可以和客户端的(BpBinder)进行通信。关于Binder的通信原理就不多做说明了。下面是BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService中部分方法的说明。
src/system/update_engine/binder_service_brillo.cc
1 Status BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService::bind(
2 const android::sp<IUpdateEngineCallback>& callback, bool* return_value) {
3 callbacks_.emplace_back(callback);
4
5 const android::sp<IBinder>& callback_binder =
6 IUpdateEngineCallback::asBinder(callback);
7 auto binder_wrapper = android::BinderWrapper::Get();
8 binder_wrapper->RegisterForDeathNotifications(
9 callback_binder,
10 base::Bind(
11 base::IgnoreResult(&BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService::UnbindCallback),
12 base::Unretained(this),
13 base::Unretained(callback_binder.get())));
14
15 // Send an status update on connection (except when no update sent so far),
16 // since the status update is oneway and we don't need to wait for the
17 // response.
18 if (last_status_ != -1)
19 callback->onStatusUpdate(last_status_, last_progress_);
20
21 *return_value = true;
22 return Status::ok();
23 }
24
25 void BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService::SendStatusUpdate(
26 int64_t /* last_checked_time */,
27 double progress,
28 update_engine::UpdateStatus status,
29 const std::string& /* new_version */,
30 int64_t /* new_size */) {
31 last_status_ = static_cast<int>(status);
32 last_progress_ = progress;
33 for (auto& callback : callbacks_) {
34 callback->onStatusUpdate(last_status_, last_progress_);
35 }
36 }
37
38 Status BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService::unbind(
39 const android::sp<IUpdateEngineCallback>& callback, bool* return_value) {
40 const android::sp<IBinder>& callback_binder =
41 IUpdateEngineCallback::asBinder(callback);
42 auto binder_wrapper = android::BinderWrapper::Get();
43 binder_wrapper->UnregisterForDeathNotifications(callback_binder);
44
45 *return_value = UnbindCallback(callback_binder.get());
46 return Status::ok();
47 }
48
49 Status BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService::applyPayload(
50 const android::String16& url,
51 int64_t payload_offset,
52 int64_t payload_size,
53 const std::vector<android::String16>& header_kv_pairs) {
54 const std::string payload_url{android::String8{url}.string()};
55 std::vector<std::string> str_headers;
56 str_headers.reserve(header_kv_pairs.size());
57 for (const auto& header : header_kv_pairs) {
58 str_headers.emplace_back(android::String8{header}.string());
59 }
60
61 brillo::ErrorPtr error;
62 if (!service_delegate_->ApplyPayload(
63 payload_url, payload_offset, payload_size, str_headers, &error)) {
64 return ErrorPtrToStatus(error);
65 }
66 return Status::ok();
67 }
当某一个客户端要使用update_engine提供的服务时,首先会通过bind(...)来获取到客户端传过来的IUpdateEngineCallback回调接口,之后获取代表客户端的callback_binder_。之后就可以根据IUpdateEngineCallback,来通知客户端更新的状态和更新是否完成。applyPayload(..)是A/B更新的入口,在这个方法中最终会调用service_delegate_->ApplyPayload(...),service_delegate_其实就是DaemonAttempterAndroid,在这个时候就把更新的工作移交给了DaemonStateAndroid。在上面的分析中涉及到了IUpdateEngine和IUpdateEngineCallback,下面是他们的源码
out/target/product/xxx/obj/STATIC_LIBRARIES/libupdate_engine_android_intermediates/aidl-generated/include/android/os/IUpdateEngine.h

1 namespace android { 2 3 namespace os { 4 5 class IUpdateEngine : public ::android::IInterface { 6 public: 7 DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(UpdateEngine) 8 virtual ::android::binder::Status applyPayload(const ::android::String16& url, int64_t payload_offset, int64_t payload_size, const ::std::vector<::android::String16>& headerKeyValuePairs) = 0; 9 virtual ::android::binder::Status bind(const ::android::sp<::android::os::IUpdateEngineCallback>& callback, bool* _aidl_return) = 0; 10 virtual ::android::binder::Status unbind(const ::android::sp<::android::os::IUpdateEngineCallback>& callback, bool* _aidl_return) = 0; 11 virtual ::android::binder::Status suspend() = 0; 12 virtual ::android::binder::Status resume() = 0; 13 virtual ::android::binder::Status cancel() = 0; 14 virtual ::android::binder::Status resetStatus() = 0; 15 enum Call { 16 APPLYPAYLOAD = ::android::IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0, 17 BIND = ::android::IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1, 18 UNBIND = ::android::IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 2, 19 SUSPEND = ::android::IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 3, 20 RESUME = ::android::IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 4, 21 CANCEL = ::android::IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 5, 22 RESETSTATUS = ::android::IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 6, 23 }; 24 }; // class IUpdateEngine 25 26 } // namespace os 27 28 } // namespace android 29 30 #endif // AIDL_GENERATED_ANDROID_OS_I_UPDATE_ENGINE_H_
out/target/product/qcs605/obj/STATIC_LIBRARIES/libupdate_engine_android_intermediates/aidl-generated/include/android/os/IUpdateEngineCallback.h

1 namespace android { 2 3 namespace os { 4 5 class IUpdateEngineCallback : public ::android::IInterface { 6 public: 7 DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(UpdateEngineCallback) 8 virtual ::android::binder::Status onStatusUpdate(int32_t status_code, float percentage) = 0; 9 virtual ::android::binder::Status onPayloadApplicationComplete(int32_t error_code) = 0; 10 enum Call { 11 ONSTATUSUPDATE = ::android::IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0, 12 ONPAYLOADAPPLICATIONCOMPLETE = ::android::IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1, 13 }; 14 }; // class IUpdateEngineCallback 15 16 } // namespace os 17 18 }
接下来接着看service_delegate_->ApplyPayload(...)
src/update_engine/update_attempter_android.cc
1 bool UpdateAttempterAndroid::ApplyPayload(
2 const string& payload_url,
3 int64_t payload_offset,
4 int64_t payload_size,
5 const vector<string>& key_value_pair_headers,
6 brillo::ErrorPtr* error) {
7 if (status_ == UpdateStatus::UPDATED_NEED_REBOOT) { //检查是否已经更新完成,需要重新启动
8 return LogAndSetError(
9 error, FROM_HERE, "An update already applied, waiting for reboot");
10 }
11 if (ongoing_update_) { //检查是否正在更新
12 return LogAndSetError(
13 error, FROM_HERE, "Already processing an update, cancel it first.");
14 }
15 DCHECK(status_ == UpdateStatus::IDLE); //检查当前是否为空闲状态
16
17 std::map<string, string> headers;
18 for (const string& key_value_pair : key_value_pair_headers) {
19 string key;
20 string value;
21 if (!brillo::string_utils::SplitAtFirst(
22 key_value_pair, "=", &key, &value, false)) {
23 return LogAndSetError(
24 error, FROM_HERE, "Passed invalid header: " + key_value_pair);
25 }
26 if (!headers.emplace(key, value).second)
27 return LogAndSetError(error, FROM_HERE, "Passed repeated key: " + key); //将传递进来的key-value保存到headers中
28 }
29
30 // Unique identifier for the payload. An empty string means that the payload
31 // can't be resumed.
32 string payload_id = (headers[kPayloadPropertyFileHash] +
33 headers[kPayloadPropertyMetadataHash]); //根据Payload的hash和元数据的hash计算一个payload_id
34
35 // Setup the InstallPlan based on the request.
36 install_plan_ = InstallPlan(); //创建一个InstallPlan
37
38 install_plan_.download_url = payload_url;
39 install_plan_.version = "";
40 base_offset_ = payload_offset;
41 InstallPlan::Payload payload;
42 payload.size = payload_size;
43 if (!payload.size) {
44 if (!base::StringToUint64(headers[kPayloadPropertyFileSize],
45 &payload.size)) {
46 payload.size = 0;
47 }
48 }
49 if (!brillo::data_encoding::Base64Decode(headers[kPayloadPropertyFileHash],
50 &payload.hash)) {
51 LOG(WARNING) << "Unable to decode base64 file hash: "
52 << headers[kPayloadPropertyFileHash];
53 }
54 if (!base::StringToUint64(headers[kPayloadPropertyMetadataSize],
55 &payload.metadata_size)) {
56 payload.metadata_size = 0;
57 }
58 // The |payload.type| is not used anymore since minor_version 3.
59 payload.type = InstallPayloadType::kUnknown;
60 install_plan_.payloads.push_back(payload); //为payload赋值完成后,将其放入到集合中,因为ApplyPayload可能被多次调用,会有多个payload
61
62 // The |public_key_rsa| key would override the public key stored on disk.
63 install_plan_.public_key_rsa = "";
64
65 install_plan_.hash_checks_mandatory = hardware_->IsOfficialBuild(); //是否进行强制性的hash验证,如果为user版则为true,如果为userdebug则为false
66 install_plan_.is_resume = !payload_id.empty() &&
67 DeltaPerformer::CanResumeUpdate(prefs_, payload_id); //是否接着上次未更新完的继续更新
68 if (!install_plan_.is_resume) { //如果从头开始更新
69 if (!DeltaPerformer::ResetUpdateProgress(prefs_, false)) { //重置更新进度
70 LOG(WARNING) << "Unable to reset the update progress.";
71 }
72 if (!prefs_->SetString(kPrefsUpdateCheckResponseHash, payload_id)) { //保存payload_id
73 LOG(WARNING) << "Unable to save the update check response hash.";
74 }
75 }
76 install_plan_.source_slot = boot_control_->GetCurrentSlot(); //当前正在运行的slot
77 install_plan_.target_slot = install_plan_.source_slot == 0 ? 1 : 0; //备用的也就是将要升级的slot
78
79 int data_wipe = 0; //是否进行数据擦除,也就是恢复出厂设置,在做升级包时可以指定该值 -w
80 install_plan_.powerwash_required =
81 base::StringToInt(headers[kPayloadPropertyPowerwash], &data_wipe) &&
82 data_wipe != 0;
83
84 NetworkId network_id = kDefaultNetworkId; //NetworkId没有使用过,估计和流式更新相关。
85 if (!headers[kPayloadPropertyNetworkId].empty()) {
86 if (!base::StringToUint64(headers[kPayloadPropertyNetworkId],
87 &network_id)) {
88 return LogAndSetError(
89 error,
90 FROM_HERE,
91 "Invalid network_id: " + headers[kPayloadPropertyNetworkId]);
92 }
93 if (!network_selector_->SetProcessNetwork(network_id)) {
94 return LogAndSetError(
95 error,
96 FROM_HERE,
97 "Unable to set network_id: " + headers[kPayloadPropertyNetworkId]);
98 }
99 }
100
101 LOG(INFO) << "Using this install plan:";
102 install_plan_.Dump();
103
104 BuildUpdateActions(payload_url); //创建Action,这一架构可以说是更新的主要架构
105 // Setup extra headers.
106 HttpFetcher* fetcher = download_action_->http_fetcher();
107 if (!headers[kPayloadPropertyAuthorization].empty())
108 fetcher->SetHeader("Authorization", headers[kPayloadPropertyAuthorization]);
109 if (!headers[kPayloadPropertyUserAgent].empty())
110 fetcher->SetHeader("User-Agent", headers[kPayloadPropertyUserAgent]);
111
112 SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus::UPDATE_AVAILABLE);
113 ongoing_update_ = true; //表式正在更新
114
115 // Just in case we didn't update boot flags yet, make sure they're updated
116 // before any update processing starts. This will start the update process.
117 UpdateBootFlags(); //修改bootFlags并且开始执行Action
118 return true;
119 }
从整体上看ApplyPayload主要进行了两个工作首先是初始化payload,之后将具体的升级流程交给了一系列的Action。先看第一部分,要想了解初始化的一些细节,首先应该知道,一个升级包中都包含了些什么。下面以差分包为例,将一个差分包解压后会得到下面的几个文件。
升级包的基本结构
├── care_map.txt #基本上用不到
├── compatibility.zip #基本上用不到
├── META-INF
│ └── com
│ └── android
│ ├── metadata #基本上用不到
│ └── otacert #基本上用不到
├── payload.bin #主要的升级文件
└── payload_properties.txt #升级文件附带的属性
payload_properties.txt文件的内容大致为:
1 FILE_HASH=4kYpprUJyMwW8NNV25v0ovMWV11PPijNANQwHy0oZwc=
2 FILE_SIZE=42897969
3 METADATA_HASH=l2ih2Xam7jqAQYhr9SRdVddG9NPeenaWzTEd+DHct+o=
4 METADATA_SIZE=300902
接下来再看一下InstallPlan这个数据结构
InstallPlan数据结构
1 namespace chromeos_update_engine {
2
3 enum class InstallPayloadType { //升级包的类型
4 kUnknown, //未知
5 kFull, //全包
6 kDelta, //差分包
7 };
8
9 std::string InstallPayloadTypeToString(InstallPayloadType type);
10
11 struct InstallPlan {
12 InstallPlan() = default;
13
14 bool operator==(const InstallPlan& that) const;
15 bool operator!=(const InstallPlan& that) const;
16
17 void Dump() const;
18
19 // Load the |source_path| and |target_path| of all |partitions| based on the
20 // |source_slot| and |target_slot| if available. Returns whether it succeeded
21 // to load all the partitions for the valid slots.
22 bool LoadPartitionsFromSlots(BootControlInterface* boot_control); //获取source_slot和target_slot中的分区path
23
24 bool is_resume{false}; // 是否未更新完成需要恢复更新
25 std::string download_url; // url to download from 升级文件的url
26 std::string version; // version we are installing. 版本号
27
28 struct Payload {
29 uint64_t size = 0; // size of the payload payload.bin的大小
30 uint64_t metadata_size = 0; // size of the metadata 元数据的大小
31 std::string metadata_signature; // signature of the metadata in base64 元数据的签名
32 brillo::Blob hash; // SHA256 hash of the payload payload.bin的hash
33 InstallPayloadType type{InstallPayloadType::kUnknown}; //升级包的类型
34 // Only download manifest and fill in partitions in install plan without
35 // apply the payload if true. Will be set by DownloadAction when resuming
36 // multi-payload.
37 bool already_applied = false; //升级包是否已经被应用
38
39 bool operator==(const Payload& that) const {
40 return size == that.size && metadata_size == that.metadata_size &&
41 metadata_signature == that.metadata_signature &&
42 hash == that.hash && type == that.type &&
43 already_applied == that.already_applied;
44 }
45 };
46 std::vector<Payload> payloads;
47
48 // The partition slots used for the update.
49 BootControlInterface::Slot source_slot{BootControlInterface::kInvalidSlot}; //定义source_slot
50 BootControlInterface::Slot target_slot{BootControlInterface::kInvalidSlot}; //定义target_slot
51
52 // The vector below is used for partition verification. The flow is:
53 //
54 // 1. DownloadAction fills in the expected source and target partition sizes
55 // and hashes based on the manifest.
56 //
57 // 2. FilesystemVerifierAction computes and verifies the partition sizes and
58 // hashes against the expected values.
59 struct Partition { //一个分区在source_slot和target_slot都存在
60 bool operator==(const Partition& that) const;
61
62 // The name of the partition.
63 std::string name;
64
65 std::string source_path; //在source_slot中的位置
66 uint64_t source_size{0}; //大小
67 brillo::Blob source_hash; //hash
68
69 std::string target_path; //在target_slot中的位置
70 uint64_t target_size{0};
71 brillo::Blob target_hash;
72
73 // Whether we should run the postinstall script from this partition and the
74 // postinstall parameters.
75 bool run_postinstall{false};
76 std::string postinstall_path;
77 std::string filesystem_type; //文件系统的类型
78 bool postinstall_optional{false};
79 };
80 std::vector<Partition> partitions;
81
82 // True if payload hash checks are mandatory based on the system state and
83 // the Omaha response.
84 bool hash_checks_mandatory{false}; //是否强制进行hash检查
85
86 // True if Powerwash is required on reboot after applying the payload.
87 // False otherwise.
88 bool powerwash_required{false}; //是否在升级时进行数据的擦除
89
90 // If not blank, a base-64 encoded representation of the PEM-encoded
91 // public key in the response.
92 std::string public_key_rsa; //public_key 一般为null,这个秘钥常常是已经被内置到了系统中了
93 };
94 }
把这个数据结构弄明白后,也就对ApplyPayload(..)中对InstallPlan的赋值有一个大体的意思了。在这里出现了source和target的概念,source代表的是现在正在运行的系统,target代表此时此刻备用的系统。也可以把source系统做为一个旧的系统,因为在升级检测新版本的时候,会根据source系统检测新的版本,而在升级的时候,先会把source系统拷贝到target中,之后再利用升级包对target进行差分升级。回到ApplyPayload(),对InstallPlan初始化完成后,就会建立Action。这个时候我们就需要明白Action是什么,又是如何运行的。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号