QEMU-KVM虚拟化
以下命令行亲自执行有效,执行环境:
Compiled against library: libvirt 4.5.0
Using library: libvirt 4.5.0
Using API: QEMU 4.5.0
Running hypervisor: QEMU 1.5.3
虚拟化的分类
- 服务器虚拟化:虚拟服务器
- 桌面虚拟化:瘦客户机连接 win7 实现普通办公
- 存储虚拟化:
- SAN ( 基于磁盘 )
- NAS ( NFS / Samba )
- GlusterFS
- 应用虚拟化:将办公软件虚拟化,最典型的就是 office
- 网络虚拟化:SDN
KVM 的虚拟化需要硬件支持(如 Intel VT 技术或者 AMD V 技术)。是基于硬件的完全虚拟化。而 Xen 早期则是基于软件模拟的 Para-Virtualization,新版本则是基于硬件支持的完全虚拟化。但 Xen 本身有自己的进程调度器,存储管理模块等,所以代码较为庞大。广为流传的商业系统虚拟化软件 VMware ESX 系列是基于软件模拟的 Full-Virtualization。
hypervisor
Hypervisor——一种运行在基础物理服务器和操作系统之间的中间软件层,可允许多个操作系统和应用共享硬件。也可叫做VMM( virtual machine monitor ),即虚拟机监视器。
Hypervisors是一种在虚拟环境中的“元”操作系统。他们可以访问服务器上包括磁盘和内存在内的所有物理设备。Hypervisors不但协调着这些硬件资源的访问,而且在各个虚拟机之间施加防护。当服务器启动并执行Hypervisor时,它会加载所有虚拟机客户端的操作系统同时会分配给每一台虚拟机适量的内存,CPU,网络和磁盘。
目前市场上各种x86 管理程序(hypervisor)的架构存在差异,三个最主要的架构类别包括:
- I型:虚拟机直接运行在系统硬件上,创建硬件全仿真实例,被称为“裸机”型。裸机型在虚拟化中Hypervisor直接管理调用硬件资源,不需要底层操作系统,也可以将Hypervisor看作一个很薄的操作系统。这种方案的性能处于主机虚拟化与操作系统虚拟化之间。
- II型:虚拟机运行在传统操作系统上,同样创建的是硬件全仿真实例,被称为“托管(宿主)”型。托管型/主机型Hypervisor运行在基础操作系统上,构建出一整套虚拟硬件平台(CPU/Memory/Storage/Adapter),使用者根据需要安装新的操作系统和应用软件,底层和上层的操作系统可以完全无关化,如Windows运行Linux操作系统。主机虚拟化中VM的应用程序调用硬件资源时需要经过:VM内核->Hypervisor->主机内核,因此相对来说,性能是三种虚拟化技术中最差的。
- Ⅲ型:虚拟机运行在传统操作系统上,创建一个独立的虚拟化实例(容器),指向底层托管操作系统,被称为“操作系统虚拟化”。操作系统虚拟化是在操作系统中模拟出运行应用程序的容器,所有虚拟机共享内核空间,性能最好,耗费资源最少。但是缺点是底层和上层必须使用同一种操作系统,如底层操作系统运行的是Windows系统,则VPS/VE就必须运行Windows。
全虚拟化
不需要对GuestOS操作系统软件的源代码做任何的修改,就可以运行在这样的VMM中
在全虚拟化的虚拟平台中,GuestOS并不知道自己是一台虚拟机,它会认为自己就是运行在计算机物理硬件设备上的HostOS。因为全虚拟化的VMM会将一个OS所能够操作的CPU、内存、外设等物理设备逻辑抽象成为虚拟CPU、虚拟内存、虚拟外设等虚拟设备后,再交由GuestOS来操作使用。这样的GuestOS会将底层硬件平台视为自己所有的,但是实际上,这些都是VMM为GuestOS制造了这种假象。
全虚拟化又分为:软件辅助的全虚拟化 & 硬件辅助的全虚拟化。
软件辅助全虚拟化架构图:
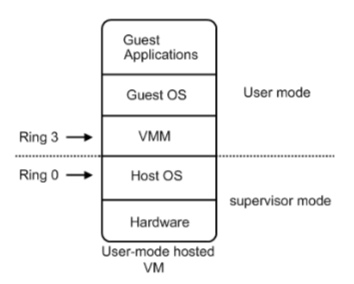
特权解除(优先级压缩):从上述的软件辅助全虚拟化架构图中可以看出,VMM、GuestOS、GuestApplications都是运行在Ring 1-3用户态中的应用程序代码。当在GuestOS中执行系统内核的特权指令时,一般都会触发异常。这是因为用户态代码不能直接运行在核心态中,而且系统内核的特权指令大多都只能运行在Ring 0核心态中。在触发了异常之后,这些异常就会被VMM捕获,再由VMM将这些特权指令进行虚拟化成为只针对虚拟CPU起作用的虚拟特权指令。其本质就是使用若干能运行在用户态中的非特权指令来模拟出只针对GuestOS有效的虚拟特权指令,从而将特权指令的特权解除掉。
虚拟化在这里就遇到了一个难题,因为宿主操作系统是工作在ring0的,客户操作系统就不能也在ring0了,但是它不知道这一点,以前执行什么指令,现在还是执行什么指令,那肯定不行啊,没权限啊,玩不转啊。所以这时候虚拟机管理程序(VMM)就要避免这件事情发生。 (VMM在ring0上,一般以驱动程序的形式体现,驱动程序都是工作在ring0上,否则驱动不了设备)
一般是这样做,客户操作系统执行特权指令时,会触发异常(CPU机制,没权限的指令,触发异常),然后VMM捕获这个异常,在异常里面做翻译,模拟,最后返回到客户操作系统内,客户操作系统认为自己的特权指令工作正常,继续运行。但是这个性能损耗,就非常的大,你想想原来,简单的一条指令,执行完,了事,现在却要通过复杂的异常处理过程。
这时候半虚拟化就来了,半虚拟化的思想就是,让客户操作系统知道自己是在虚拟机上跑的,工作在非ring0状态,那么它原先在物理机上执行的一些特权指令,就会修改成其他方式,这种方式是可以和VMM约定好的,这就相当于,我通过修改代码把操作系统移植到一种新的架构上来,就是定制化。所以像XEN这种半虚拟化技术,客户机操作系统都是有一个专门的定制内核版本,和x86、mips、arm这些内核版本等价。这样以来,就不会有捕获异常、翻译、模拟的过程了,性能损耗非常低。这就是XEN这种半虚拟化架构的优势。这也是为什么XEN只支持虚拟化Linux,无法虚拟化windows原因,微软不改代码啊。
半虚拟化 Paravirtualization
半虚拟化是需要GuestOS协助的虚拟化。因为在半虚拟化VVMM中运行的GuestOS,都需要将其内核源码进行都进过了特别的修改。半虚拟化VMM在处理敏感指令和内核态指令的流程上相对更简单一些。在半虚拟化VMM上运行的GuestOS都需要修改内核代码,主要是修改GuestOS指令集中的敏感指令和核心态指令。让HostOS在捕抓到没有经过半虚拟化VMM模拟和翻译处理的GuestOS内核态指令或敏感指令时,HostOS也能够准确的判断出该指令是否属于GuestOS(GuestOS知道自己是虚拟机)。这样就可以高效的避免了上述问题。典型的半虚拟化软件有——Xen、KVM-PowerPC(简易指令集).
可以后来,CPU厂商,开始支持虚拟化了,情况有发生变化,拿X86 CPU来说,引入了Intel-VT 技术,支持Intel-VT 的CPU,有VMX root operation 和 VMX non-root operation两种模式,两种模式都支持Ring 0 ~ Ring 3 这 4 个运行级别。这下好了,VMM可以运行在VMX root operation模式下,客户OS运行在VMX non-root operation模式下。也就说,硬件这层做了些区分,这样全虚拟化下,有些靠“捕获异常-翻译-模拟”的实现就不需要了。而且CPU厂商,支持虚拟化的力度越来越大,靠硬件辅助的全虚拟化技术的性能逐渐逼近半虚拟化,再加上全虚拟化不需要修改客户操作系统这一优势,全虚拟化技术应该是未来的发展趋势。
XEN是最典型的半虚拟化,不过现在XEN也支持硬件辅助的全虚拟化,大趋势,拗不过啊。。。
KVM、VMARE这些一直都是全虚拟化。
硬件辅助虚拟化 HVM
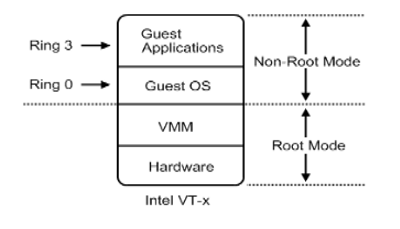
005年 — Intel提出并开发了由CPU直接支持的虚拟化技术。这种虚拟化技术引入新的CPU运行模式和新的指令集,使得VMM和GuestOS运行于不同的模式下(VMM=Root Mode;GuestOS=Non-Root Mode),GuestOS运行于受控模式,原来的一些敏感指令在受控模式下会全部陷入VMM,由VMM来实现模拟,这样就解决了部分非内核态敏感指令的陷入——模拟难题,而且模式切换时上下文的保存恢复由硬件来完成,这样就大大提高了陷入——模拟时上下文切换的效率 。该技术的引入使x86 CPU可以很容易地实现完全虚拟化。故皆被几乎所有之前分歧的各大流派所采用,包括KVM-x86,VMWare ESX Server 3,Xen 3.0 。
HVM的分类:
1). Intel –> VT-X
2). AMD –> AMD-V
内存虚拟化
原来的GuestOS使用的是虚拟内存,不可以缺少虚拟内存到物理内存的翻译,影响了虚拟机的效率。后来Intel EPT AMD RVI表示支持内存虚拟化。
内存虚拟化的映射实现
- A –> 虚拟地址(VA),指GuestOS提供给其应用程序使用的线性地址空间。
- B –> 物理地址(PA),经VMM抽象的,虚拟机看到的伪物理地址
- C –> 机器地址(MA),真是的机器物理地址,即地址总线上出现的地址信号
内存地址的映射关系::
GuestOS:PA = f(VA) #GuestOS维护着一套页表,负责VA到PA的映射
VMM:MA = g(PA) #VMM维护着一套页表,负责PA到MA的映射
通过转换方法实现了从虚拟地址到机器地址的映射。实际运行时,用户程序访问VA1,经过GuestOS的页表转换得到PA1,再由VMM介入并使用VMM的页表将PA1转换为MA1 。
总线虚拟化
分类:
- 1). Intel –> VT/d
- 2). AMD –> iommu
总线虚拟化可以实现将一块网卡分给若干个GuestOS使用,每个虚拟机1/N,性能高,接近真机。
从软件的角度出发,IO设备就是一堆状态寄存器,控制寄存器,中断并与其交互.
主要的虚拟化方式:设备接口完全模拟、前端-后端模拟(Xen)
直接划分:直接把物理设备划分给Guest OS,无须经过VMM。Intel VT-d
内存虚拟化和总线虚拟化进一步的拉近了GuestOS和HostOS的运行性能。
安装KVM
安装步骤
确认 CPU 已经支持虚拟化,intel 的 CPU 虚拟化技术叫 vmx,AMD 的 CPU 叫 svm
grep -E "vmx|svm" /proc/cpuinfo
安装kvm-qemu平台及工具包
yum install qemu-kvm qemu-kvm-tools libvirt virt-manager virt-install
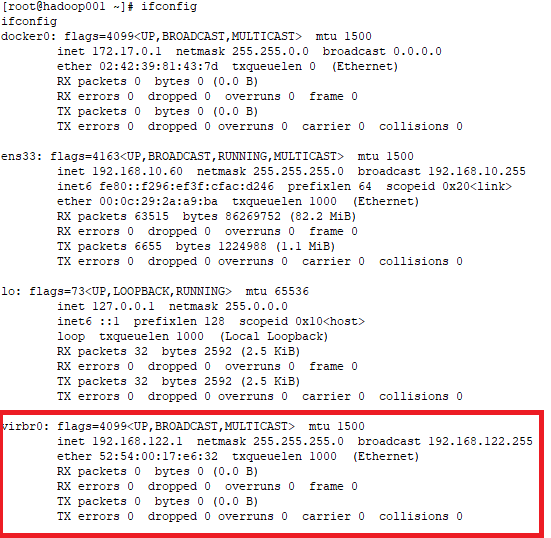
启动libvirtsd并设置为开机启动,librirtd会创建一个桥接的网卡virbr0而且IP地址是192.168.122.1
systemctl start libvirtd & systemctl enable libvirtd
查看网卡virbr0, ifconfig virbr0
创建一个格式为raw大小为10G的裸磁盘
mkdir /data qemu-img create -f raw /data/centos7.raw 10G 成功后显示:Formatting '/data/centos7.raw', fmt=raw size=10737418240
使用本地 iso镜像进行安装
# 默认网络 virt-install --virt-type kvm --name centos7 --ram 1024 --cdrom=/home/CentOS-7-x86_64-Minimal-2003.iso --disk path=/data/centos7.raw --network network=default --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0 --noautoconsole # 桥接网络: virt-install --virt-type kvm --name openstack-middleware1 --ram 4096 --vcpus 4 --cdrom=/usr/local/src/CentOS-7-x86_64-Minimal-1511.iso --disk path=/var/lib/libvirt/images/CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud-1511-ok.qcow2 --network bridge=br0 --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0 --noautoconsole
链接VNS
开始你的虚拟机中嵌套虚拟机的旅程吧。虚机安装过程略,过程中给内核传递 net.ifnames=0 以及 biosdevname=0 使网卡的命名为 eth*
查看正在运行的虚拟机,查看virsh帮助

[root@hadoop001 ~]# virsh -help virsh [options]... [<command_string>] virsh [options]... <command> [args...] options: -c | --connect=URI hypervisor connection URI -d | --debug=NUM debug level [0-4] -e | --escape <char> set escape sequence for console -h | --help this help -k | --keepalive-interval=NUM keepalive interval in seconds, 0 for disable -K | --keepalive-count=NUM number of possible missed keepalive messages -l | --log=FILE output logging to file -q | --quiet quiet mode -r | --readonly connect readonly -t | --timing print timing information -v short version -V long version --version[=TYPE] version, TYPE is short or long (default short) commands (non interactive mode): Domain Management (help keyword 'domain') attach-device attach device from an XML file attach-disk attach disk device attach-interface attach network interface autostart autostart a domain blkdeviotune Set or query a block device I/O tuning parameters. blkiotune Get or set blkio parameters blockcommit Start a block commit operation. blockcopy Start a block copy operation. blockjob Manage active block operations blockpull Populate a disk from its backing image. blockresize Resize block device of domain. change-media Change media of CD or floppy drive console connect to the guest console cpu-stats show domain cpu statistics create create a domain from an XML file define define (but don't start) a domain from an XML file desc show or set domain's description or title destroy destroy (stop) a domain detach-device detach device from an XML file detach-device-alias detach device from an alias detach-disk detach disk device detach-interface detach network interface domdisplay domain display connection URI domfsfreeze Freeze domain's mounted filesystems. domfsthaw Thaw domain's mounted filesystems. domfsinfo Get information of domain's mounted filesystems. domfstrim Invoke fstrim on domain's mounted filesystems. domhostname print the domain's hostname domid convert a domain name or UUID to domain id domif-setlink set link state of a virtual interface domiftune get/set parameters of a virtual interface domjobabort abort active domain job domjobinfo domain job information domname convert a domain id or UUID to domain name domrename rename a domain dompmsuspend suspend a domain gracefully using power management functions dompmwakeup wakeup a domain from pmsuspended state domuuid convert a domain name or id to domain UUID domxml-from-native Convert native config to domain XML domxml-to-native Convert domain XML to native config dump dump the core of a domain to a file for analysis dumpxml domain information in XML edit edit XML configuration for a domain event Domain Events inject-nmi Inject NMI to the guest iothreadinfo view domain IOThreads iothreadpin control domain IOThread affinity iothreadadd add an IOThread to the guest domain iothreaddel delete an IOThread from the guest domain send-key Send keycodes to the guest send-process-signal Send signals to processes lxc-enter-namespace LXC Guest Enter Namespace managedsave managed save of a domain state managedsave-remove Remove managed save of a domain managedsave-edit edit XML for a domain's managed save state file managedsave-dumpxml Domain information of managed save state file in XML managedsave-define redefine the XML for a domain's managed save state file memtune Get or set memory parameters perf Get or set perf event metadata show or set domain's custom XML metadata migrate migrate domain to another host migrate-setmaxdowntime set maximum tolerable downtime migrate-getmaxdowntime get maximum tolerable downtime migrate-compcache get/set compression cache size migrate-setspeed Set the maximum migration bandwidth migrate-getspeed Get the maximum migration bandwidth migrate-postcopy Switch running migration from pre-copy to post-copy numatune Get or set numa parameters qemu-attach QEMU Attach qemu-monitor-command QEMU Monitor Command qemu-monitor-event QEMU Monitor Events qemu-agent-command QEMU Guest Agent Command reboot reboot a domain reset reset a domain restore restore a domain from a saved state in a file resume resume a domain save save a domain state to a file save-image-define redefine the XML for a domain's saved state file save-image-dumpxml saved state domain information in XML save-image-edit edit XML for a domain's saved state file schedinfo show/set scheduler parameters screenshot take a screenshot of a current domain console and store it into a file set-lifecycle-action change lifecycle actions set-user-password set the user password inside the domain setmaxmem change maximum memory limit setmem change memory allocation setvcpus change number of virtual CPUs shutdown gracefully shutdown a domain start start a (previously defined) inactive domain suspend suspend a domain ttyconsole tty console undefine undefine a domain update-device update device from an XML file vcpucount domain vcpu counts vcpuinfo detailed domain vcpu information vcpupin control or query domain vcpu affinity emulatorpin control or query domain emulator affinity vncdisplay vnc display guestvcpus query or modify state of vcpu in the guest (via agent) setvcpu attach/detach vcpu or groups of threads domblkthreshold set the threshold for block-threshold event for a given block device or it's backing chain element Domain Monitoring (help keyword 'monitor') domblkerror Show errors on block devices domblkinfo domain block device size information domblklist list all domain blocks domblkstat get device block stats for a domain domcontrol domain control interface state domif-getlink get link state of a virtual interface domifaddr Get network interfaces' addresses for a running domain domiflist list all domain virtual interfaces domifstat get network interface stats for a domain dominfo domain information dommemstat get memory statistics for a domain domstate domain state domstats get statistics about one or multiple domains domtime domain time list list domains Host and Hypervisor (help keyword 'host') allocpages Manipulate pages pool size capabilities capabilities cpu-baseline compute baseline CPU cpu-compare compare host CPU with a CPU described by an XML file cpu-models CPU models domcapabilities domain capabilities freecell NUMA free memory freepages NUMA free pages hostname print the hypervisor hostname hypervisor-cpu-baseline compute baseline CPU usable by a specific hypervisor hypervisor-cpu-compare compare a CPU with the CPU created by a hypervisor on the host maxvcpus connection vcpu maximum node-memory-tune Get or set node memory parameters nodecpumap node cpu map nodecpustats Prints cpu stats of the node. nodeinfo node information nodememstats Prints memory stats of the node. nodesuspend suspend the host node for a given time duration sysinfo print the hypervisor sysinfo uri print the hypervisor canonical URI version show version Interface (help keyword 'interface') iface-begin create a snapshot of current interfaces settings, which can be later committed (iface-commit) or restored (iface-rollback) iface-bridge create a bridge device and attach an existing network device to it iface-commit commit changes made since iface-begin and free restore point iface-define define an inactive persistent physical host interface or modify an existing persistent one from an XML file iface-destroy destroy a physical host interface (disable it / "if-down") iface-dumpxml interface information in XML iface-edit edit XML configuration for a physical host interface iface-list list physical host interfaces iface-mac convert an interface name to interface MAC address iface-name convert an interface MAC address to interface name iface-rollback rollback to previous saved configuration created via iface-begin iface-start start a physical host interface (enable it / "if-up") iface-unbridge undefine a bridge device after detaching its slave device iface-undefine undefine a physical host interface (remove it from configuration) Network Filter (help keyword 'filter') nwfilter-define define or update a network filter from an XML file nwfilter-dumpxml network filter information in XML nwfilter-edit edit XML configuration for a network filter nwfilter-list list network filters nwfilter-undefine undefine a network filter nwfilter-binding-create create a network filter binding from an XML file nwfilter-binding-delete delete a network filter binding nwfilter-binding-dumpxml network filter information in XML nwfilter-binding-list list network filter bindings Networking (help keyword 'network') net-autostart autostart a network net-create create a network from an XML file net-define define an inactive persistent virtual network or modify an existing persistent one from an XML file net-destroy destroy (stop) a network net-dhcp-leases print lease info for a given network net-dumpxml network information in XML net-edit edit XML configuration for a network net-event Network Events net-info network information net-list list networks net-name convert a network UUID to network name net-start start a (previously defined) inactive network net-undefine undefine a persistent network net-update update parts of an existing network's configuration net-uuid convert a network name to network UUID Node Device (help keyword 'nodedev') nodedev-create create a device defined by an XML file on the node nodedev-destroy destroy (stop) a device on the node nodedev-detach detach node device from its device driver nodedev-dumpxml node device details in XML nodedev-list enumerate devices on this host nodedev-reattach reattach node device to its device driver nodedev-reset reset node device nodedev-event Node Device Events Secret (help keyword 'secret') secret-define define or modify a secret from an XML file secret-dumpxml secret attributes in XML secret-event Secret Events secret-get-value Output a secret value secret-list list secrets secret-set-value set a secret value secret-undefine undefine a secret Snapshot (help keyword 'snapshot') snapshot-create Create a snapshot from XML snapshot-create-as Create a snapshot from a set of args snapshot-current Get or set the current snapshot snapshot-delete Delete a domain snapshot snapshot-dumpxml Dump XML for a domain snapshot snapshot-edit edit XML for a snapshot snapshot-info snapshot information snapshot-list List snapshots for a domain snapshot-parent Get the name of the parent of a snapshot snapshot-revert Revert a domain to a snapshot Storage Pool (help keyword 'pool') find-storage-pool-sources-as find potential storage pool sources find-storage-pool-sources discover potential storage pool sources pool-autostart autostart a pool pool-build build a pool pool-create-as create a pool from a set of args pool-create create a pool from an XML file pool-define-as define a pool from a set of args pool-define define an inactive persistent storage pool or modify an existing persistent one from an XML file pool-delete delete a pool pool-destroy destroy (stop) a pool pool-dumpxml pool information in XML pool-edit edit XML configuration for a storage pool pool-info storage pool information pool-list list pools pool-name convert a pool UUID to pool name pool-refresh refresh a pool pool-start start a (previously defined) inactive pool pool-undefine undefine an inactive pool pool-uuid convert a pool name to pool UUID pool-event Storage Pool Events Storage Volume (help keyword 'volume') vol-clone clone a volume. vol-create-as create a volume from a set of args vol-create create a vol from an XML file vol-create-from create a vol, using another volume as input vol-delete delete a vol vol-download download volume contents to a file vol-dumpxml vol information in XML vol-info storage vol information vol-key returns the volume key for a given volume name or path vol-list list vols vol-name returns the volume name for a given volume key or path vol-path returns the volume path for a given volume name or key vol-pool returns the storage pool for a given volume key or path vol-resize resize a vol vol-upload upload file contents to a volume vol-wipe wipe a vol Virsh itself (help keyword 'virsh') cd change the current directory echo echo arguments exit quit this interactive terminal help print help pwd print the current directory quit quit this interactive terminal connect (re)connect to hypervisor
# 当前正在运行的所有虚拟机:virsh list --all # 命令帮助:virsh list --help # 列出关闭的虚拟机:virsh list --inactive
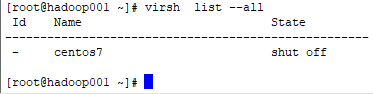 可以看到状态是关闭的。
可以看到状态是关闭的。
启动虚拟机
virsh start centos7

关闭虚拟机
virsh shutdown centos7
查看配置文件:/etc/libvirt/qemu/这个目录下保存已经安装虚拟机的信息
查看centos7.xml
<!-- WARNING: THIS IS AN AUTO-GENERATED FILE. CHANGES TO IT ARE LIKELY TO BE OVERWRITTEN AND LOST. Changes to this xml configuration should be made using: virsh edit centos7 or other application using the libvirt API. --> <domain type='kvm'> <name>centos7</name> <uuid>6f0b80d9-4e1a-4d19-97d4-79459e5985d8</uuid> <memory unit='KiB'>1048576</memory> <currentMemory unit='KiB'>1048576</currentMemory> <vcpu placement='static'>1</vcpu> <os> <type arch='x86_64' machine='pc-i440fx-rhel7.0.0'>hvm</type> <boot dev='hd'/> </os> <features> <acpi/> <apic/> </features> <cpu mode='custom' match='exact' check='partial'> <model fallback='allow'>Broadwell-noTSX-IBRS</model> <feature policy='require' name='md-clear'/> <feature policy='require' name='spec-ctrl'/> <feature policy='require' name='ssbd'/> </cpu> <clock offset='utc'> <timer name='rtc' tickpolicy='catchup'/> <timer name='pit' tickpolicy='delay'/> <timer name='hpet' present='no'/> </clock> <on_poweroff>destroy</on_poweroff> <on_reboot>restart</on_reboot> <on_crash>destroy</on_crash> <pm> <suspend-to-mem enabled='no'/> <suspend-to-disk enabled='no'/> </pm> <devices> <emulator>/usr/libexec/qemu-kvm</emulator> <disk type='file' device='disk'> <driver name='qemu' type='raw'/> <source file='/data/centos7.raw'/> <target dev='vda' bus='virtio'/> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x06' function='0x0'/> </disk> <disk type='file' device='cdrom'> <driver name='qemu' type='raw'/> <target dev='hda' bus='ide'/> <readonly/> <address type='drive' controller='0' bus='0' target='0' unit='0'/> </disk> <controller type='usb' index='0' model='ich9-ehci1'> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x04' function='0x7'/> </controller> <controller type='usb' index='0' model='ich9-uhci1'> <master startport='0'/> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x04' function='0x0' multifunction='on'/> </controller> <controller type='usb' index='0' model='ich9-uhci2'> <master startport='2'/> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x04' function='0x1'/> </controller> <controller type='usb' index='0' model='ich9-uhci3'> <master startport='4'/> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x04' function='0x2'/> </controller> <controller type='pci' index='0' model='pci-root'/> <controller type='ide' index='0'> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x01' function='0x1'/> </controller> <controller type='virtio-serial' index='0'> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x05' function='0x0'/> </controller> <interface type='network'> <mac address='52:54:00:93:61:2e'/> <source network='default'/> <model type='virtio'/> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x03' function='0x0'/> </interface> <serial type='pty'> <target type='isa-serial' port='0'> <model name='isa-serial'/> </target> </serial> <console type='pty'> <target type='serial' port='0'/> </console> <channel type='unix'> <target type='virtio' name='org.qemu.guest_agent.0'/> <address type='virtio-serial' controller='0' bus='0' port='1'/> </channel> <input type='tablet' bus='usb'> <address type='usb' bus='0' port='1'/> </input> <input type='mouse' bus='ps2'/> <input type='keyboard' bus='ps2'/> <graphics type='vnc' port='-1' autoport='yes' listen='0.0.0.0'> <listen type='address' address='0.0.0.0'/> </graphics> <video> <model type='cirrus' vram='16384' heads='1' primary='yes'/> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x02' function='0x0'/> </video> <memballoon model='virtio'> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x07' function='0x0'/> </memballoon> <rng model='virtio'> <backend model='random'>/dev/urandom</backend> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x08' function='0x0'/> </rng> </devices> </domain>
备份虚拟机
virsh dumpxml CentOS7 > CentOS7.xml.bak
删除一个虚拟机
virsh undefine centos7
从备份的 xml 文件中恢复
virsh define /root/CentOS7.xml.bak
到这里,一个完整的安装、删除、备份流程完成了,接下来开始进行CPU、内存、网络的配置。
目前维护的开源产品:https://gitee.com/475660




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号