决策树和随机森林分类
import graphviz from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, export_graphviz from IPython.display import display import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import matplotlib as mt import pandas as pd cancer = load_breast_cancer() #决策树 # X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( # cancer.data, cancer.target, stratify=cancer.target, random_state=42) # tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4,random_state=0) # tree.fit(X_train, y_train) # print("Accuracy on training set: {:.3f}".format(tree.score(X_train, y_train))) # print("Accuracy on test set: {:.3f}".format(tree.score(X_test, y_test))) #随机森林 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( cancer.data, cancer.target, random_state=0) tree = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100,max_features=15,random_state=0) tree.fit(X_train, y_train) print("RandomForestClassifier Accuracy on training set: {:.3f}".format(tree.score(X_train, y_train))) print("RandomForestClassifier Accuracy on test set: {:.3f}".format(tree.score(X_test, y_test))) # export_graphviz(tree, out_file="tree.dot", class_names=["malignant", "benign"], # feature_names=cancer.feature_names, impurity=False, filled=True) # with open("tree.dot") as f: # dot_graph = f.read() # display(graphviz.Source(dot_graph)) # # def plot_feature_importances_cancer(model): # n_features = cancer.data.shape[1] # plt.barh(np.arange(n_features), model.feature_importances_, align='center') # plt.yticks(np.arange(n_features), cancer.feature_names) # plt.xlabel("Feature importance") # plt.ylabel("Feature") # plt.ylim(-1, n_features) # plt.show() # # plot_feature_importances_cancer(tree)
决策树:
默认深度,因为深度过大,造成过拟合,训练精度是1
Accuracy on training set: 1.000
Accuracy on test set: 0.937
设置为4,tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4,random_state=0)
Accuracy on training set: 0.988
Accuracy on test set: 0.951
设置为3,
Accuracy on training set: 0.977
Accuracy on test set: 0.944
设置为5,训练精度和4的时候一样,所以4是比较适合的
Accuracy on training set: 0.995
Accuracy on test set: 0.951
随机森林:
通过预剪枝进一步提升了测试精度
n_estimators=100,max_features=15
RandomForestClassifier Accuracy on training set: 1.000
RandomForestClassifier Accuracy on test set: 0.979
树算法的缺点是测试数据不可超出训练数据的特征范围,而且容易过拟合,泛化性能较差。
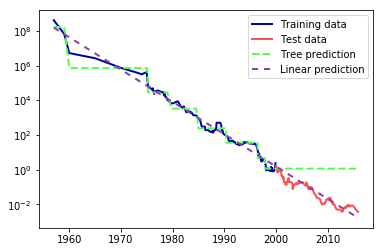
比如预测数据,出现了泛化异常。
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor # use historical data to forecast prices after the year 2000 data_train = ram_prices[ram_prices.date < 2000] data_test = ram_prices[ram_prices.date >= 2000] # predict prices based on date X_train = data_train.date[:, np.newaxis] # we use a log-transform to get a simpler relationship of data to target y_train = np.log(data_train.price) tree = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=3).fit(X_train, y_train) linear_reg = LinearRegression().fit(X_train, y_train) # predict on all data X_all = ram_prices.date[:, np.newaxis] pred_tree = tree.predict(X_all) pred_lr = linear_reg.predict(X_all) # undo log-transform price_tree = np.exp(pred_tree) price_lr = np.exp(pred_lr) plt.semilogy(data_train.date, data_train.price, label="Training data") plt.semilogy(data_test.date, data_test.price, label="Test data") plt.semilogy(ram_prices.date, price_tree, label="Tree prediction") plt.semilogy(ram_prices.date, price_lr, label="Linear prediction") plt.legend()
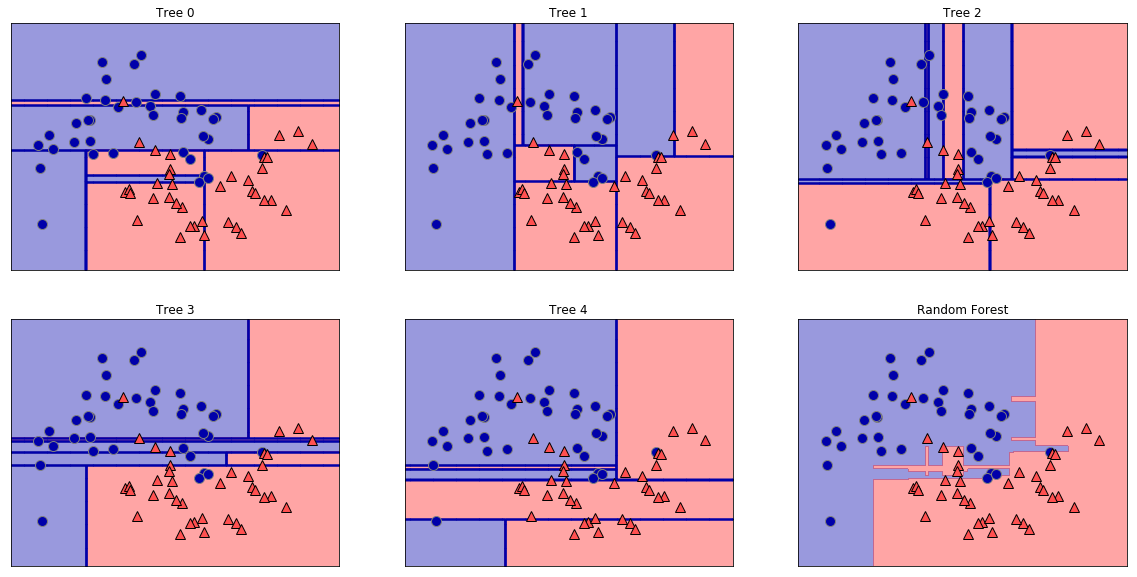
随机森林本质是多个决策树的集合,避免单一决策树的过拟合。
可以看出下图在深度为4的决策树,依然有过拟合,而随机森林要好很多。
在sklearn中的随机森林只有预剪枝,没有后剪枝,梯度提升树也是一样。使用xgboost包在速度和功能上都更强于sklearn。
xgboost:https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost
关于作者:
王昕(QQ:475660)
在广州工作生活30余年。十多年开发经验,在Java、即时通讯、NoSQL、BPM、大数据等领域较有经验。
目前维护的开源产品:https://gitee.com/475660
目前维护的开源产品:https://gitee.com/475660



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号