sqlalchemy中让MySQL支持中文字符
engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:mysql8@localhost/mysqltest?charset=utf8", encoding='utf-8')
数据库:
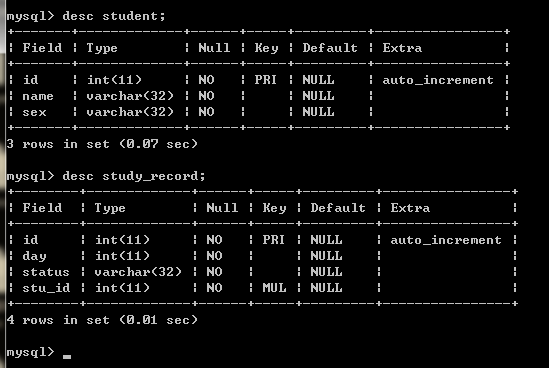
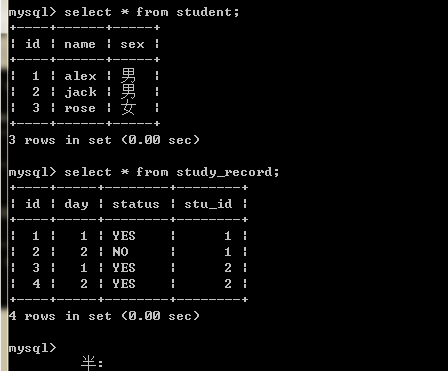
联表查询:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import Column,String,Integer from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:mysql8@localhost/mysqltest") Base = declarative_base() class Student(Base): __tablename__ = 'student' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) name = Column(String(32)) sex = Column(String(32)) def __repr__(self): return "%s,%s,%s" %(self.id, self.name, self.sex) class Study_record(Base): __tablename__ = 'study_record' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) day = Column(Integer) status = Column(String(32)) stu_id = Column(Integer) def __repr__(self): return "%s,%s,%s" %(self.day, self.status, self.stu_id) Session_class = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session_class() # select a.*,b.* from a,b where a.id=b.s_id result = session.query(Student, Study_record).filter(Student.id==Study_record.stu_id).all() print(result) # [(1,alex,男, 1,YES,1), (1,alex,男, 2,NO,1), (2,jack,男, 1,YES,2), (2,jack,男, 2,YES,2)] # 此处报错!!有外键关联的时候才能用,而且外键也需要用类映射出来。真TM麻烦! result1 = session.query(Student).join(Study_record).all() print(result1)
外键关联之双向反查:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import Column,String,Integer from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker,relationship from sqlalchemy import ForeignKey engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:mysql8@localhost/mysqltest") Base = declarative_base() # 学员表student跟考勤表study_record是一对多的关系 class Student(Base): __tablename__ = 'student' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) name = Column(String(32)) sex = Column(String(32)) def __repr__(self): return "%s,%s,%s" %(self.id, self.name, self.sex) class Study_record(Base): __tablename__ = 'study_record' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) day = Column(Integer) status = Column(String(32)) stu_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('student.id')) # 双向反查关系,通过student字段可以看记录对应的学生,反过来通过my_study_record可看学生对应的记录 student = relationship("Student", backref="my_study_record") def __repr__(self): # self.student.name 这是它的牛逼之处: return "%s,%s,%s" %(self.day, self.status, self.student.name) Session_class = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session_class() # 上面加了外键关联,可以用了 result1 = session.query(Student).join(Study_record, isouter=True).all() print(result1) # [1,alex,男, 2,jack,男, 3,rose,女] alex = session.query(Student).filter(Student.name == 'alex').first() print(alex) # 1,alex,男 # 如果想查Alex的上课记录咋查呢?在上面加一个双向反查关系 print(alex.my_study_record) # [1,YES,alex, 2,NO,alex]
顾客表有两个外键,两个外键指向同一张表,此时的双向查询:

from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import Column,String,Integer from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship from sqlalchemy import ForeignKey engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:mysql8@localhost/mysqltest") Base = declarative_base() # 顾客表Customer有两个外键,订单地址ID,邮寄地址ID。都关联了同一张表 class Customer(Base): __tablename__ = 'customer' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) name = Column(String(32)) bill_addr_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("address.id")) post_addr_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("address.id")) bill_addr = relationship("Address", foreign_keys=[bill_addr_id], backref="bill_customers") post_addr = relationship("Address", foreign_keys=[post_addr_id], backref="post_customers") def __repr__(self): return "%s" %(self.name) class Address(Base): __tablename__ = 'address' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) detail_address = Column(String(32)) def __repr__(self): return "%s" %(self.detail_address) Base.metadata.create_all(engine)

from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker import orms Session_class = sessionmaker(bind=orms.engine) session = Session_class() a1 = orms.Address(detail_address="BeiJing") a2 = orms.Address(detail_address="ShangHai") a3 = orms.Address(detail_address="TianJin") session.add_all([a1, a2, a3]) # 注意这里赋值的牛逼之处!!!直接用对象进行赋值 c1 = orms.Customer(name="Alex", bill_addr=a1, post_addr=a2) c2 = orms.Customer(name="Jack", bill_addr=a2, post_addr=a3) c3 = orms.Customer(name="Rain", bill_addr=a3, post_addr=a3) session.add_all([c1, c2, c3]) session.commit()
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker import orms Session_class = sessionmaker(bind=orms.engine) session = Session_class() alex = session.query(orms.Customer).filter(orms.Customer.name=="Alex").first() print(alex.bill_addr, alex.post_addr) # BeiJing ShangHai sh = session.query(orms.Address).filter(orms.Address.detail_address=="ShangHai").first() print(sh.bill_customers) # [Jack]
多对多映射。book表和author表,和book_author对应关系表。book和author形成多对多关系
建表模块orms

from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import Column,String,Integer,Table from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship from sqlalchemy import ForeignKey engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:mysql8@localhost/mysqltest") Base = declarative_base() # 这个表不会手动管理。用户不操作它就不需要创建类,但是反查的时候需要关联这张表 book_to_author = Table("book_to_author", Base.metadata, Column("id",Integer,primary_key=True), Column("book_id",Integer,ForeignKey("book.id")), Column("author_id",Integer,ForeignKey("author.id"))) class Author(Base): __tablename__="author" id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) name = Column(String(32), nullable=False) books = relationship('Book',secondary=book_to_author,backref='authors') def __repr__(self): return "author_name:%s" %(self.name) class Book(Base): __tablename__="book" id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) name = Column(String(32), nullable=False) def __repr__(self): return "book_name:%s" %(self.name) Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
插入数据模块init_data

from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker import orms Session_class = sessionmaker(bind=orms.engine) session = Session_class() b1 = orms.Book(name="Book111") b2 = orms.Book(name="Book222") b3 = orms.Book(name="Book333") a1 = orms.Author(name="Alex") a2 = orms.Author(name="Jack") a3 = orms.Author(name="Rain") a1.books = [b1, b2] a2.books = [b2, b3] a3.books = [b1, b2, b3] session.add_all([a1,a2,a3,b1,b2,b3]) session.commit()
查询,删除模块
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker import orms Session_class = sessionmaker(bind=orms.engine) session = Session_class() # 查询Alex的所有书 alex = session.query(orms.Author).filter(orms.Author.name=="Alex").first() print(alex.books) # [book_name:Book111, book_name:Book222] # 查询book111的所有作者 book1 = session.query(orms.Book).filter(orms.Book.name=="book111").first() print(book1.authors) # [author_name:Alex, author_name:Rain] # alex删除书book1 alex.books.remove(book1) # 删除Alex作者 session.delete(alex) session.commit()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号