内网环境搭建NTP服务器
由ceph需用到时间同步,重温下ntp的相关技术。
简介:ntp全名 network time protocol 。NTP服务器可以为其他主机提供时间校对服务。
环境准备:
两台服务器,一台作为NTP服务器,另一台作为client端向服务器同步时间测试。
NTP服务器:192.168.0.151
client端:192.168.0.152
安装与配置:
yum install ntpd
从配置文件的角度来讲解一下ntp的配置
1 # For more information about this file, see the man pages
2 # ntp.conf(5), ntp_acc(5), ntp_auth(5), ntp_clock(5), ntp_misc(5), ntp_mon(5).
3
4 driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift #默认即可。driftfile用来指定记录本机与上层NTP server之间的频率误差。单位是百万分之一秒。
5
6 # Permit time synchronization with our time source, but do not
7 # permit the source to query or modify the service on this system.
8 restrict default nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
#restrict用来管理权限控制。格式为 restrict [单个ip|网络|default] parameter
parameter:
ignore:拒绝所有的ntp连接
nomodify:客户端不能使用ntpc和ntpq这两个程序来更改服务器的时间参数,但客户端可以通过此主机来进行网络校时。
noquery:客户端不能使用ntpc和ntpq等命令来查询时间服务器,等于不提供网络校时服务。
notrap:不提供trap这个网络时间登陆的功能
notrust:拒绝没有认证的客户端
示例:restrict 192.168.0.152 nomodify
9
10 # Permit all access over the loopback interface. This could
11 # be tightened as well, but to do so would effect some of
12 # the administrative functions.
13 restrict 127.0.0.1 #以下两条默认,放行本机来源
14 restrict ::1
15
16 # Hosts on local network are less restricted.
17 #restrict 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
18
19 # Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
20 # Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
21 server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst #以下四条为默认,注释掉即可
22 server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
23 server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
24 server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
25 server:用来设置上层NTP服务器,说白了就是client向谁请求NTP时间同步。
特别注意,在内网环境中由于无法连接到内网,所以没有办法向例如国家授时服务中心210.72.145.44同步时间
只能将内网中的某台主机设置为server,用以向其他内网服务器提供NTP服务。
server 127.127.1.0 prefer #以本机时间作为时间服务。内网中这个配置一定要加上,否则会导致NTP服务不可用
#prefer代表这台主机优先级最高。
26 #broadcast 192.168.1.255 autokey # broadcast server
27 #broadcastclient # broadcast client
28 #broadcast 224.0.1.1 autokey # multicast server
29 #multicastclient 224.0.1.1 # multicast client
30 #manycastserver 239.255.254.254 # manycast server
31 #manycastclient 239.255.254.254 autokey # manycast client
32
33 # Enable public key cryptography.
34 #crypto
35
36 includefile /etc/ntp/crypto/pw
37
38 # Key file containing the keys and key identifiers used when operating
39 # with symmetric key cryptography.
40 keys /etc/ntp/keys ##除了restrict来限制客户端连接外,还可以通过秘钥方式来给客户端认证。
41
42 # Specify the key identifiers which are trusted.
43 #trustedkey 4 8 42
44
45 # Specify the key identifier to use with the ntpdc utility.
46 #requestkey 8
47
48 # Specify the key identifier to use with the ntpq utility.
49 #controlkey 8
50
51 # Enable writing of statistics records.
52 #statistics clockstats cryptostats loopstats peerstats
53
54 # Disable the monitoring facility to prevent amplification attacks using ntpdc
55 # monlist command when default restrict does not include the noquery flag. See
56 # CVE-2013-5211 for more details.
57 # Note: Monitoring will not be disabled with the limited restriction flag.
58 disable monitor
示例
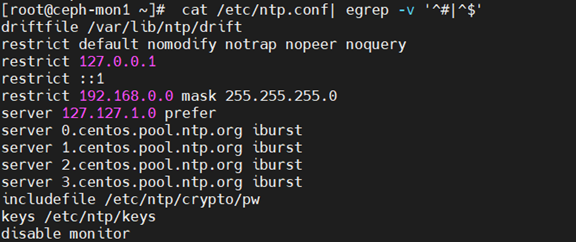
服务器端需要修改/etc/ntp.conf,添加以下内容
server 127.127.1.0 prefer #设置本机为NTP服务器
restrict 192.168.0.152 #允许客户端192.168.0.152向本机请求时间同步
restrict 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 #允许客户端192.168.0.0网段的所有主机向本机请求时间同步
systemctl start ntpd
systemctl enable ntpd
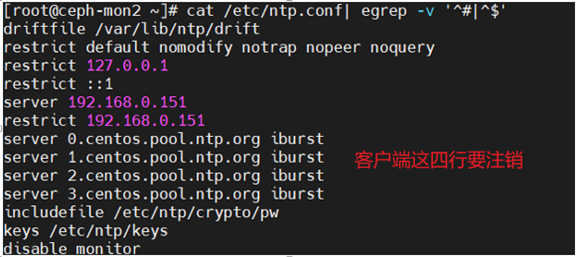
客户端需要修改/etc/ntp.conf,添加以下内容
server 192.168.0.151 #指名上层NTP服务器
restrict 192.168.0.151 #放行192.168.0.151
验证
首先验证服务是否启动成功(服务端和客户端都启用ntpd服务)
启动服务 :service ntpd start
查看服务是否启动:netstat -tunlp |grep ntp
ntp默认监听于UDP的123端口
其次验证NTP是否正常工作
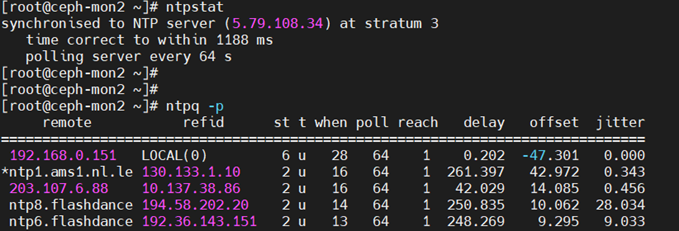
此处需要使用192.168.0.152这台Client服务器,在此主机上可以使用命令ntpstat或ntpq -p这两个命令。
ntpstat:这条命令可以查看我们的客户端(此处为192.168.0.152)是否与server(192.168.0.151) 连接成功。
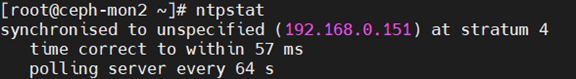
上图的大致意思是:本机已经和192.168.0.151这台位于第七层的NTP服务器同步时间,时间精确到57ms以内。每个64s去同步一次时间。
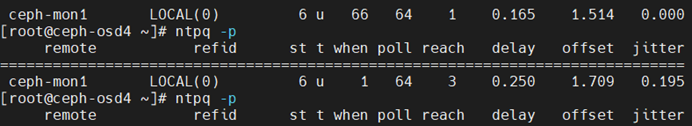
ntpq -p:此命令可以列出当前主机的NTP和上层NTP的状态。
客户端显示如下

服务端显示如下
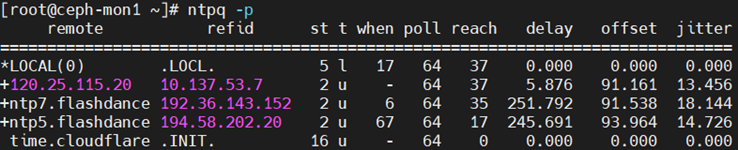
remote:上层NTP服务器的IP或者主机名。主要最左边的*
*:代表目前正在使用中的上层NTP
+:已经连接成功,且可以作为下一个提供时间服务的候选人。
refid:它指的是给远程服务器(192.168.0.151)提供时间同步的服务器,本机上级的上级NTP服务器。
为什么显示为LOCAL(0)?
由于此处为内网环境,无法去外网公用的主机同步时间,因此我们在192.168.0.151上设置的是192.168.0.151自身作为时间服务器同时,使用server 127.127.1.0 prefer指名他的上级NTP为自身。
如果可以服务端可以联网,客户端refid就不一定LOCAL(0),而是外网NTP服务器
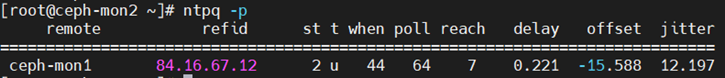
服务端查看到的外网NTP服务器

st:就是stratum层级。 类似于DNS,NTP是层级结构,有顶端的服务器,最多有15层。 为了减缓负荷和网络堵塞,原则上应该避免直接连接到级别为1的服务器。
when:几秒之前同步过时间
poll:在过多长时间去同步时间。
reach:已经同步时间的次数
delay:网络传输过程中的延迟,单位是10的-6次方秒。
offset:时间修正值,这是个最关键的值, 它告诉了我们本地机和服务器之间的时间差别.。单位是10的-3次方。
jitter:linux系统时间(软件时间)与BIOS硬件时间的差异时间,单位是10的-6次方秒。可以使用 hwclock -w将系统时间写入BIOS.
排错1:
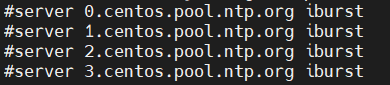
客户端不是将内网NTP作为上层NTP服务器(通常是这台客户端也是可以上外网的)
注释掉默认的4台ntp服务器即可
排错2:客户端无法同步unsynchronised
[root@ceph-osd4 ~]# ntpstat
unsynchronised
polling server every 8 s
解决方法:
手动同步某一台机器的时间
依次执行下面命令实现:
systemctl stop ntpd # 先停止服务,否则ntp socket会被占用
ntpdate 192.168.0.151 # 手动执行同步
systemctl start ntpd # 继续启动服务
systemctl stop ntpd
ntpdate 192.168.0.151
systemctl start ntpd
实测同步时间:
ntpd启动过程需要4分钟左右!
[root@ceph-mon2 ~]# ntpstat
unsynchronised
time server re-starting
polling server every 8 s
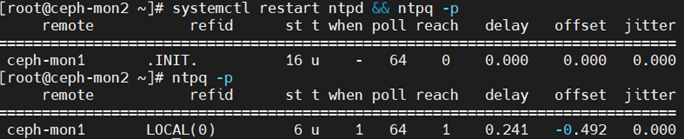
在ntp server上重新启动ntp服务后,ntp server自身或者与其server同步的客户端需要一个时间段,这个过程约4分钟
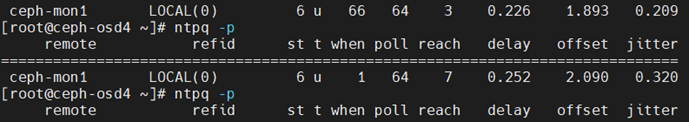
reach这个值是在启动ntp server服务后,就从0开始不断增加,当增加到17的时候,netstat就变成同步状态。
从0到17中间进行了4次的变更(0-->1-->3-->7-->17),每一次变更是poll的值(秒数)
除了0到1只有不到1秒,1-->3-->7-->17每次都是64秒,所以同步总时间是1+64秒*3 约200秒的时间。

参考和引用文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/wxxjianchi/p/10531582.html>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号