数据结构(四)树---哈夫曼树了解以及代码实现
哈夫曼树
(一)定义
带权路径长度WPL:

哈夫曼树(最优二叉树):
WPL最小的二叉树
(二)构造
将权值从小到大排序,后将权值最小的两个并在一起成新的二叉树
A5,E10,B15,D30,C40
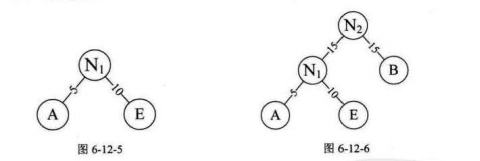
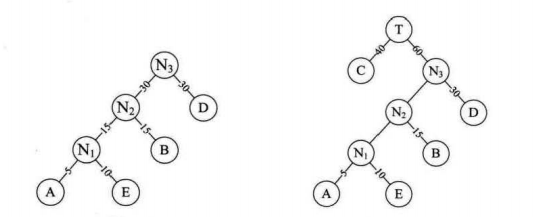

(三)哈夫曼树特点
1.没有度为1的结点
2.n个叶子节点的哈夫曼树共有2n-1个结点
树的特点:度为2结点和叶结点的关系n2=n0-1 所以:当叶结点为n时,度为二的结点数为n-1 因为哈夫曼没有度为一的结点,所以一共在树中有2n-1个结点
3.哈夫曼树任意非叶结点的左右子树交换后还是哈夫曼树
4.对同一组权值{w1,w2,...,wn},是会存在不同结构的哈夫曼树
哈夫曼编码
固定一段字符串,如何对字符串进行编码,可以使得该字符串的编码存储空间最少
例如一串文字BADCADFEED,我们要在网络中传递,显然是要传递二进制(0/1)来表示。
法一:直接传递字符的ASCII码,每个字符占八位,一共传递80位
法二:我们发现数据只是从A-F,一共6个字符,我们完全可以使用3位二进制来表示这些数据(网络对方需要知道我们的编码才能解码)
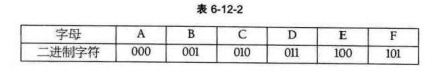
001000011010000011101100100011(30)
变为传递30位数据,对法一进行了极大的优化。
法三:我们发现一段文字中各个数字出现的频率是不一样的,各个字母频率相加100%,可以使用哈夫曼编码,对数据再次进行压缩
假设各个字母频率为 A 27,B 8,C 15,D 15,E 30,F 5
1.先构造哈夫曼树

2.获取前缀码
(1)左右分支分别用0,1表示(避免了二义性)
(2)字符只在叶子节点
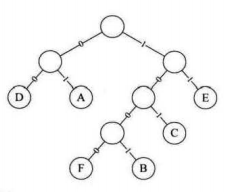
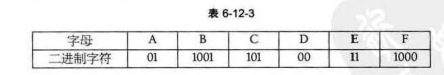
哈夫曼压缩后的数据二进制串:1001010010101001000111100(25)
哈夫曼编码实现
头文件

#pragma once #ifndef _HUFFMAN_H #define _HUFFMAN_H //下面两个结构体对于霍夫曼树 typedef struct _htNode { char symbol; struct _htNode* left, *right; }htNode; typedef struct _htTree { htNode* root; }htTree; //下面两个结构体对应霍夫曼编码表 typedef struct _hlNode { char symbol; char* code; //类似'0001\0' struct _hlNode* next; }hlNode; typedef struct _hlTable { hlNode *first; hlNode *last; }hlTable; //根据字符串创建霍夫曼树 htTree* buildTree(char* str); //根据霍夫曼树创建霍夫曼前缀码表 hlTable* buildTable(htTree* HT); //根据字符串进行编码,str是一串ASCII码字符串 void encode(hlTable* ht, char *str); //根据霍夫曼树,进行解码,str类似于'00001101' void decode(htTree* ht,char *str); #endif // !_HUFFMAN_H

#pragma once #ifndef _QUEUE_H #define _QUEUE_H #include "huffman.h" #define TYPE htNode * #define MAX_SZ 256 typedef struct _pQueueNode { TYPE val; unsigned int priority; struct _pQueueNode* next; }pQueueNode; typedef struct _pQueue { pQueueNode* first; unsigned int size; //无符号扩大空间 }pQueue; void initPQueue(pQueue** queue); //初始化队列 void addPQueue(pQueue** queue,TYPE val,unsigned int priority); //添加数据 TYPE getPQueue(pQueue** queue); //获取数据 #endif
源文件

#include "queue.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> //初始化队列 void initPQueue(pQueue** queue) { *queue = (pQueue*)malloc(sizeof(pQueue)); (*queue)->size = 0; (*queue)->first = NULL; //初始化头指针 } //添加数据,这里不是简单添加到队列队尾,而是按照优先级 void addPQueue(pQueue** queue, TYPE val, unsigned int priority) { pQueueNode *aux,*cur; //aux是新加入结点,cur是优先级判断的游标 //满队列 if ((*queue)->size == MAX_SZ) { printf("\nQueue is full\n"); return; } //创建该新的结点 aux = (pQueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(pQueueNode)); aux->priority = priority; aux->val = val; //若是空队列,直接加入 if ((*queue)->size == 0 || !(*queue)->first) { aux->next = NULL; (*queue)->first = aux; (*queue)->size++; return; } else { //进行循环判断优先级,优先级低的在前面,根据霍夫曼编码,每次或取出两个最小的进行合并 //首先判断,优先级小于首结点 if (priority<=(*queue)->first->priority) { aux->next=(*queue)->first; (*queue)->first = aux; (*queue)->size++; return; } else { cur = (*queue)->first; while (cur->next) //上面的if判断过首结点,我们这里只需要判断他下面结点即可 { if (priority <= cur->next->priority) { aux->next = cur->next; cur->next = aux; (*queue)->size++; return; } cur = cur->next; } //直到走到末尾,发现全部优先级都比他低,所以加入结尾 if (cur->next == NULL) { aux->next = NULL; cur->next = aux; (*queue)->size++; return; } } } } //获取数据 TYPE getPQueue(pQueue** queue) { TYPE returnVal; if ((*queue)->size == 0 || (*queue)->first == NULL) { printf("queue is empty\n"); return; } returnVal = (*queue)->first->val; (*queue)->first = (*queue)->first->next; (*queue)->size--; return returnVal; }

#include "huffman.h" #include "queue.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> //根据字符串创建霍夫曼树 htTree* buildTree(char* str) { //先创建一个字符统计数组 int proprity[256] = { 0 }; for (int j = 0; j < strlen(str);j++) { proprity[(unsigned char)str[j]]++; } //创建一个队列,利用队列来创建一个完整的霍夫曼树 pQueue *queue; initPQueue(&queue); for (int k = 0; k < 256;k++) { if (proprity[k]!=0) { htNode* hn = (htNode*)malloc(sizeof(htNode)); hn->left = NULL; hn->right = NULL; hn->symbol = (char)k; addPQueue(&queue, hn, proprity[k]); } } //将所有队列中的数据开始合并 while (queue->size != 1) { htNode* left, *right,*tnode; //优先级必须从这里获取 int proprity = queue->first->priority; proprity += queue->first->next->priority; //下面返回的是霍夫曼结点,其中不含有优先级 left = getPQueue(&queue); right = getPQueue(&queue); tnode = (htNode*)malloc(sizeof(htNode)); tnode->left = left; tnode->right = right; addPQueue(&queue, tnode, proprity); } //队列中最后一个元素就是霍夫曼树的根节点,我们将它赋值给霍夫曼树即可 htTree *ht = (htTree*)malloc(sizeof(htTree)); ht->root = getPQueue(&queue); return ht; } //我们通过遍历到二叉树叶子节点,从而获取到前缀码 void preOrderGetTb(htNode* root,hlTable **table,int level, char* code) { if (root->left||root->right) { if (root->left) { code[level] = '0'; preOrderGetTb(root->left, table,level+1,code); } if (root->right) { code[level] = '1'; preOrderGetTb(root->right, table, level + 1, code); } } else { code[level] = '\0'; hlNode* aux = (hlNode*)malloc(sizeof(hlNode)); aux->symbol = root->symbol; aux->code = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(level + 1)); strcpy(aux->code, code); aux->next = NULL; if ((*table)->first==NULL) { (*table)->first = aux; (*table)->last = aux; } else { (*table)->last->next = aux; (*table)->last = aux; } } } //根据霍夫曼树创建霍夫曼前缀码表 hlTable* buildTable(htTree* HT) { hlTable* hl; hl = (hlTable*)malloc(sizeof(hlTable)); hl->first = NULL; hl->last = NULL; int k = 0; char code[255] = { 0 }; preOrderGetTb(HT->root, &hl, k, code); return hl; } //根据字符串进行编码,str是一串ASCII码字符串 void encode(hlTable* table, char *str) { hlNode* cur = table->first; char *s = str; while (*s!='\0') { while (cur->symbol!=*s) cur = cur->next; printf("%s", cur->code); s++; cur = table->first; } } //根据霍夫曼树,进行解码,str类似于'00001101' void decode(htTree* ht, char *str) { char* s = str; htNode* tn = ht->root; while (*s!='\0') { if (*s=='0') { tn = tn->left; if (!tn->left&&!tn->right) { printf("%c", tn->symbol); tn = ht->root; } } else { tn = tn->right; if (!tn->left&&!tn->right) { printf("%c", tn->symbol); tn = ht->root; } } s++; } }
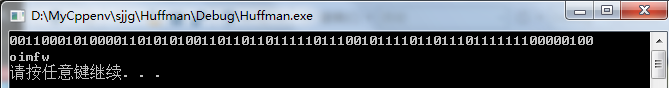
#include "huffman.h" #include "queue.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { htTree *ht; hlTable *hl; ht = buildTree("i love www.fishc.com");//创建霍夫曼树 hl = buildTable(ht); //根据霍夫曼树创建前缀码表 encode(hl, "i love www.fishc.com"); //根据前缀码表获取全部前缀码 decode(ht, "000001010010111110");//oimfw system("pause"); return 0; }
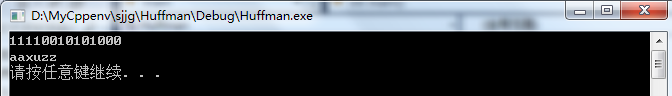
int main() { htTree *ht; hlTable *hl; ht = buildTree("aaaauxxz");//创建霍夫曼树 hl = buildTable(ht); //根据霍夫曼树创建前缀码表 encode(hl, "aaaauxxz"); //根据前缀码表获取全部前缀码 decode(ht, "1101001000000");//aaxuzz system("pause"); return 0; }
补充:
1.编写代码前先实现队列的操作
2.队列实现是优先级队列,优先级低的放在前面
3.队列中存放的是哈夫曼树节点, 我们每次从队列中获取两个优先级最低的,进行合并,优先级为二者之和,然后又放回队列中。
4.直到我们队列中只有一个结点,这就是我们的根节点,结点下面是带有我们所有数据的哈夫曼树
5.获取哈夫曼树后,我们根据递归一路找到叶子结点(字符),将路径转前缀码,根据结点字符和路径前缀码,创建前缀码表
6.根据前缀码表,我们可以获取到各个字符的前缀码,然后进行编码即可
7.我们同样可以根据前缀码串,通过对哈夫曼树的遍历,找到前缀码对应的字符



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号