OpenCV---Numpy数组的使用以及创建图片
一:对头像的所有像素进行访问,并UI图像进行像素取反
(一)for循环取反
import cv2 as cv import numpy as np def access_pixels(image): #对图像的所有像素进行访问 print(image.size) height,width,channel = image.shape #每个像素3个通道,通道顺序b,g,r print("height:%s\r\nwidth:%s\r\nchannel:%s\r\n"%(height,width,channel)) ''' height:608 width:343 channel:3 ''' for row in range(height): for col in range(width): for c in range(channel): #循环会变慢,经过625632循环 pv = image[row,col,c] image[row,col,c] = 255 - pv #像素取反 cv.imshow("pixels_demo",image) src = cv.imread("./1.png") #读取图片 cv.namedWindow("input image",cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE) #创建GUI窗口,形式为自适应 cv.imshow("input image",src) #通过名字将图像和窗口联系 t1 = cv.getTickCount() #获取时间,用于精度计时,操作系统启动所经过(elapsed)的毫秒数 access_pixels(src) t2 = cv.getTickCount() print((t2-t1)/cv.getTickFrequency()) #getTickFrequency()是获取一秒钟结果的点数,获取秒数 cv.waitKey(0) #等待用户操作,里面等待参数是毫秒,我们填写0,代表是永远,等待用户操作 cv.destroyAllWindows() #销毁所有窗口
625632 height:608 width:343 channel:3 15.740029368334588 #经历了15秒,是十分耗时的循环,我们可以使用Numpy数组访问,更加方便快捷
(二)使用内置方法取反(直接使用c代码执行,效率更高)
def inverse(image): img = cv.bitwise_not(image) cv.imshow("inverse image",img)
t1 = cv.getTickCount() #获取时间,用于精度计时,操作系统启动所经过(elapsed)的毫秒数
inverse(src)
t2 = cv.getTickCount()
0.09940230583146789
二:使用Numpy数组,创建图片
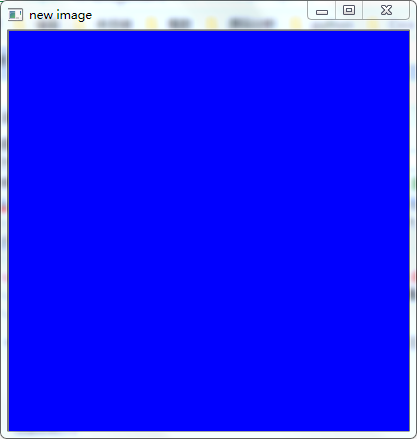
(一)使用多个信道创建图片
def create_img(): img = np.zeros([400,400,3],np.uint8) #创建一个三维数组高400,宽400,信号通道3个,初始都为0,每通道占8位个 img[:,:,0] = np.ones([400,400])*255 #将0号通道下[400,400]面积使用ones设置为1,之后乘以255,将其设置为255,注意:3个信道分别是b,g,r所以这里显示为蓝色 cv.imshow("new image",img) create_img() cv.waitKey(0) #等待用户操作,里面等待参数是毫秒,我们填写0,代表是永远,等待用户操作 cv.destroyAllWindows() #销毁所有窗口
(二)使用单个信道创建图像(灰度图像)
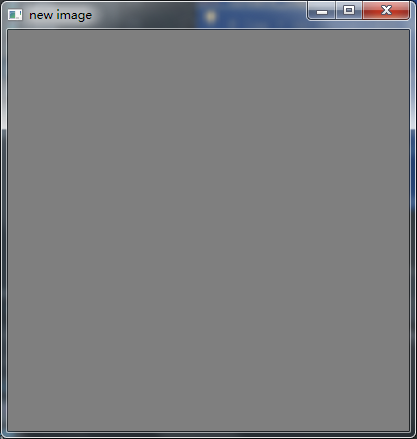
def create_img(): img = np.zeros([400,400,1],np.uint8) #创建一个只有一个信道的三维数组,初始为0 img[:,:,0] = np.ones([400,400])*127 #修改这个图像的信道为127,灰色 cv.imshow("new image",img)
或者(所以初始时候使用ones会更加灵活)
def create_img(): img = np.ones([400,400,1],np.uint8) #创建一个只有一个信道的三维数组,初始为1 img = img * 127 #可以直接进行运算 cv.imshow("new image",img)
cv.imwrite(".3.png",img) #可以进行保存
三:补充Numpy的使用
(一)二维数组的使用(选择正确的类型)
1.float类型
def create_arr(): ml = np.ones([3,3],np.float32) #float类型,允许小数存在 ml.fill(122.388) print(ml) create_arr()
[[122.388 122.388 122.388] [122.388 122.388 122.388] [122.388 122.388 122.388]]
2.int类型
def create_arr(): ml = np.ones([3,3],np.uint8) #不允许小数的存在,且有最大是255 ml.fill(122.388) print(ml) create_arr()
[[122 122 122] [122 122 122] [122 122 122]]
def create_arr(): ml = np.ones([3,3],np.uint8) #有位数限制,高位被截断了,低位留下了 ml.fill(256.388) print(ml) create_arr()
[[0 0 0] [0 0 0] [0 0 0]]
(二)维数转换reshape
def create_arr(): ml = np.ones([3,3],np.uint8) ml.fill(122.388) m2 = ml.reshape([1,9]) #注意:转换维度,数组大小还是要一致的,不然报错 print(m2)
[[122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122]]
(三)使用array自定义数组
def create_arr(): m3 = np.array([[2,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]],np.uint8) print(m3)
[[2 2 3] [4 5 6] [7 8 9]]
作者:山上有风景
欢迎任何形式的转载,但请务必注明出处。
限于本人水平,如果文章和代码有表述不当之处,还请不吝赐教。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?