统计学习方法---感知机模型
作业:

一:感知机算法原始形式实现
(一)伪代码

(二)实现感知机算法
class MyPerceptron: def __init__(self): # 属性初始化 self.w = None self.b = 0 self.l_rate = 1 def fit(self, X_train, y_train): global history_w, history_b #保持w,b信息,方便一会绘制图像 # 根据X形状,设置w self.w = np.zeros(X_train.shape[1]) i = 0 while i < X_train.shape[0]: # 注意我们按顺序查看误分类点 X = X_train[i] y = y_train[i] # 如果y*(wX+b)<=0,则是误分类点,我们就要更新一次w,b,我们每更新一次w,b,我们就要从新查找整个数据集 if y * (np.dot(self.w, X) + self.b) <= 0: self.w = self.w + self.l_rate * np.dot(y, X) self.b = self.b + self.l_rate * y i = 0 history_w.append(self.w) history_b.append(self.b) else: i += 1
(三)设置数据,进行训练
if __name__ == "__main__": # 构建数据集和标签值 X_train = np.array([[3, 3], [4, 3], [1, 1]]) y = np.array([1, 1, -1]) history_w = [] history_b = [] perc = MyPerceptron() perc.fit(X_train, y) # 进行训练 获取w,b信息
![]()
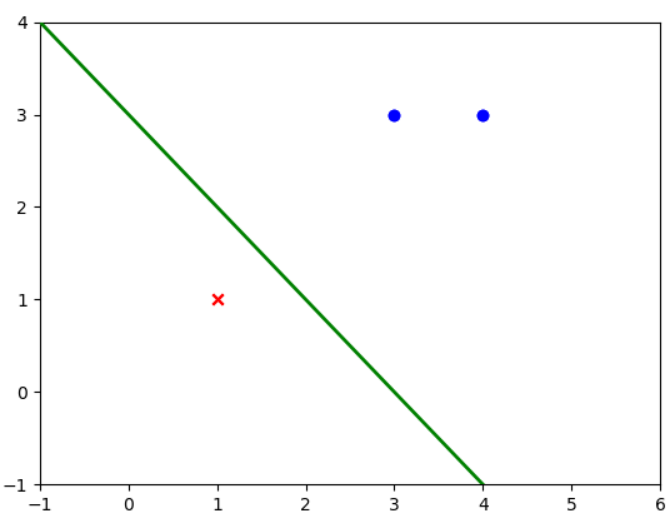
(四)数据可视化
# 数据集可视化 fig = plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() line, = ax.plot([], [], 'g', lw=2) def init(): line.set_data([], []) plt.scatter(X_train[np.where(y == 1), 0], X_train[np.where(y == 1), 1], marker="o", c="b") plt.scatter(X_train[np.where(y == -1), 0], X_train[np.where(y == -1), 1], marker="x", c="r") return line, def update(i): global history_w, history_b, ax, line w = history_w[i] b = history_b[i] if w[1] == 0: return line, x1 = -1 y1 = -(b + w[0] * x1) / w[1] x2 = 6 y2 = -(b + w[0] * x2) / w[1] line.set_data([x1, x2], [y1, y2]) return line, plt.xlim(-1, 6) plt.ylim(-1, 4) print(history_w) print(history_b) #[[[3, 3], 1], [[2, 2], 0], [[1, 1], -1], [[0, 0], -2], [[3, 3], -1], [[2, 2], -2], [[1, 1], -3]] ani = anim.FuncAnimation(fig=fig, func=update,init_func=init, frames=len(history_b), interval=1000, repeat=True, blit=True) plt.show()
参数详解:
fig进行动画绘制的figurefunc自定义动画函数,即传入刚定义的函数animateframes动画长度,一次循环包含的帧数init_func自定义开始帧,即传入刚定义的函数initinterval更新频率,以ms计blit选择更新所有点,还是仅更新产生变化的点。应选择True,但mac用户请选择False,否则无法显示动画
注意:我们要实现Animation动画,需要设置pycharm中(File->Settings->Tools->Python Scientific)的Show plots in tool window选项(disable不使用)
(五)结果显示

import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.animation as anim class MyPerceptron: def __init__(self): # 属性初始化 self.w = None self.b = 0 self.l_rate = 1 def fit(self, X_train, y_train): global history_w, history_b # 根据X形状,设置w self.w = np.zeros(X_train.shape[1]) i = 0 while i < X_train.shape[0]: # 注意我们按顺序查看误分类点 X = X_train[i] y = y_train[i] # 如果y*(wX+b)<=0,则是误分类点,我们就要更新一次w,b,我们每更新一次w,b,我们就要从新查找整个数据集 if y * (np.dot(self.w, X) + self.b) <= 0: self.w = self.w + self.l_rate * np.dot(y, X) self.b = self.b + self.l_rate * y i = 0 history_w.append(self.w) history_b.append(self.b) else: i += 1 if __name__ == "__main__": # 构建数据集和标签值 X_train = np.array([[3, 3], [4, 3], [1, 1]]) y = np.array([1, 1, -1]) history_w = [] history_b = [] perc = MyPerceptron() perc.fit(X_train, y) # 进行训练 获取w,b信息 # 数据集可视化 fig = plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() line, = ax.plot([], [], 'g', lw=2) def init(): line.set_data([], []) plt.scatter(X_train[np.where(y == 1), 0], X_train[np.where(y == 1), 1], marker="o", c="b") plt.scatter(X_train[np.where(y == -1), 0], X_train[np.where(y == -1), 1], marker="x", c="r") return line, def update(i): global history_w, history_b, ax, line w = history_w[i] b = history_b[i] if w[1] == 0: return line, x1 = -1 y1 = -(b + w[0] * x1) / w[1] x2 = 6 y2 = -(b + w[0] * x2) / w[1] line.set_data([x1, x2], [y1, y2]) return line, plt.xlim(-1, 6) plt.ylim(-1, 4) print(history_w) print(history_b) #[[[3, 3], 1], [[2, 2], 0], [[1, 1], -1], [[0, 0], -2], [[3, 3], -1], [[2, 2], -2], [[1, 1], -3]] ani = anim.FuncAnimation(fig=fig, func=update,init_func=init, frames=len(history_b), interval=1000, repeat=True, blit=True) plt.show()
二:感知机算法对偶形式实现
(一)伪代码

(二)实现感知机对偶算法
class MyPerceptron: def __init__(self): # 属性初始化 self.a = None self.b = 0 self.l_rate = 1 self.gram = None self.gram_diag = None def cal_gram(self,X_train): self.gram = np.zeros((X_train.shape[0],X_train.shape[0])) self.gram = np.dot(X_train,X_train.T) def fit(self, X_train, y_train): global history_a, history_b self.cal_gram(X_train) # 根据X形状,设置a 对于每一个样本,都有一个a self.a = np.zeros(X_train.shape[0]) i = 0 while i < X_train.shape[0]: # 注意我们按顺序查看误分类点 y = y_train[i] sigma_gram = np.sum(self.gram[i]*self.a*y_train) #使用了gram矩阵,减少计算量 # 如果y*(wX+b)<=0,则是误分类点,我们就要更新一次w,b,我们每更新一次w,b,我们就要从新查找整个数据集 if y * (sigma_gram + self.b) <= 0: self.a[i] = self.a[i]+ self.l_rate self.b = self.b + self.l_rate * y i = 0 history_a.append(self.a.copy()) history_b.append(self.b) else: i += 1
(三)训练数据
if __name__ == "__main__": # 构建数据集和标签值 X_train = np.array([[3, 3], [4, 3], [1, 1]]) y_train = np.array([1, 1, -1]) history_a = [] history_b = [] perc = MyPerceptron() perc.fit(X_train, y_train) # 进行训练 获取w,b信息 # 数据集可视化 fig = plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() line, = ax.plot([], [], 'g', lw=2) print(history_a) print(history_b)
![]()
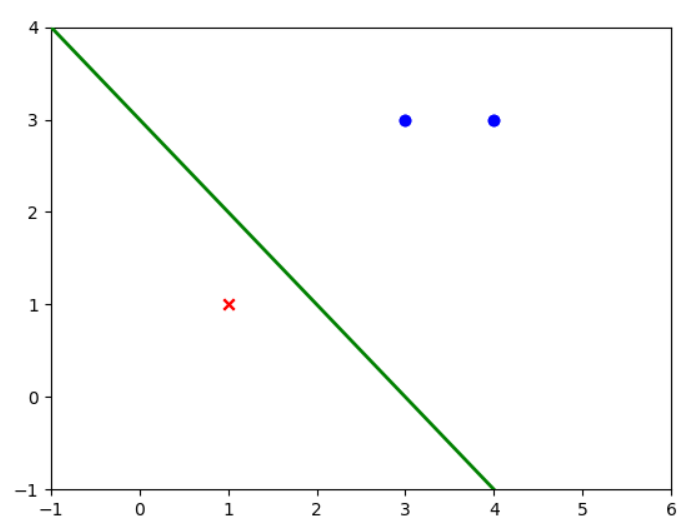
(四)数据可视化
if __name__ == "__main__": # 构建数据集和标签值 X_train = np.array([[3, 3], [4, 3], [1, 1]]) y_train = np.array([1, 1, -1]) history_a = [] history_b = [] perc = MyPerceptron() perc.fit(X_train, y_train) # 进行训练 获取w,b信息 # 数据集可视化 fig = plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() line, = ax.plot([], [], 'g', lw=2) print(history_a) print(history_b) def init(): line.set_data([], []) plt.scatter(X_train[np.where(y_train == 1), 0], X_train[np.where(y_train == 1), 1], marker="o", c="b") plt.scatter(X_train[np.where(y_train == -1), 0], X_train[np.where(y_train == -1), 1], marker="x", c="r") return line, def update(i): global history_a, history_b, line,X_train,y_train a = history_a[i] b = history_b[i] w = np.sum(X_train*np.array([a]).T*np.array([y_train]).T,0) #这一步实现获取w if w[1] == 0: return line, x1 = -1 y1 = -(b + w[0] * x1) / w[1] x2 = 6 y2 = -(b + w[0] * x2) / w[1] line.set_data([x1, x2], [y1, y2]) return line, plt.xlim(-1, 6) plt.ylim(-1, 4) ani = anim.FuncAnimation(fig=fig, func=update,init_func=init, frames=len(history_b), interval=1000, repeat=True, blit=True) plt.show()

(五)结果显示

import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.animation as anim class MyPerceptron: def __init__(self): # 属性初始化 self.a = None self.b = 0 self.l_rate = 1 self.gram = None self.gram_diag = None def cal_gram(self,X_train): self.gram = np.zeros((X_train.shape[0],X_train.shape[0])) self.gram = np.dot(X_train,X_train.T) def fit(self, X_train, y_train): global history_a, history_b self.cal_gram(X_train) # 根据X形状,设置a 对于每一个样本,都有一个a self.a = np.zeros(X_train.shape[0]) i = 0 while i < X_train.shape[0]: # 注意我们按顺序查看误分类点 y = y_train[i] sigma_gram = np.sum(self.gram[i]*self.a*y_train) #使用了gram矩阵,减少计算量 # 如果y*(wX+b)<=0,则是误分类点,我们就要更新一次w,b,我们每更新一次w,b,我们就要从新查找整个数据集 if y * (sigma_gram + self.b) <= 0: self.a[i] = self.a[i]+ self.l_rate self.b = self.b + self.l_rate * y i = 0 history_a.append(self.a.copy()) history_b.append(self.b) else: i += 1 if __name__ == "__main__": # 构建数据集和标签值 X_train = np.array([[3, 3], [4, 3], [1, 1]]) y_train = np.array([1, 1, -1]) history_a = [] history_b = [] perc = MyPerceptron() perc.fit(X_train, y_train) # 进行训练 获取w,b信息 # 数据集可视化 fig = plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() line, = ax.plot([], [], 'g', lw=2) print(history_a) print(history_b) def init(): line.set_data([], []) plt.scatter(X_train[np.where(y_train == 1), 0], X_train[np.where(y_train == 1), 1], marker="o", c="b") plt.scatter(X_train[np.where(y_train == -1), 0], X_train[np.where(y_train == -1), 1], marker="x", c="r") return line, def update(i): global history_a, history_b, line,X_train,y_train a = history_a[i] b = history_b[i] w = np.sum(X_train*np.array([a]).T*np.array([y_train]).T,0) print(w,b) if w[1] == 0: return line, x1 = -1 y1 = -(b + w[0] * x1) / w[1] x2 = 6 y2 = -(b + w[0] * x2) / w[1] line.set_data([x1, x2], [y1, y2]) return line, plt.xlim(-1, 6) plt.ylim(-1, 4) ani = anim.FuncAnimation(fig=fig, func=update,init_func=init, frames=len(history_b), interval=1000, repeat=True, blit=True) plt.show()
(六)原始算法对比对偶算法

三:Sklearn实现感知机
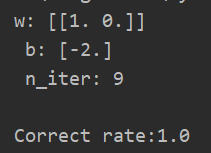
(一)代码实现
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron if __name__ == "__main__": # 构建数据集和标签值 X_train = np.array([[3, 3], [4, 3], [1, 1]]) y_train = np.array([1, 1, -1]) #构建Perceptron对象,训练数据并输出结果 perc = Perceptron() perc.fit(X_train,y_train) print("w:",perc.coef_,"\n","b:",perc.intercept_,"\n","n_iter:",perc.n_iter_,"\n") #获取模型预测的准确率 res = perc.score(X_train,y_train) print("Correct rate:{}".format(res))
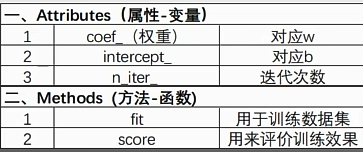
(二)方法参数说明
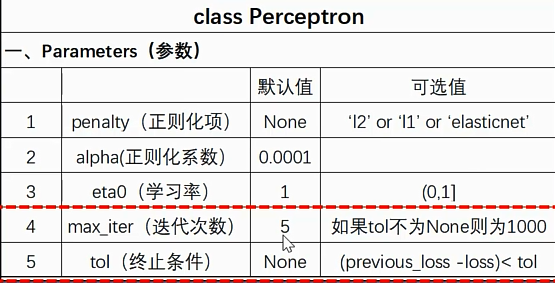
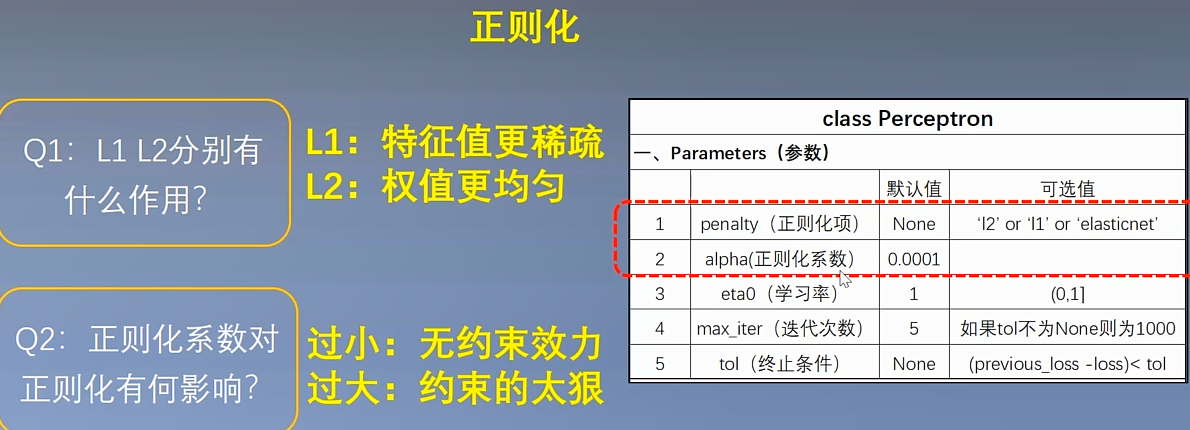
作者:山上有风景
欢迎任何形式的转载,但请务必注明出处。
限于本人水平,如果文章和代码有表述不当之处,还请不吝赐教。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构