C++回顾day02---<运算符重载>
一:运算符重载的限制
(一)可以重载的运算符:
+ - * / % ^ & | ~ ! = < > += -= *= /= %= ^= &= |= << >> <<= >>= == != <= >= && || ++ -- , ->* -> () [] new new[] delete delete[]
(二)不允许重载的运算符:
(三)原有基本语义不变
1.不改变运算符的优先级
|
运算符
|
描述
|
例子
|
可重载性
|
|
第一级别
|
|||
|
::
|
作用域解析符
|
Class::age = 2;
|
不可重载
|
|
第二级别
|
|||
|
()
|
函数调用
|
isdigit('1')
|
可重载
|
|
()
|
成员初始化
|
c_tor(int x, int y) : _x(x), _y(y*10){};
|
可重载
|
|
[]
|
数组数据获取
|
array[4] = 2;
|
可重载
|
|
->
|
指针型成员调用
|
ptr->age = 34;
|
可重载
|
|
.
|
对象型成员调用
|
obj.age = 34;
|
不可重载
|
|
++
|
后自增运算符
|
for( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) cout << i;
|
可重载
|
|
--
|
后自减运算符
|
for( int i = 10; i > 0; i-- ) cout << i;
|
可重载
|
|
const_cast
|
特殊属性转换
|
const_cast<type_to>(type_from);
|
不可重载
|
|
dynamic_cast
|
特殊属性转换
|
dynamic_cast<type_to>(type_from);
|
不可重载
|
|
static_cast
|
特殊属性转换
|
static_cast<type_to>(type_from);
|
不可重载
|
|
reinterpret_cast
|
特殊属性转换
|
reinterpret_cast<type_to>(type_from);
|
不可重载
|
|
typeid
|
对象类型符
|
cout « typeid(var).name();
cout « typeid(type).name();
|
不可重载
|
|
第三级别(具有右结合性)
|
|||
|
!
|
逻辑取反
|
if( !done ) …
|
可重载
|
|
not
|
! 的另一种表达
|
||
|
~
|
按位取反
|
flags = ~flags;
|
可重载
|
|
compl
|
~的另一种表达
|
||
|
++
|
预自增运算符
|
for( i = 0; i < 10; ++i ) cout << i;
|
可重载
|
|
--
|
预自减运算符
|
for( i = 10; i > 0; --i ) cout << i;
|
可重载
|
|
-
|
负号
|
int i = -1;
|
可重载
|
|
+
|
正号
|
int i = +1;
|
可重载
|
|
*
|
指针取值
|
int data = *intPtr;
|
可重载
|
|
&
|
值取指针
|
int *intPtr = &data;
|
可重载
|
|
new
|
动态元素内存分配
|
long *pVar = new long;
MyClass *ptr = new MyClass(args);
|
可重载
|
|
new []
|
动态数组内存分配
|
long *array = new long[n];
|
可重载
|
|
delete
|
动态析构元素内存
|
delete pVar;
|
可重载
|
|
delete []
|
动态析构数组内存
|
delete [] array;
|
可重载
|
|
(type)
|
强制类型转换
|
int i = (int) floatNum;
|
可重载
|
|
sizeof
|
返回类型内存
|
int size = sizeof floatNum;
int size = sizeof(float);
|
不可重载
|
|
第四级别
|
|||
|
->*
|
类指针成员引用
|
ptr->*var = 24;
|
可重载
|
|
.*
|
类对象成员引用
|
obj.*var = 24;
|
不可重载
|
|
第五级别
|
|||
|
*
|
乘法
|
int i = 2 * 4;
|
可重载
|
|
/
|
除法
|
float f = 10.0 / 3.0;
|
可重载
|
|
%
|
取余数(模运算)
|
int rem = 4 % 3;
|
可重载
|
|
第六级别
|
|||
|
+
|
加法
|
int i = 2 + 3;
|
可重载
|
|
-
|
减法
|
int i = 5 - 1;
|
可重载
|
|
第七级别
|
|||
|
<<
|
位左移
|
int flags = 33 << 1;
|
可重载
|
|
>>
|
位右移
|
int flags = 33 >> 1;
|
可重载
|
|
第八级别
|
|||
|
<
|
小于
|
if( i < 42 ) …
|
可重载
|
|
<=
|
小于等于
|
if( i <= 42 ) ...
|
可重载
|
|
>
|
大于
|
if( i > 42 ) …
|
可重载
|
|
>=
|
大于等于
|
if( i >= 42 ) ...
|
可重载
|
|
第九级别
|
|||
|
==
|
恒等于
|
if( i == 42 ) ...
|
可重载
|
|
eq
|
== 的另一种表达
|
||
|
!=
|
不等于
|
if( i != 42 ) …
|
可重载
|
|
not_eq
|
!=的另一种表达
|
||
|
第十级别
|
|||
|
&
|
位且运算
|
flags = flags & 42;
|
可重载
|
|
bitand
|
&的另一种表达
|
||
|
第十一级别
|
|||
|
^
|
位异或运算
|
flags = flags ^ 42;
|
可重载
|
|
xor
|
^的另一种表达
|
||
|
第十二级别
|
|||
|
|
|
位或运算
|
flags = flags | 42;
|
可重载
|
|
bitor
|
|的另一种表达
|
||
|
第十三级别
|
|||
|
&&
|
逻辑且运算
|
if( conditionA && conditionB ) …
|
可重载
|
|
and
|
&&的另一种表达
|
||
|
第十四级别
|
|||
|
||
|
逻辑或运算
|
if( conditionA || conditionB ) ...
|
可重载
|
|
or
|
||的另一种表达
|
||
|
第十五级别(具有右结合性)
|
|||
|
? :
|
条件运算符
|
int i = (a > b) ? a : b;
|
不可重载
|
|
第十六级别(具有右结合性)
|
|||
|
=
|
赋值
|
int a = b;
|
可重载
|
|
+=
|
加赋值运算
|
a += 3;
|
可重载
|
|
-=
|
减赋值运算
|
b -= 4;
|
可重载
|
|
*=
|
乘赋值运算
|
a *= 5;
|
可重载
|
|
/=
|
除赋值运算
|
a /= 2;
|
可重载
|
|
%=
|
模赋值运算
|
a %= 3;
|
可重载
|
|
&=
|
位且赋值运算
|
flags &= new_flags;
|
可重载
|
|
and_eq
|
&= 的另一种表达
|
||
|
^=
|
位异或赋值运算
|
flags ^= new_flags;
|
可重载
|
|
xor_eq
|
^=的另一种表达
|
||
|
|=
|
位或赋值运算
|
flags |= new_flags;
|
可重载
|
|
or_eq
|
|=的另一种表达
|
||
|
<<=
|
位左移赋值运算
|
flags <<= 2;
|
可重载
|
|
>>=
|
位右移赋值运算
|
flags >>= 2;
|
可重载
|
|
第十七级别
|
|||
|
throw
|
异常抛出
|
throw EClass(“Message”);
|
不可重载
|
|
第十八级别
|
|||
|
,
|
逗号分隔符
|
for( i = 0, j = 0; i < 10; i++, j++ ) …
|
可重载
|
2.不改变运算符的结合性
例如:=结合性是从右向左 a=b=3; 先执行b=3,再执行a=b
3.不改变运算符所需要的操作数
+-*/等需要两个操作数 ++ --等一个操作数 .....
4.不能创建新的运算符
二:运算符重载两种方法(传参方式不同,实现代码不同,应用场合不同)
(一)成员函数进行运算符重载(有this指针,所以传参少一个)
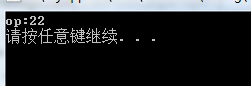
class A { private: int op; public: A(int a1) :op(a1) { } A& operator+(const A& a) //二元运算符,第一数为this对象,第二个是a对象 { A nonObj(this->op + a.op); return nonObj; //返回匿名对象 } void getInfo() { cout << "op:" << op << endl; } }; void main() { A a1(10); A a2(12); A a3 = a1 + a2; a3.getInfo(); system("pause"); }
或者A& A::operator+(const A& a){}
(二)友元函数进行运算符重载(无this指针)
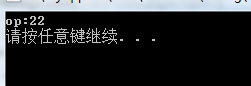
class A { friend A& operator+(const A& a, const A& b); //补充:默认访问修饰符为private private: int op; public: A(int a1) :op(a1) { } void getInfo() { cout << "op:" << op << endl; } }; A& operator+(const A& a, const A& b) //私有是对于类,友元函数可以使用类的所有成员,不管访问修饰符 { A nonObj(a.op + b.op); return nonObj; } void main() { A a1(10); A a2(12); A a3 = a1 + a2; a3.getInfo(); system("pause"); }
(三)上面实现的是二元运算符重载,这里来实现一元运算符重载(区分符号前置后置)
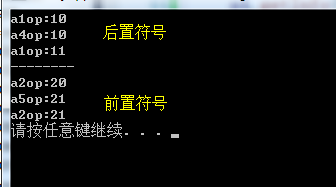
友元函数和成员函数操作运算符需要区分前置和后置(符号前后置) 前置 operator++() ++a 后置 operator++(int) //int进行占位区分 后面多一个,为后置 a++

class A { friend A& operator++(const A& a); private: int op; public: A(int a1) :op(a1) { } A& operator--() //无伪参数占位,是前置--a { this->op--; A nonObj(this->op); return nonObj; } A& operator--(int) //使用int伪参数占位,为后置a-- { A nonObj(this->op); this->op--; return nonObj; } void getInfo() { cout << "op:" << op << endl; } }; void main() { A a1(10); A a2(20); cout << "a1"; a1.getInfo(); A a4 = a1--; cout << "a4"; a4.getInfo(); cout << "a1"; a1.getInfo(); cout <<"--------"<< endl; cout << "a2"; a2.getInfo(); A a5 = --a2; cout << "a5"; a5.getInfo(); cout << "a2"; a2.getInfo(); system("pause"); }


class A { friend A& operator++(A& a); friend A& operator++(A& a,int); private: int op; public: A(int a1) :op(a1) { } void getInfo() { cout << "op:" << op << endl; } }; A& operator++(A& a) //对于一目运算符不能设置为const,因为要对自己进行修改 { a.op++; A nonObj(a.op); return nonObj; } A& operator++(A& a, int) { A nonObj(a.op); a.op++; return nonObj; } void main() { A a1(10); A a2(20); cout << "a1"; a1.getInfo(); A a4 = a1++; cout << "a4"; a4.getInfo(); cout << "a1"; a1.getInfo(); cout <<"--------"<< endl; cout << "a2"; a2.getInfo(); A a5 = ++a2; cout << "a5"; a5.getInfo(); cout << "a2"; a2.getInfo(); system("pause"); }
三:运算符重载应用场景
(一)友元函数和成员函数选择方法
1.当无法修改左操作数的类是,使用全局友元函数进行重载
对<<或者>>重载 cout<<数 cin>>数 左操作都是ostream或者istream无法修改的类, 所以重载<<或者>>只能用全局友元函数
2.=,[],(),->操作符只能使用成员函数进行重载
(二)使用友元函数方法实现<<和>>操作符重载
注意:
<<返回ostream类型 cout<<a<<b //连续输出a b两个变量 >>返回istream类型 cin>>a>>b; //连续输入两个变量到a b
实现:
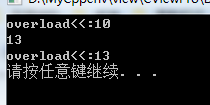
class A { friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, A& a); friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, A& a); private: int op; public: A(int a1) :op(a1) { } void getInfo() { cout << "op:" << op << endl; } }; ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, A& a) { out <<"overload<<:"<< a.op << endl; return out; } istream& operator>>(istream& in, A& a) { in >> a.op; return in; } void main() { A a(10); cout << a; cin >> a; cout << a; system("pause"); }
(三)使用成员函数方法实现=,数组下标运算符[],函数调用符(),操作符重载
1.=和[]
class A { friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, A& a); friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, A& a); private: int op; int *pArr; public: A(int a1) :op(a1) { pArr = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*a1); for (int i = 0; i < a1;i++) { pArr[i] = i+5; } } void getInfo() { cout << "op:" << op << endl; } //赋值运算符 A& operator=(const A& a1) { cout << "operator=" << endl; A nonObj(this->op + a1.op); return nonObj; } //数组下标运算符 int& operator[](int i) { cout << "operator[]" << endl; return this->pArr[i]; } ~A() { if (this->pArr != NULL) free(this->pArr); } }; ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, A& a) { out <<"overload<<:"<< a.op << endl; return out; } istream& operator>>(istream& in, A& a) { in >> a.op; return in; } void main() { A a(10); //A b = a; 是错误的,不会调用=重载操作符,是初始化操作 A b(5); b = a; //会调用=重载运算符 cout << a[3]; system("pause"); }
2.函数调用符():用于函数调用,实现数学函数的抽象
class Func { public: double operator()(double x, double y); //第一个()是重载的符号 }; double Func::operator()(double x, double y) { return x*x + y*y; } void main() { Func func; //调用默认构造函数 double ret = func(3.0, 4.0); cout << ret << endl; system("pause"); }
(四)&&和||虽然可以实现重载,但是由于重载后我们无法实现短路规则(还是要靠&& ||),所以最好不要重载



