142. Linked List Cycle II

这道题是要在链表里头判断是否构成一个环,并返回环的开始节点。主要思路是使用快慢指针,如果链表存在环的话,那么快指针到最后是会追上慢指针的。那么,这里关键在于如何判断某个节点就是环的开始节点。
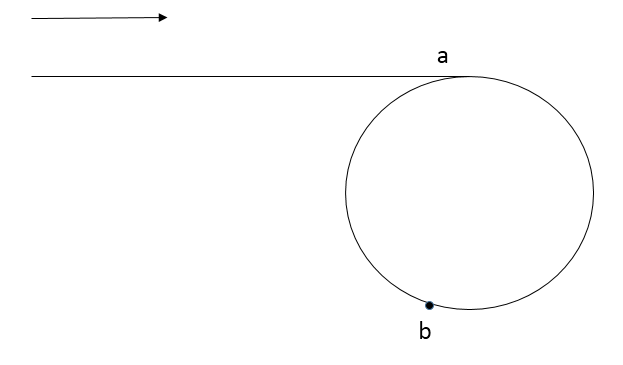
如上图,假设a 点为环开始的地方,b点为快慢指针第一次相遇的地方。由开始到a点距离为 d1 , a 到 b 点的顺时针长度为 L , 逆时针长度为 d2, 慢指针走过的长度为 s,我们设置快指针速度比慢指针快一倍,因此快指针距离为 2s。在相遇前快指针环绕环走了n圈,圈的长度为 r。
因此有两个等式:
1) 2s = nr + s -> s = nr
2) s = d1 + L
合并上面两个等式有 :
3) nr = d1 + L -> (n-1)r + r = d1+ L -> d1 = (n-1)r + (r - L)
因为 4) r = d2 + L
合并3)与4)的等式,有: d1 = (n-1)L + d2
这就是说如果有两个指针以相同速度分别从开始往 a 点出发以及 由b点顺时针往 a 点出发,最后当从开始出发的指针到达a点时,另一个指针将会绕环若干圈(包括0圈)后回到b点并继续往前走长度为d2的距离,也就是到达a点。最后我们有如下代码:
1 /**
2 * Definition for singly-linked list.
3 * class ListNode {
4 * int val;
5 * ListNode next;
6 * ListNode(int x) {
7 * val = x;
8 * next = null;
9 * }
10 * }
11 */
12 public class Solution {
13 public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
14 if(head == null || head.next == null){
15 return null;
16 }
17
18 ListNode fast = head;
19 ListNode slow = head;
20
21 while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
22
23 fast = fast.next.next;
24 slow = slow.next;
25
26 if( fast == slow ){
27 break;
28 }
29 }
30
31 if(fast == null || fast.next == null){
32 return null;
33 }
34
35 slow = head;
36
37 while( fast != slow ){
38 fast = fast.next;
39 slow = slow.next;
40
41 }
42
43 return fast;
44 }
45 }
END


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号