[[TOC]]
常用操作指令
show databases:显示所有的数据库;use dbName: 使用指定数据库show tables: 显示所有的数据表;desc tableName: 查看数据表的字段信息;show create table tableName: 查询创建表的所有信息;show create database dbName: 查看数据库创建指令;show full processlist: 查看所有进程drop table tableName: 删除表alter table tableName add constraint 主键(如:PK_TableName) primary key tableName(主键字段):添加主键约束alter table tableName add constraint 从表 (如:FK_从表_主表) foreign key 从表(外键字段) references 主表(主键字段): 添加外键约束alter table tableName add constraint 唯一约束 (如:uk_t_1) unique(字段名): 添加唯一约束;alter table tableName drop primary key: 删除主键约束alter table tableName drop foreign key 外键(区分大小写): 删除外键约束alter table tableName add index value_domain_idx(domain_id, value): 添加索引value_domain_idxalter table tableName drop index pool_domain_idx: 删除索引 pool_domain_idxshow index from table: 显示表的所有索引;mysqldump -uroot -pXXXX -h19.168.5.2 -P30118 --databases mgmt >/tmp/mgmt.sql: 导出指定数据库
Demo
查看变量(两种方式)
// 查看事务隔离级别: 方式1
MySQL [(none)]> show variables like "%iso%";
+---------------+-----------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-----------------+
| tx_isolation | REPEATABLE-READ |
+---------------+-----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
// 方式2
MySQL [(none)]> select @tx_isolation;
+---------------+
| @tx_isolation |
+---------------+
| NULL |
+---------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
// 查看最大连接数: 方式1
MySQL [(none)]> show variables like "%max_conn%";
+--------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------+-------+
| max_connect_errors | 100 |
| max_connections | 2000 |
+--------------------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
// 方式2:
MySQL [(none)]> select @@max_connections;
+-------------------+
| @@max_connections |
+-------------------+
| 2000 |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
设置变量的值
MySQL [(none)]> select @@max_connections;
+-------------------+
| @@max_connections |
+-------------------+
| 3000 |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> set global max_connections=4000;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> select @@max_connections;
+-------------------+
| @@max_connections |
+-------------------+
| 4000 |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
创建数据库
create database if not exists `myTestDB`
创建数据表
create table if not exists `t_user`(
`userid` int(11) not null auto_increment,
`userName` varchar(32) not null DEFAULT '',
`password` varchar(32) DEFAULT null,
`createTime` timestamp not null DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`status` smallint(4) default null,
`lastLoginTime` datetime DEFAULT null,
primary key (`userid`),
UNIQUE key `userName`(`userName`)
)ENGINE=InnoDB auto_increment=3 default CHARSET=utf8;
插入数据
在指定的列中插入数据
insert into t_user(userName,password,createTime,status,lastLoginTime) values("Tom","12345","2016-12-12 13:45:12",1,"2016-12-12 13:45:12");
insert into t_user(userName,password,createTime,status,lastLoginTime) values("Lily","12345","2016-12-12 14:45:12",1,"2016-12-12 14:45:12");
insert into t_user(userName,password,status,lastLoginTime) values("Jenny","12345",1,"2016-12-12 14:45:12");
性能优化
索引的设计
Innodb表尽量使用自己指定的主键
Innodb表,主键使用聚合索引,聚合索引会保存完整记录的值,即:数据文件本身就是索引文件,同时数据文件还是一个BTREE结构;
- Innodb表的主键索引--聚合索引
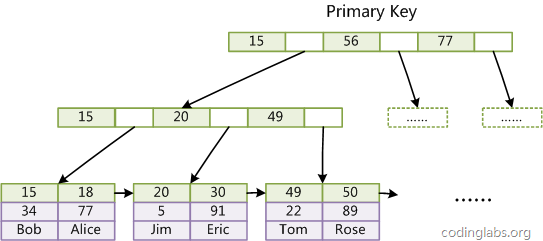
Innodb的主键应该尽可能的 短
Innodb表中,普通索引都会保存主键的键值,所以主键长度越短越好
- Innodb表的普通索引: 叶子节点会保存主键的值
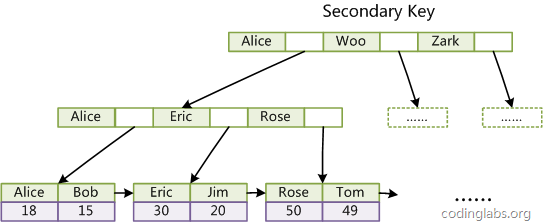
问题:为什么选择保存主键值,而不是保存记录的物理地址?
这样的策略减少了当出现行移动或者数据分页时二级索引的维护工作;
二级索引会占用更多的空间,换来的好处是,Innodb在移动行时,无需更新二级索引中的“指针”;
即:以空间换取二级索引的维护工作;
使用唯一索引
开启profiles
查看是否开启:默认时没有开启
MySQL [test]> show variables like "%profi%";
+------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------------+-------+
| have_profiling | YES |
| profiling | OFF|
| profiling_history_size | 15 |
+------------------------+-------+
开启:
set profiling=1;
MySQL [test]> show variables like "%profi%";
+------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------------+-------+
| have_profiling | YES |
| profiling | ON |
| profiling_history_size | 15 |
+------------------------+-------+
显示查询性能:
MySQL [test]> show profiles;
+----------+------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Query_ID | Duration | Query |
+----------+------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | 0.00077150 | show variables like "%profi%" |
| 2 | 0.00098675 | select * from pool_configs where pool_id like "7b8f0f5e2fbb4d9aa2d5fd55466dsij%" |
+----------+------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
索引的选择性
另一种不建议建索引的情况是索引的选择性较低。所谓索引的选择性(Selectivity),是指不重复的索引值(也叫基数,Cardinality)与表记录数(#T)的比值:
Index Selectivity = Cardinality / #T
显然选择性的取值范围为(0, 1],选择性越高的索引价值越大,这是由B+Tree的性质决定的。
使用示例:
CREATE TABLE `pool_configs` (
`id` char(32) NOT NULL,
`pool_id` char(32) NOT NULL,
`region_name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`domain_id` char(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`value` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `pool_id_index` (`pool_id`),
KEY `domain_index` (`domain_id`),
KEY `pool_domain_value_idx` (`pool_id`,`domain_id`,`value`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 |
上面的索引pool_domain_value_idx由3列组成:pool_id,domain_id,value;
则该索引的选择性:
MySQL [test]> select count(distinct(concat(pool_id,domain_id,value)))/count(*) as selectivity from pool_configs;
+-------------+
| selectivity |
+-------------+
| 0.2254 |
+-------------+
索引的选择性 与 前缀索引 组合
假设有两列:pool_id, domain_id,长度都为32;
CREATE TABLE `pool_configs` (
`id` char(32) NOT NULL,
`pool_id` char(32) NOT NULL,
`region_name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`domain_id` char(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`value` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
计算如下两个选择性:
- pool_id+domain_id组合:总共64位;
- pool_id+domain_id(前8)组合:总共40位;
MySQL [test]> select count(distinct(concat(pool_id, domain_id)))/count(*) as selectivity from pool_configs;
+-------------+
| selectivity |
+-------------+
| 0.9127 |
+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL [test]> select count(distinct(concat(pool_id, left(domain_id,8))))/count(*) as selectivity from pool_configs;
+-------------+
| selectivity |
+-------------+
| 0.8563 |
+-------------+
从上面可以发现,使用组合2可以节省将近一半的索引长度,但是选择性并没有降低多少;
那在建立索引的时候,就可以这样进行建立:
alter table pool_configs add index poolId_domainId8_idx(pool_id, domain_id(8)); // 只使用前8位
CREATE TABLE `pool_configs` (
`id` char(32) NOT NULL,
`pool_id` char(32) NOT NULL,
`region_name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`domain_id` char(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`value` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `poolId_domainId8_idx` (`pool_
这种方式,既满足了选择性较高,且索引长度较短,此种建立索引的方式就是前缀索引:只使用最左前缀的部分列长度;
前缀索引的局限性
前缀索引不能用于ORDER BY和GROUP BY操作,也不能用于Covering index(即当索引本身包含查询所需全部数据时,不再访问数据文件本身)
查看索引使用情况
- Handler_read_key: 代表行被索引读取的次数,
越高越好,很低表名索引没怎么起作用; - Handler_read_rnd_next: 高,通常表名索引使用不争取,或没有使用索引;
MySQL [test]> show status like "handler_read%";
+-----------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------------+-------+
| Handler_read_first | 12 |
| Handler_read_key | 12 |
| Handler_read_last | 0 |
| Handler_read_next | 6 |
| Handler_read_prev | 0 |
| Handler_read_rnd | 0 |
| Handler_read_rnd_next | 644 |
+-----------------------+-------+
死锁排查相关指令
查看事务隔离级别
mysql> select @@tx_isolation;
+-----------------+
| @@tx_isolation |
+-----------------+
| REPEATABLE-READ |
+-----------------+
1 row in set
设置打印死锁日志
set global innodb_print_all_deadlocks = 1;
查看最近一次死锁
show engine innodb status;
然后在打印的日志中,定位到:LATEST DETECTED DEADLOCK
示例
遇到死锁,第一步就是阅读死锁日志。
死锁日志通常分为两部分:
- 上半部分说明事务1在
等待什么锁; - 下半部分说明事务2当前只有的锁以及等待的锁;
死锁日志的术语:
S锁:共享锁;X锁:排它锁;RECORD LOCKS:记录锁(行锁);
------------------------
LATEST DETECTED DEADLOCK
------------------------
2018-01-05 07:42:47 7f97a6aaf700
*** (1) TRANSACTION:
TRANSACTION 633399987, ACTIVE 21 sec starting index read
//## 事务活跃了21秒,当前状态为读索引
mysql tables in use 1, locked 1
//## 有一个table被使用,表上有一个表锁
LOCK WAIT 2 lock struct(s), heap size 360, 1 row lock(s)
//## 当前事务持有1个行锁
MySQL thread id 83758029, OS thread handle 0x7f97a8823700, query id 1497915714 172.30.29.0 root updating
delete from test where a=2 //###当前事务正在执行该语句
*** (1) WAITING FOR THIS LOCK TO BE GRANTED:
RECORD LOCKS space id 3441 page no 4 n bits 72 index `a` of table `test`.`test` trx id 633399987 lock_mode X waiting
//### 事务1正在申请索引a的X锁(排它锁)
Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 32
0: len 4; hex 00000002; asc ;;
1: len 4; hex 00000002; asc ;;
*** (2) TRANSACTION:
TRANSACTION 633399683, ACTIVE 55 sec inserting
mysql tables in use 1, locked 1
4 lock struct(s), heap size 1184, 3 row lock(s), undo log entries 2
MySQL thread id 83757528, OS thread handle 0x7f97a6aaf700, query id 1497916206 172.30.29.0 root update
insert into test (id, a) values (10, 2)
*** (2) HOLDS THE LOCK(S):
RECORD LOCKS space id 3441 page no 4 n bits 72 index `a` of table `test`.`test` trx id 633399683 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap
//### 事务2持有X锁,并且是记录锁
Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 32
0: len 4; hex 00000002; asc ;;
1: len 4; hex 00000002; asc ;;
*** (2) WAITING FOR THIS LOCK TO BE GRANTED:
RECORD LOCKS space id 3441 page no 4 n bits 72 index `a` of table `test`.`test` trx id 633399683 lock mode S waiting
//### 事务2正在申请索引a的S锁(共享锁),因为事务1提前申请了该锁,所以造成了死锁
Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 32
0: len 4; hex 00000002; asc ;;
1: len 4; hex 00000002; asc ;;
*** WE ROLL BACK TRANSACTION (1)
InnoDB目前处理死锁的方法
InnoDB目前处理死锁的方法是将持有最少行级排他锁的事务进行回滚。
Sql慢查询日志
TODO
Mysql优秀博文-好文
mysql事务和锁InnoDB
深入浅出的讲解了数据库死锁原理;
MySQL索引背后的数据结构及算法原理
- 讲解索引的好文章
- Innodb和myisam索引实现原理:B+TREE索引、聚合索引、非聚合索引;
- 最左前缀原理与相关优化




