JAVA基础—适配器设计模式
适配器概念
在计算机编程中,适配器模式将一个类的接口适配成用户所期待的。使用适配器,可以使接口不兼容而无法在一起工作的类协调工作,做法是将类自己包裹在一个已经存在的类中。
JDK对适配器设计模式的应用
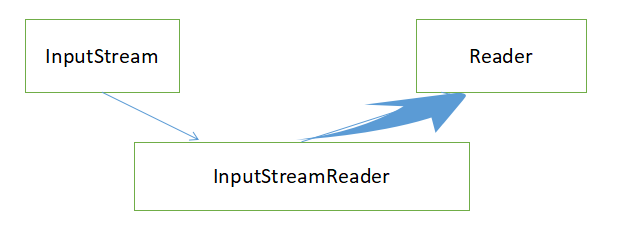
InputStreamReader(InputStream in)
创建一个使用默认字符集的 InputStreamReader。
并且InputStreamReader继承了Reader(字符流)
所以:InputStreamReader 类本身采用了适配器设计模式,把InputStream(字节流)类型转换为Reader类型(将字节流转换为字符流)。使得程序能够对传过来的InputStream 一个字符一个字符的进行操作
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\text.txt"),"UTF-8"); char c = (char) inputStreamReader.read();
假设InputStreamReader的read()方法从输入流中读取的字符为"好",read()方法实际上执行了以下步骤。
1)从输入流中读取三个字节:229、165和189,这三个字节代表"好"的UTF-8编码。
2)计算出字符"好"的Unicode编码为89和125
3)为"好"分配两个字节的内存空间,这两个字节的取值分别为89和125.为提供读的操作效率,可以用BufferReader来装饰InputStreamReader。
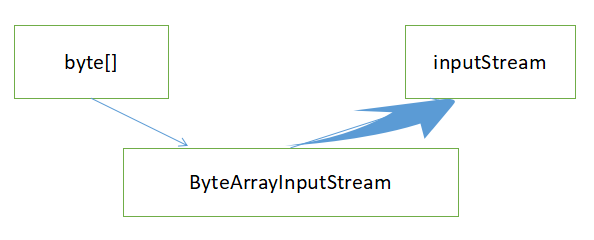
ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] buf)
创建一个 ByteArrayInputStream,使用 buf 作为其缓冲区数组。
并且ByteArrayInputStream 继承了InputStream。
所以:ByteArrayInputStream 采用了适配器设计模式,把字节数组转换为输入流类型,使得程序能够对字节数组进行读操作
构造方法 public ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] buf,int offset,int length) 参数buff指定字节数组类型的数据源,参数offset指定从数组中开始读数据的起始下标位置,length指定从数组中读取的字节数
byte[] buff = new byte[]{1,2,3,4,-1}; ByteArrayInputStream bin = new ByteArrayInputStream(buff,3,4); int data = bin.read(); while(-1!=data){ System.out.println(data); data = bin.read(); } bin.close();
打印结果是4 255(-1的二进制表示形式是11111111所以打印出来255)
SpringMVC的HandlerAdapter接口就有SpringMVC默认提供了几个适配器类供我们选择
AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter, AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter, HttpRequestHandlerAdapter, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter, SimpleServletHandlerAdapter



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号