IO流
InputStream字节输入流,outPutStream字节输出流
1)InputStream类提供了一系列读取数据有关的方法。它们都是抽象类,不能被实列化。
int read():从输入流中读取一个8位的bit,把它转换成一个0-255的整数,返回这一整数。列如:如果读到的字节为9,则返回9,如果读到的字节为-9,则返回247。如果输入流的结尾,则返回-1。
int read(byte[] byte):从输入流读取若干字节,把他们保存到参数b指定的字节数组中,返回的整数表示读取的字节数。如果输入流的结尾,则返回-1。
int read(byte[],int off ,int len):从输入流读取若干字节,把他们保存到参数B指定的字节数组中。参数off指定在字节数组中开始保存数据的起始下标,参数len指定读取的字节数目。返回的整数表示实际读取的字节数。如果读到输入流的结尾,则返回-1。
以上第一个read()方法从输入流读取一个字节,其余两个read方法从输入流批量读取若干字节。
2)outputStream类提供了一系列读取数据有关的方法。
void write(int b):向输入流写入一个字节。
void write(byte[] b):把参数b指定的字节数组中的所有字节写到输出流。
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len):把参数b指定的字节数组的若干字节写到输出流,参数off指定字节数组的起始下标,从这个位置开始输出由参数len指定数目的字节。
以上第一个write方法向输入流写入一个字节,而其余两个write方法向输出流批量写入若干字节。在向文件或控制台写数据时,采用后面两个write方法可以减少进行物理写文件或控制台的次数。
子类实现
1)字节数组输入流: ByteArrayInputStream类
ByteArrayInputStream从内存中的字节数组中读取数据,因此它的数据源是一个字节数组。这个类的构造方法包括。
ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] b):参数buff指定字节数组类型的数据源。
ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] b, int off, int len):参数buf指定字节数组类型的数据源,参数off指定从字节数组中开始读取数据的起始下标位置,len指定从数组中读取的字节数。
类似字节数组输出流: ByteArrayOutStream
2)文件输入流:FileInputStream
FileInputStream从文件中读取数据,它有以下构造方法。
FileInputStream(File file) 参数file指定文件数据源。
FileInputStream(String name) 参数name指定文件数据源。在参数name中包含文件路径信息。
类似的有文件输出流:FIleOutputStream
3)管道输入流:PiedInputStream
PipedInputStream 和PipedOutputStream进行多线程消息通信。(没什么人用这种方法)
首先写ReadData和WriteData两个工具类,分别利用PipedInputStream 和PipedOutputStream进行读写操作。
ReadData(read()方法是阻塞式的)

public class ReadData { public void readMethod(PipedInputStream input ){ System.out.println("开始read:"); byte[] byteArray = new byte[1000]; int len; try { //len读入缓冲区的字节总数 len = input.read(byteArray); while(-1!=len){ String newData = new String(byteArray,0,len); System.out.print(newData); len=input.read(byteArray); } System.out.println(); input.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
WriteData

public class WriteData { public void writeMethod(PipedOutputStream out){ try { System.out.println("开始write:"); String outData = ("写数据的内容"); out.write(outData.getBytes()); System.out.print(outData); System.out.println(); out.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
开一个读的线程(因为read()方法阻塞 如果没有数据会一直等待)

public class ThreadRead extends Thread{ private ReadData readData; private PipedInputStream input; public ThreadRead(javaee.net.cn.thread.mythread.ReadData readData, PipedInputStream input) { super(); this.readData = readData; this.input = input; } @Override public void run(){ readData.readMethod(input); } }
开一个写的线程

public class ThreadWriter extends Thread{ private WriteData writeData; private PipedOutputStream out; public ThreadWriter(WriteData writeData, PipedOutputStream out) { super(); this.writeData = writeData; this.out = out; } @Override public void run(){ writeData.writeMethod(out); } }
测试:

public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { WriteData writeData = new WriteData(); ReadData readData = new ReadData(); PipedOutputStream out = new PipedOutputStream(); PipedInputStream input = new PipedInputStream(); out.connect(input); ThreadRead threadRead = new ThreadRead(readData,input); threadRead.start(); Thread.sleep(2000); ThreadWriter threadWriter = new ThreadWriter(writeData,out); threadWriter.start(); } }
过滤输入流FilterInputStream(装饰者设计模式)
InputStream类声明的read()方法按照流中字节的先后顺序读取字节,FileInputStream和ByteArrayInputStream等具体的输入流都按照这种方式读数据。
假如希望进一步扩展读数据的功能,一种方式是创建FileInputStream等输入流的子类,但这样会大大增加输入流类的数目,使输入流的层次结构更加复杂;
还有一种方式是创建输入流的装饰器,它本身继承了InputStream类,还可以用来装饰其他的输入流类。I/O类库中的FilterInputStream类就是一种装饰器。他有几个子类,分别用来扩展输入流的某一功能。
1)BufferedInputStream
BufferedInputStream类覆盖了被装饰的输入流的读数据行为,利用缓冲区来提高读数据的效率。BufferedInputStream类先把一批数据读入到缓冲区,
接下来read()方法只需从缓冲区内获取数据,这样就能减少物理性读取数据的次数。
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in , int size)构造方法中参数in指定被需要被装饰的输入流,参数size指定缓冲区的大小,以字节为单位。
当数据源为文件时,可以用BufferedInputStream来装饰输入流,从而提高IO的操作效率。列如在以下程序代码中,文件输入流先被BufferedInputStream装饰。
在被DataInputStream装饰。
InputStream in1 = new FileInputStream("D:\\text.txt"); BufferedInputStream in2 = new BufferedInputStream(in1);//装饰文件输入流 DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(in2);//装饰缓冲输入流
利用字节数组缓冲区快速进行文件复制
public void test2() throws Exception { Long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ InputStream ins = new FileInputStream(startPath); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(endPath); BufferedInputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(ins); BufferedOutputStream bout = new BufferedOutputStream(out); byte[] buff = new byte[2048]; while (-1 != (bin.read(buff))) { bout.write(buff); } ins.close(); out.close(); } Long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(endTime-startTime);//640 }
2)DataInputStream
DataInputStream的readUTF()方法能够从输入流中读取采用UTF-8编码的字符串。UTF-8编码是Unicode编码的变体。Unicode编码把所有的字符都存储为两个字节的形式。
如果实际上要存储的字节都是ASCII字符(只占7位),采用Unicode编码及其浪费存储空间。UTF-8编码能够更加有效的利用存储空间,它对ASCII字符采用一个字节形式的编码,对非ASCII字符则采用两个或两个以上字节形式的编码。
DataOutputStream的writeUTF()方法向输入流中写入采用UTF-8编码的字符串。实际上,writeUTF()方法和readUTF()方法是适合java语言的UTF变体。
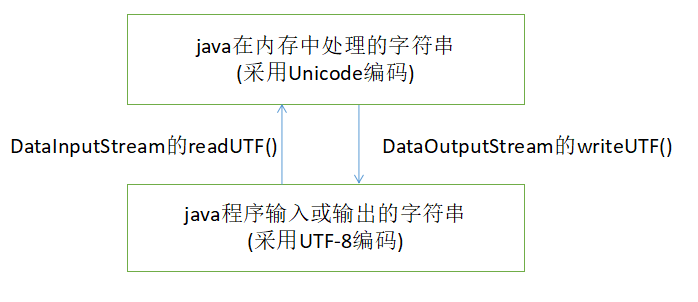
利用DataInputStream 的一些方法不需要把要读写的数据进行字节数组来回转换(inputStream只提供了读写字节和字节数组的方法).
通常数据输出流按照一定的格式输出,在通过数据输入流按照一定的格式输入,这样可以方便的对数据进行处理。
如:通过writeUTF()把一个Unicode字符串写进去,可以使用readUTF()直接读进来。
tip:String str = "abc";等效于: char data[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'}; String str = new String(data);




