Redis 列表阻塞命令的实现
前言
在 Redis 的 列表(list) 命令中,有一些命令是阻塞模式的,比如:BRPOP, BLPOP, BRPOPLPUSH, 这些命令都有可能造成客户端的阻塞。下面总结一下 Redis 实现阻塞和取消阻塞的过程。
阻塞过程
当一个阻塞原语的处理目标为空键时, 执行该阻塞原语的客户端就会被阻塞。有以下步骤:
1:将客户端的状态设为“正在阻塞”, 并记录阻塞这个客户端的各个键,以及阻塞的最长时限(timeout) 等数据;
2:将客户端的信息记录到 server.db[i]->blocking_keys 中(其中 i 为客户端所使用的数据库号码);
3:继续维持客户端和服务器之间的网络连接,但不再向客户端传送任何信息,造成客户端阻塞;
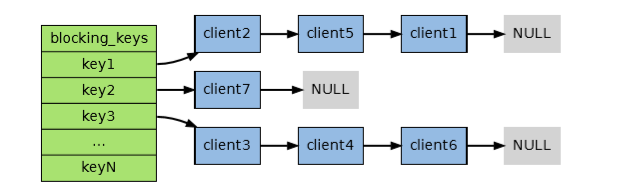
note: step2 中 service.db[i]->blocking_keys 是一个字典,键是那些造成客户端阻塞的键, 值是一个链表,链表里保存了所有因这个键而被阻塞的客户端,如下图所示:
阻塞的取消过程
阻塞的取消有三种方法:
【1】被动脱离:有其它客户端为造成阻塞的键推入了新元素;
【2】主动脱离:到达执行阻塞原语时设定的最大阻塞时间(timeout);
【3】强制脱离:客户端强制终止和服务端的连接,或者服务器停机;
被动脱离
阻塞因 LPUSH, RPUSH, LINSERT 等添加命令而被取消,这三个添加新元素的命令,在底层都有一个 pushGenericCommand 的函数实现(在下方源码部分增加的 TODO 标志标识关键步骤):

void lpushCommand(redisClient *c) { pushGenericCommand(c,REDIS_HEAD); } void rpushCommand(redisClient *c) { pushGenericCommand(c,REDIS_TAIL); }
下面是 pushGenericCommand 函数的源码实现(在下方源码部分增加的 TODO 标志标识关键步骤):

/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------- * List Commands *----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ void pushGenericCommand(redisClient *c, int where) { int j, waiting = 0, pushed = 0; // 取出列表对象 robj *lobj = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[1]); // 如果列表对象不存在,那么可能有客户端在等待这个键的出现 int may_have_waiting_clients = (lobj == NULL); if (lobj && lobj->type != REDIS_LIST) { addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr); return; } // 将列表状态设置为就绪 if (may_have_waiting_clients) signalListAsReady(c,c->argv[1]); //TODO 1: 如果有 client 可能被阻塞,则新加 readyList 到 service.ready_Keys 的字典中的相应链表中 // 遍历所有输入值,并将它们添加到列表中 for (j = 2; j < c->argc; j++) { //TODO 2: 此处把新 push 的值加入到对应 key 的列表中 // 编码值 c->argv[j] = tryObjectEncoding(c->argv[j]); // 如果列表对象不存在,那么创建一个,并关联到数据库 if (!lobj) { lobj = createZiplistObject(); dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[1],lobj); } // 将值推入到列表 listTypePush(lobj,c->argv[j],where); pushed++; } // 返回添加的节点数量 addReplyLongLong(c, waiting + (lobj ? listTypeLength(lobj) : 0)); // 如果至少有一个元素被成功推入,那么执行以下代码 if (pushed) { char *event = (where == REDIS_HEAD) ? "lpush" : "rpush"; // 发送键修改信号 signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]); // 发送事件通知 notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_LIST,event,c->argv[1],c->db->id); } server.dirty += pushed; }
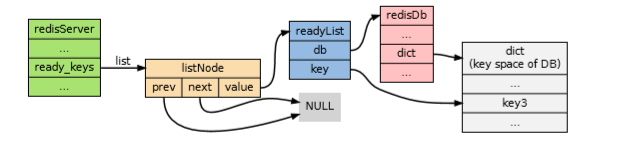
pushGenericCommand 函数主要做了两件事情:
【1】向 readyList 添加到服务器;
【2】将新元素 value 添加到该 key 中
到此处为止,被该 key 阻塞的客户端还没有任何一个被解除阻塞状态,为了做到这一点,Redis 的主进程在执行完 pushGenericCommand 函数后,会继续调用 handleClientsBlockedOnLists 函数,该函数的源码如下(在下方源码部分增加的 TODO 标志标识关键步骤):

/* This function should be called by Redis every time a single command, * a MULTI/EXEC block, or a Lua script, terminated its execution after * being called by a client. * * 这个函数会在 Redis 每次执行完单个命令、事务块或 Lua 脚本之后调用。 //TODO 0: NOTICE * * All the keys with at least one client blocked that received at least * one new element via some PUSH operation are accumulated into * the server.ready_keys list. This function will run the list and will * serve clients accordingly. Note that the function will iterate again and * again as a result of serving BRPOPLPUSH we can have new blocking clients * to serve because of the PUSH side of BRPOPLPUSH. * * 对所有被阻塞在某个客户端的 key 来说,只要这个 key 被执行了某种 PUSH 操作 * 那么这个 key 就会被放到 serve.ready_keys 去。 * * 这个函数会遍历整个 serve.ready_keys 链表, * 并将里面的 key 的元素弹出给被阻塞客户端, * 从而解除客户端的阻塞状态。 * * 函数会一次又一次地进行迭代, * 因此它在执行 BRPOPLPUSH 命令的情况下也可以正常获取到正确的新被阻塞客户端。 */ void handleClientsBlockedOnLists(void) { // 遍历整个 ready_keys 链表 while(listLength(server.ready_keys) != 0) { list *l; /* Point server.ready_keys to a fresh list and save the current one * locally. This way as we run the old list we are free to call * signalListAsReady() that may push new elements in server.ready_keys * when handling clients blocked into BRPOPLPUSH. */ // 备份旧的 ready_keys ,再给服务器端赋值一个新的 l = server.ready_keys; server.ready_keys = listCreate(); while(listLength(l) != 0) { //TODO 1: 不断取出 server.ready_keys 的所有元素(可能对应多个不同的阻塞 Key) // 取出 ready_keys 中的首个链表节点 listNode *ln = listFirst(l); // 指向 readyList 结构 readyList *rl = ln->value; /* First of all remove this key from db->ready_keys so that * we can safely call signalListAsReady() against this key. */ // 从 ready_keys 中移除就绪的 key dictDelete(rl->db->ready_keys,rl->key); /* If the key exists and it's a list, serve blocked clients * with data. */ // 获取键对象,这个对象应该是非空的,并且是列表 robj *o = lookupKeyWrite(rl->db,rl->key); if (o != NULL && o->type == REDIS_LIST) { dictEntry *de; /* We serve clients in the same order they blocked for * this key, from the first blocked to the last. */ // 取出所有被这个 key 阻塞的客户端 de = dictFind(rl->db->blocking_keys,rl->key); if (de) { list *clients = dictGetVal(de); int numclients = listLength(clients); while(numclients--) { //TODO 2: 不断取出因为等待该 key 被阻塞的客户端 // 取出客户端 listNode *clientnode = listFirst(clients); redisClient *receiver = clientnode->value; // 设置弹出的目标对象(只在 BRPOPLPUSH 时使用) robj *dstkey = receiver->bpop.target; // 从列表中弹出元素 // 弹出的位置取决于是执行 BLPOP 还是 BRPOP 或者 BRPOPLPUSH int where = (receiver->lastcmd && receiver->lastcmd->proc == blpopCommand) ? REDIS_HEAD : REDIS_TAIL; robj *value = listTypePop(o,where); //TODO 3: 从该 key 已添加的元素中 pop 出第一个元素,并用于阻塞客户端的返回值 // 还有元素可弹出(非 NULL) if (value) { /* Protect receiver->bpop.target, that will be * freed by the next unblockClient() * call. */ if (dstkey) incrRefCount(dstkey); // 取消客户端的阻塞状态 unblockClient(receiver); //TODO 4: 从 service.blocking_keys 中移除对应阻塞的客户端 // 将值 value 推入到造成客户度 receiver 阻塞的 key 上 if (serveClientBlockedOnList(receiver, rl->key,dstkey,rl->db,value, where) == REDIS_ERR) { /* If we failed serving the client we need * to also undo the POP operation. */ listTypePush(o,value,where); } if (dstkey) decrRefCount(dstkey); decrRefCount(value); } else { // 如果执行到这里,表示还有至少一个客户端被键所阻塞 // 这些客户端要等待对键的下次 PUSH break; } } } // 如果列表元素已经为空,那么从数据库中将它删除 if (listTypeLength(o) == 0) dbDelete(rl->db,rl->key); /* We don't call signalModifiedKey() as it was already called * when an element was pushed on the list. */ } /* Free this item. */ decrRefCount(rl->key); zfree(rl); listDelNode(l,ln); } listRelease(l); /* We have the new list on place at this point. */ } }
handleClientsBlockedOnLists 函数主要执行如下操作:
【1】如果 service.ready_keys 不为空,那么弹出该链表的表头元素,并取出其中的 readyList 值;
【2】根据 readyList 值中保存的 key 和 db, 在 service.blocking_keys 中查找所有因为该 key 而被阻塞的客户端(以链表形式保存);
【3】如果 Key 不为空,那么从 Key 的列表中弹出一个元素,并获取客户端链表的第一个客户端,然后将被弹出元素作为被阻塞的客户端的返回值;
【4】根据 readyList 结构的属性,删除 service.blocking_keys 中相应的客户端数据,取消客户端的阻塞状态;
【5】继续执行步骤 【3】和 【4】,知道 key 没有元素可弹出,或者因为 key 而阻塞的客户端都取消阻塞为止;
【6】继续执行步骤 【1】,直到 ready_keys 字典所有链表里的所有 readyList 结构都被处理完为止;
主动脱离
阻塞因超过最大等待时间而被取消。当客户端被阻塞时,所有造成它阻塞的键,以及阻塞的最长时限都会被记录在客户端里面,并且盖客户端的状态会被设置为”正在阻塞“。每次 Redis 服务器常规操作函数(redis.c/serverCron) 执行时,程序都会检查所有连接到服务器的客户端,查看哪些处于”正在阻塞“状态的客户端时限是否已经过期,如果是的话,就给客户端返回一个空白回复,然后撤销对客户端的阻塞。下面是相关源码:

void clientsCron(void) { /* Make sure to process at least 1/(server.hz*10) of clients per call. * * 这个函数每次执行都会处理至少 1/server.hz*10 个客户端。 * * Since this function is called server.hz times per second we are sure that * in the worst case we process all the clients in 10 seconds. * * 因为这个函数每秒钟会调用 server.hz 次, * 所以在最坏情况下,服务器需要使用 10 秒钟来遍历所有客户端。 * * In normal conditions (a reasonable number of clients) we process * all the clients in a shorter time. * * 在一般情况下,遍历所有客户端所需的时间会比实际中短很多。 */ // 客户端数量 int numclients = listLength(server.clients); // 要处理的客户端数量 int iterations = numclients / (server.hz * 10); // 至少要处理 50 个客户端 if (iterations < 50) iterations = (numclients < 50) ? numclients : 50; while (listLength(server.clients) && iterations--) { redisClient *c; listNode *head; /* Rotate the list, take the current head, process. * This way if the client must be removed from the list it's the * first element and we don't incur into O(N) computation. */ // 翻转列表,然后取出表头元素,这样一来上一个被处理的客户端会被放到表头 // 另外,如果程序要删除当前客户端,那么只要删除表头元素就可以了 listRotate(server.clients); head = listFirst(server.clients); c = listNodeValue(head); /* The following functions do different service checks on the client. * The protocol is that they return non-zero if the client was * terminated. */ // 检查客户端,并在客户端超时时关闭它 if (clientsCronHandleTimeout(c)) continue; // 根据情况,缩小客户端查询缓冲区的大小 if (clientsCronResizeQueryBuffer(c)) continue; } }
阻塞的取消策略
当程序添加一个新的被阻塞客户端到 server.blocking_keys 字典的链表中时,他将客户端放在链表的最后,而当 handleClientsBlockedOnLists 取消客户端的阻塞时候,它从链表的最前面开始取消阻塞;这个链表形成了一个 FIFO 队列,最先被阻塞的客户端总是最先脱离阻塞状态,Redis 文档称这种模式为先阻塞先服务(FBFS, first-block-first-server)。
参考内容:
[1]:The Design and Implementation of Redis 黄健宏




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
· AI Agent开发,如何调用三方的API Function,是通过提示词来发起调用的吗