C++实验二——函数重载、函数模板、简单类的定义和实现
2019-03-19 14:29 孙乾(小U) 阅读(911) 评论(1) 编辑 收藏 举报一、实验过程
函数重载编程练习
实验要求:编写重载函数add(),实现对int型,double型,complex型数据的加法。在main函数中定义不同类型的数据,调用测试。
代码实现:
先是简单的体验函数重载:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; struct Complex { double real; double imag; }; int add(int, int); double add(double,double); Complex add(Complex, Complex); int main() { cout<<add(3,12)<<endl; cout<<add(5.7,12.7) <<endl; cout<<add(3,6)<<"+"<<add(3,4)<<"i"<<endl; } int add(int a,int b) { return a+b; } double add(double a,double b) { return a+b; } Complex add(Complex a,Complex b) { Complex r; r.real=a.real+b.real; r.imag=a.imag+b.imag; return r; }
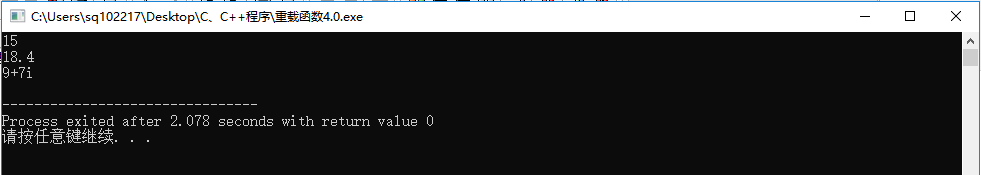
在前面内容的基础上,对代码和功能做了完善,使它更符合这个实验对代码的运行要求。
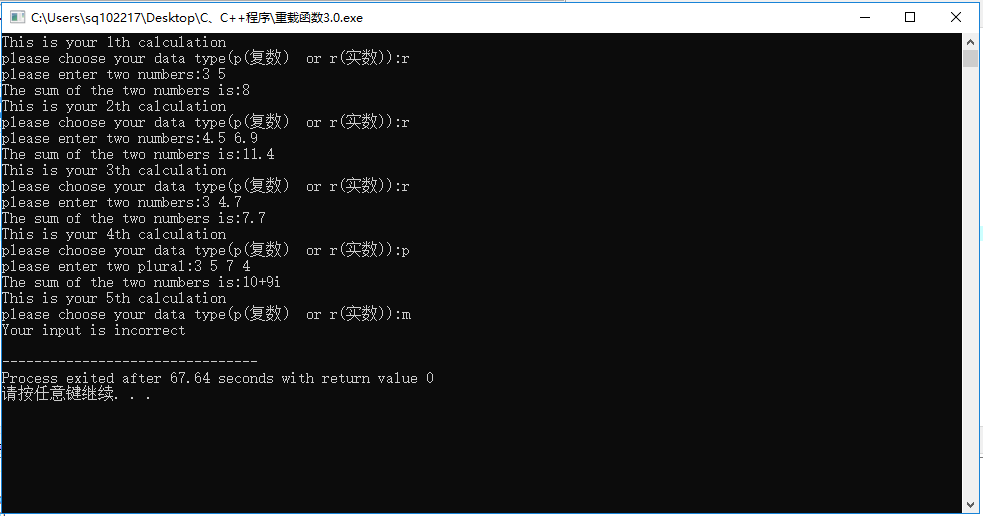
#include<iostream> using namespace std; struct Complex { double real; double imag; }; int add(int, int); double add(double,double); Complex add(Complex, Complex); int main() { char c; int tries=0; while(true) { tries++; cout<<"This is your "<<tries<<"th calculation"<<endl; cout<<"please choose your data type(p(复数) or r(实数)):"; cin>>c; if(c=='r') { cout<<"please enter two numbers:" ; double a,b; cin>>a>>b; cout<<"The sum of the two numbers is:" <<add(a,b)<<endl; } else if(c=='p') { cout<<"please enter two plural:"; Complex p,q; cin>>p.real>>p.imag; cin>>q.real>>q.imag; cout<<"The sum of the two numbers is:"<<(add(p,q)).real<<"+"<<(add(p,q)).imag<<"i"<<endl; } else { cout<<"Your input is incorrect" <<endl; break; } } return 0; } int add(int a,int b) { return a+b; } double add(double a,double b) { return a+b; } Complex add(Complex a,Complex b) { Complex r; r.real=a.real+b.real; r.imag=a.imag+b.imag; return r; }
运行结果如下:
函数模板编程练习
实验要求:编写实现快速排序函数模板,并在main函数中,定义不同类型数据,调用测试。
算法设计:快速排序用了二分的思想,先通过一个数把一组数分成两部分,其中一部分均比另一部分要小。之后分别再对这两个部分继续分割排序,最后使整个数组有序排列。排序分成了三个步骤:选择一个数(pivot)作为分割标准、分割、递归。这个排序函数模板的核心就是最后的递归。
代码实现
#include<iostream> using namespace std; void QuickSort(double ar[], int left ,int right) { if(left<right) { int i = left; int j = right; double x = ar[i]; while(i<j) { while(i<j&&ar[j]>x) j--; if(i<j) { ar[i] = ar[j]; i++; } while(i<j&&ar[i]<x) i++; if(i<j) { ar[j] = ar[i]; j--; } } ar[i] = x; QuickSort(ar, left, i-1); QuickSort(ar, i+1, right); } } int main() { int n = 8 ; double ar[]={4,3,5,2,7,1,9,6,8}; int i; cout<<"The remote arry is:"; for(i=0;i<n;++i) cout<<ar[i]<<' '; cout<<endl; QuickSort(ar,0,n-1); cout<<"The arranged arry is: "; for(i=0;i<n;++i) cout<<ar[i]<<' '; cout<<endl; return 0; }
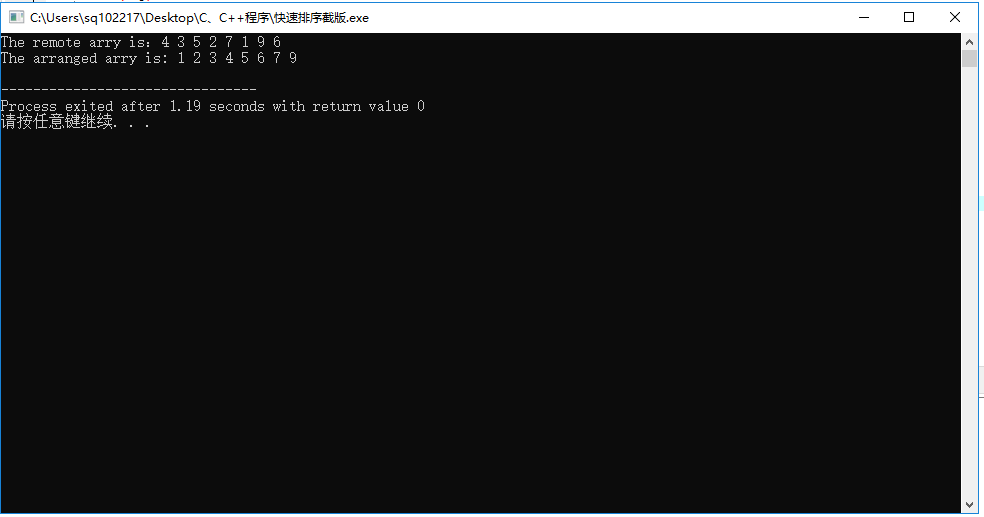
类的定义、实现和使用编程练习
实验要求:设计并实现一个用户类User,并在主函数中使用和测试这个类。具体要求如下:
- 每一个用户有用户名(name), 密码(passwd),联系邮箱(email)三个属性。
- 支持设置用户信息setInfo()。允许设置信息时密码默认为6个1,联系邮箱默认为空串。
- 支持打印用户信息printInfo()。打印用户名、密码、联系邮箱。其中,密码以6个*方式显示。
- 支持修改密码changePasswd(),。在修改密码前,要求先输入旧密码,验证无误后,才允许修改。
- 如果输入旧密码时,连续三次输入错误,则提示用户稍后再试,暂时退出修改密码程序。
在main()函数中创建User类实例,测试User类的各项操作(设置用户信息,修改密码,打印用户信
息)
User类功能的完善及拓展丰富(===选做===)
自行设计。在前述内容的基础上,对代码和功能做完善,使其更符合实际应用场景。比如:
- 支持修改邮箱;用户设置邮箱时对邮箱地址合法性的检测提示(比如是否包含@)
- 用户更改密码时,当用户输入旧密码和新密码时,屏幕上均以星号代替,而不会显示用户实际
- 输入的密码;设置密码时对密码的长度、合法性进行有效性校验,等等
代码实现
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; class User { public: User(); ~User(); public: //设置用户信息 void setInfo(); //打印用户信息 void printInfo(); //修改密码 void changePassword(); //修改邮箱 void changeEmail(); //设置*号 string getXinghao(); private: string user_name_; //用户名 string user_password_; //密码 string user_email_; //邮箱 }; User::User() { user_password_ = "111111"; //密码默认为6个1 user_email_ = ""; } User::~User() { } void User::setInfo() { cout << "请输入用户名:"; cin >> user_name_; cout << "请输入密码:"; cin >> user_password_; cout << "邮箱:"; cin >> user_email_; } void User::printInfo() { cout << "用户名:" << user_name_ <<endl; cout << "密码:" << user_password_ <<endl; cout << "邮箱:" << user_email_ <<endl; } void User::changePassword() { string strOld, strNew; int nCount = 0; do { cout << "请输入旧密码:" <<endl; strOld = getXinghao(); if (strOld.compare(user_password_) != 0) { int tries=0; tries++; cout << "旧密码不正确!" << "这是您第"<<tries<<"输错密码"<<endl; if(tries>=3) { break; } } else { cout << "请输入新密码:" << endl; strNew = getXinghao(); if (strNew.size() != 6) //密码6位数 { cout << "密码长度不正确!" <<endl; } else { user_password_ = strNew; cout << "修改密码成功!" <<endl; break; } } nCount++; } while (nCount < 3); } void User::changeEmail() { cout << "请输入新邮箱:"; string strEmail; cin >> strEmail; if (strEmail.find("@") != string::npos) { user_email_ = strEmail; } else { cout << "邮箱地址不正确!" << endl; } } string User::getXinghao() { string password; int i = 0; char ch; while ((ch = _getch()) != 13) { i++; if (ch != '\0') { password += ch; cout << "*"; } } cout <<endl; return password; } int main() { User user; //设置信息 user.setInfo(); //显示信息 user.printInfo(); //修改密码 user.changePassword(); //显示信息 user.printInfo(); //修改邮箱 user.changeEmail(); //显示信息 user.printInfo(); }
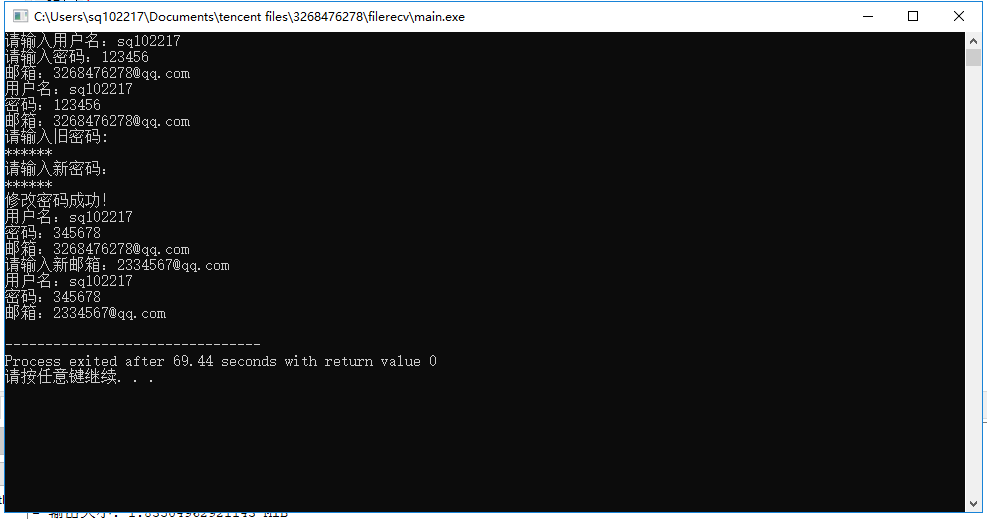
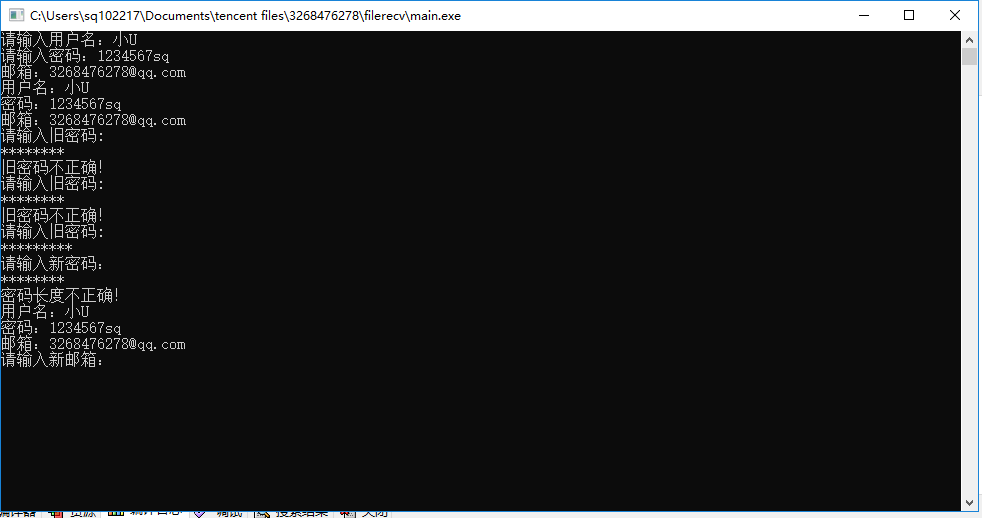
二、实验反思
1、实验一中关于复数的运算,可以写一个复数类。实验二中快排的优点就是速度极快,数据移动少,但是当快排到后期,当待排数组割到一定大小后,快排不如其他一些排序方法好,此时可以用插排等,后期查了些资料,三数取中+插排效率要更高一点。总而言之,各排序方法都有各自的优缺点。
2、函数重载减少了函数名的数量,让代码更清晰,代码可读性提高。类有很多优点,我认为很大一部分体现在模块化编程上,将具有特定功能的一个组件封装到一个类中。将各个模块独立,能够使得程序结构更加清晰,可以减少程序的bug。
互评地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yidaoyigexiaopenyou/p/10556646.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/sjn1/p/10556014.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/elise00/p/10555817.html


