optuna框架下lightgbm参数调优
针对最近参加的移动梧桐杯比赛,为了尽可能的优化模型超参数,经调研后,应用optuna框架进行超参数优化。主要解决问题:
1. LightGBMPruningCallback 回调函数的使用
2. LightGBM自定义验证集评估函数
1. 自定义评估函数Accuracy,由于比赛采用Accuracy为衡量标准,但是阅读源码发现,LightGBM本身没有集成Accuracy,如下所示为fit函数eval_metric的源码
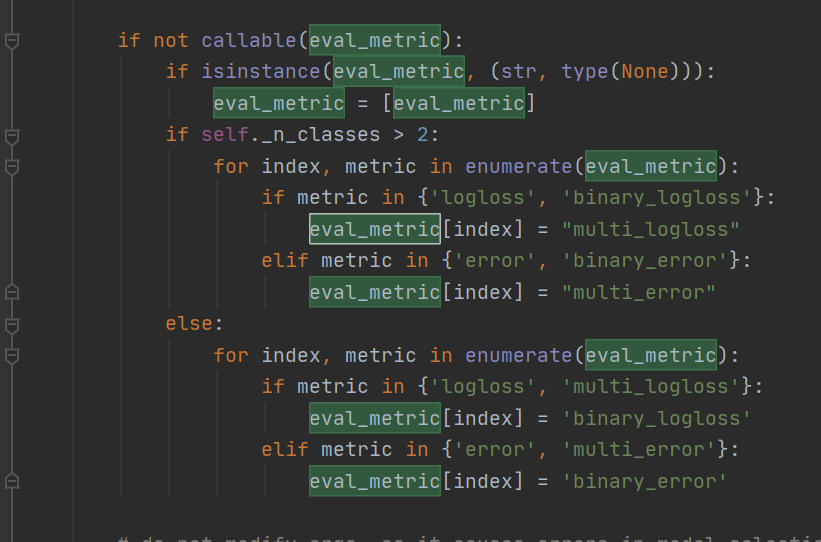
上图可知,实际上分类问题中,LightGBM仅有logloss和error作为评估标准,因此,我们利用sklearn的accuracy_score实现自定义accuracy,代码如下:
def Accuracy_score(labels, preds): preds = preds.argmax(axis=1) # 对预测结果进行argmax操作,得到类别标签 accuracy = accuracy_score(labels, preds) return 'accuracy', accuracy, True
上述代码中,核心问题包括两个,即输入和输出:
(1)明确fit每次迭代评估的输出,也就是自定义评估函数的输入。
通过print输出,可以观察到第一参数为label,即标签,第二个参数是预测结果,为二维数组,shape为(nums,num_class),可见输出为类别概率的向量,采用argmax获取最大值所在的索引即为预测结果类别。
(2)明确评估后的输出
通过报错显示,评估后的输出应保持 'accuracy', accuracy, True 形式,其中,第一个参数为 指标名称,第二个参数为具体数值,第三个为bool类型。
2 LightGBMPruningCallback 回调函数的使用
1 设置LightGBM模型参数 2 def objective(trial, X, y): 3 # 参数网格 4 param_grid = { 5 "n_estimators": trial.suggest_int("n_estimators", 100, 1000, step=100), 6 "learning_rate": trial.suggest_float("learning_rate", 0.01, 0.3), 7 "num_leaves": trial.suggest_int("num_leaves", 20, 250, step=10), 8 "max_depth": trial.suggest_int("max_depth", -1, 8, step=1), 9 "min_data_in_leaf": trial.suggest_int("min_data_in_leaf", 50, 300, step=50), 10 "lambda_l1": trial.suggest_int("lambda_l1", 0, 50, step=5), 11 "lambda_l2": trial.suggest_int("lambda_l2", 0, 50, step=5), 12 "min_gain_to_split": trial.suggest_float("min_gain_to_split", 0, 15), 13 "bagging_fraction": trial.suggest_float("bagging_fraction", 0.2, 0.95, step=0.1), 14 "bagging_freq": trial.suggest_categorical("bagging_freq", [1]), 15 "feature_fraction": trial.suggest_float("feature_fraction", 0.2, 0.95, step=0.1), 16 "random_state": 2021, 17 'early_stopping_rounds': 200, 18 'num_class': 11, 19 'verbose': -1, 20 'metric': 'multi_logloss' 21 } 22 # 5折交叉验证 23 cv = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=1121218) 24 25 cv_scores = np.empty(5) 26 for idx, (train_idx, test_idx) in enumerate(cv.split(X, y)): 27 X_train, X_test = X.iloc[train_idx], X.iloc[test_idx] 28 y_train, y_test = y[train_idx], y[test_idx] 29 30 # LGBM建模 31 model = lgb.LGBMClassifier(objective="multiclass", **param_grid) 32 model.fit( 33 X_train, 34 y_train, 35 eval_set=[(X_test, y_test)], 36 eval_metric=Accuracy_score, 37 callbacks=[ 38 LightGBMPruningCallback(trial, 'accuracy') 39 ], 40 ) 41 # 模型预测 42 preds = model.predict(X_test) 43 print(preds) 44 # 优化指标logloss最小 45 # try: 46 # cv_scores[idx] = log_loss(y_test, preds) 47 # except Exception as e: 48 # print(str(e)) 49 # return 100.0 50 # 优化指标accuracy_score最大 51 cv_scores[idx] = accuracy_score(y_test, preds) 52 53 return np.mean(cv_scores) 54 # study = optuna.create_study(direction="minimize", study_name="LGBM Classifier") 55 # maximize 56 study = optuna.create_study(direction="maximize", study_name="LGBM Classifier") 57 58 func = lambda trial: objective(trial, X, y) 59 study.optimize(func, n_trials=20)






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)