Logistic Regression and Newton's Method
Data
For this exercise, suppose that a high school has a dataset representing 40 students who were admitted to college and 40 students who were not admitted. Each training example contains a student's score on two standardized exams and a label of whether the student was admitted.
Your task is to build a binary classification model that estimates college admission chances based on a student's scores on two exams. In your training data,
a. The first column of your x array represents all Test 1 scores, and the second column represents all Test 2 scores.
b. The y vector uses '1' to label a student who was admitted and '0' to label a student who was not admitted.
Plot the data
Load the data for the training examples into your program and add the
intercept term into your x matrix.
Before beginning Newton's Method, we will first plot the data using different symbols to represent the two classes. In Matlab/Octave, you can separate the positive class and the negative class using the find command:
% find returns the indices of the % rows meeting the specified condition pos = find(y == 1); neg = find(y == 0); % Assume the features are in the 2nd and 3rd % columns of x plot(x(pos, 2), x(pos,3), '+'); hold on plot(x(neg, 2), x(neg, 3), 'o')Your plot should look like the following:
Newton's Method
在logistic regression问题中,logistic函数表达式如下:
这样做的好处是可以把输出结果压缩到0~1之间。而在logistic回归问题中的损失函数与线性回归中的损失函数不同,这里定义的为:
如果采用牛顿法来求解回归方程中的参数,则参数的迭代公式为:
其中一阶导函数和hessian矩阵表达式如下:
code
% Exercise 4 -- Logistic Regression clear all; close all; clc x = load('ex4x.dat'); y = load('ex4y.dat'); [m, n] = size(x); % Add intercept term to x x = [ones(m, 1), x]; % Plot the training data % Use different markers for positives and negatives figure pos = find(y); neg = find(y == 0);%find是找到的一个向量,其结果是find函数括号值为真时的值的编号 plot(x(pos, 2), x(pos,3), '+') hold on plot(x(neg, 2), x(neg, 3), 'o') hold on xlabel('Exam 1 score') ylabel('Exam 2 score') % Initialize fitting parameters theta = zeros(n+1, 1); % Define the sigmoid function 匿名函数 g = inline('1.0 ./ (1.0 + exp(-z))'); % Newton's method MAX_ITR = 7; J = zeros(MAX_ITR, 1); for i = 1:MAX_ITR % Calculate the hypothesis function z = x * theta; h = g(z);%转换成logistic函数 % Calculate gradient and hessian. % The formulas below are equivalent to the summation formulas % given in the lecture videos. grad = (1/m).*x' * (h-y);%梯度的矢量表示法 H = (1/m).*x' * diag(h) * diag(1-h) * x;%hessian矩阵的矢量表示法 % Calculate J (for testing convergence) J(i) =(1/m)*sum(-y.*log(h) - (1-y).*log(1-h));%损失函数的矢量表示法 theta = theta - H\grad;%是这样子的吗? end % Display theta theta % Calculate the probability that a student with % Score 20 on exam 1 and score 80 on exam 2 % will not be admitted prob = 1 - g([1, 20, 80]*theta) %画出分界面 % Plot Newton's method result % Only need 2 points to define a line, so choose two endpoints plot_x = [min(x(:,2))-2, max(x(:,2))+2]; % Calculate the decision boundary line,plot_y的计算公式见博客下面的评论。 plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x +theta(1)); plot(plot_x, plot_y) legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted', 'Decision Boundary') hold off % Plot J figure plot(0:MAX_ITR-1, J, 'o--', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'r', 'MarkerSize', 8) xlabel('Iteration'); ylabel('J') % Display J J
matlab
diag函数功能:矩阵对角元素的提取和创建对角阵
设以下X为方阵,v为向量
1、X = diag(v,k)当v是一个含有n个元素的向量时,返回一个n+abs(k)阶方阵X,向量v在矩阵X中的第k个对角线上,k=0表示主对角线,k>0表示在主对角线上方,k<0表示在主对角线下方。例1:
v=[1 2 3];
diag(v, 3)ans =
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 2 0
0 0 0 0 0 3
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0注:从主对角矩阵上方的第三个位置开始按对角线方向产生数据的
例2:
v=[1 2 3];
diag(v, -1)
ans =
0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0
0 2 0 0
0 0 3 0注:从主对角矩阵下方的第一个位置开始按对角线方向产生数据的
2、X = diag(v)
向量v在方阵X的主对角线上,类似于diag(v,k),k=0的情况。
例3:
v=[1 2 3];
diag(v)ans =
1 0 0
0 2 0
0 0 3注:写成了对角矩阵的形式
3、v = diag(X,k)
返回列向量v,v由矩阵X的第k个对角线上的元素形成
例4:
v=[1 0 3;2 3 1;4 5 3];
diag(v,1)ans =
0
1注:把主对角线上方的第一个数据作为起始数据,按对角线顺序取出写成列向量形式
4、v = diag(X)返回矩阵X的主对角线上的元素,类似于diag(X,k),k=0的情况例5:
v=[1 0 0;0 3 0;0 0 3];
diag(v)ans =
1
3
3或改为:
v=[1 0 3;2 3 1;4 5 3];
diag(v)ans =
1
3
3注:把主对角线的数据取出写成列向量形式
5、diag(diag(X))
取出X矩阵的对角元,然后构建一个以X对角元为对角的对角矩阵。
例6:X=[1 2;3 4]
diag(diag(X))X =
1 2
3 4ans =
1 0
0 4


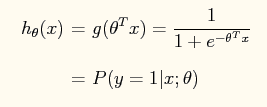
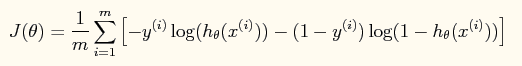
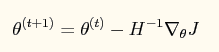


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号