字符流
使用字节流该如何正确地读出中文:
try (FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("a.txt")) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
}
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) {
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
// 该构造方法有解码功能
this.value = StringCoding.decode(bytes, offset, length);
}
// StringCoding.decode() 方法调用的 defaultCharset() 方法
public static Charset defaultCharset() {
if (defaultCharset == null) {
synchronized (Charset.class) {
if (cs != null)
defaultCharset = cs;
else
// 默认编码是UTF-8
defaultCharset = forName("UTF-8");
}
}
return defaultCharset;
}
static char[] decode(byte[] ba, int off, int len) {
String csn = Charset.defaultCharset().name();
try {
// use charset name decode() variant which provides caching.
return decode(csn, ba, off, len);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException x) {
warnUnsupportedCharset(csn);
}
}
在 Java 中,常用的字符编码有 ASCII、ISO-8859-1、UTF-8、UTF-16 等。其中,ASCII 和 ISO-8859-1 只能表示部分字符,而 UTF-8 和 UTF-16 可以表示所有的 Unicode 字符,包括中文字符。
当我们使用 new String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) 将字节流转换为字符串时,Java 会根据 UTF-8 的规则将每 3 个字节解码为一个中文字符,从而正确地解码出中文。
尽管字节流也有办法解决乱码问题,但不够直接,于是就有了字符流,专门用于处理文本文件(音频、图片、视频等为非文本文件)。
从另一角度来说:字符流 = 字节流 + 编码表
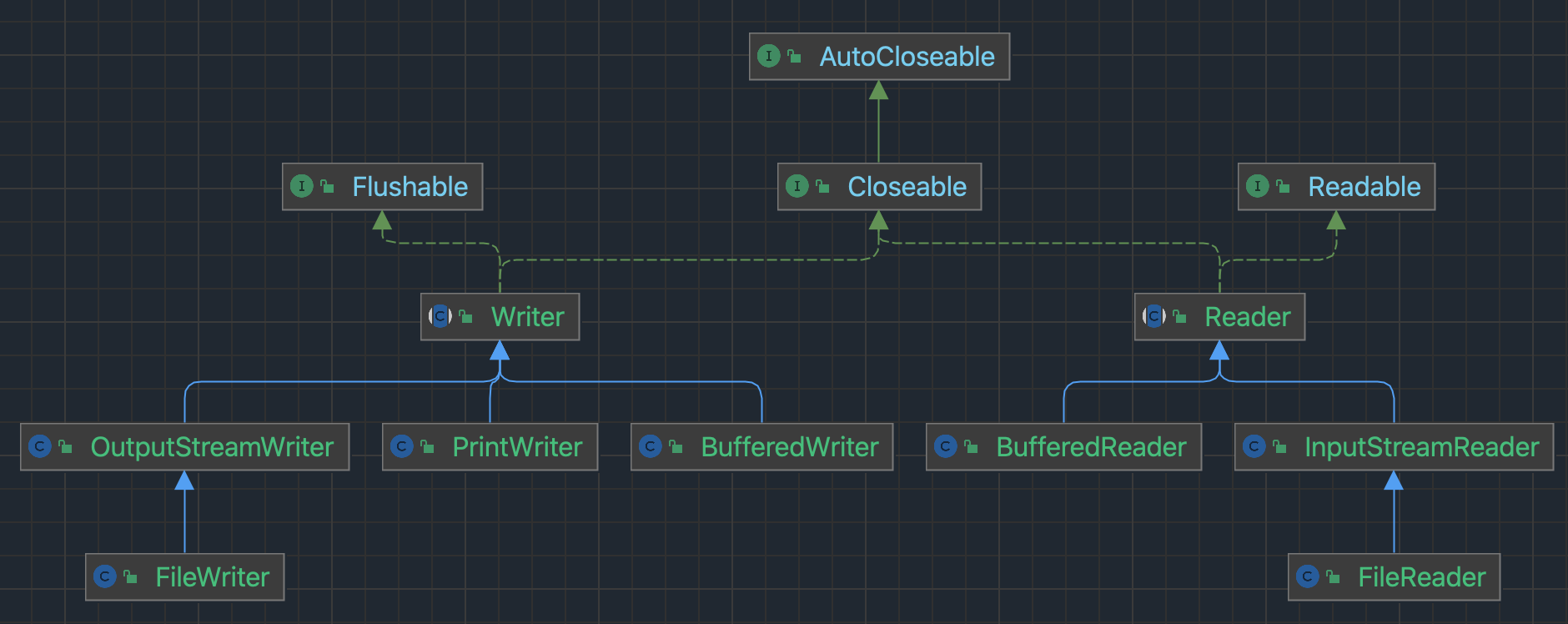
字符输入流 Reader
java.io.Reader是字符输入流的超类(父类),它定义了字符输入流的一些共性方法:
- 1、
close():关闭此流并释放与此流相关的系统资源。 - 2、
read():从输入流读取一个字符。 - 3、
read(char[] cbuf):从输入流中读取一些字符,并将它们存储到字符数组cbuf中
FileReader 是 Reader 的子类,用于从文件中读取字符数据。它的主要特点如下:
- 可以通过构造方法指定要读取的文件路径。
- 每次可以读取一个或多个字符。
- 可以读取 Unicode 字符集中的字符,通过指定字符编码来实现字符集的转换。
FileReader 构造方法
FileReader(File file):创建一个新的 FileReader,参数为File对象。FileReader(String fileName):创建一个新的 FileReader,参数为文件名。
// 使用File对象创建流对象
File file = new File("a.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader("b.txt");
FileReader 读取字符数据
读取字符:read方法
每次可以读取一个字符,返回读取的字符(转为 int 类型),当读取到文件末尾时,返回-1。
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader("abc.txt");
// 定义变量,保存数据
int b;
// 循环读取
while ((b = fr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.println((char)b);
}
// 关闭资源
fr.close();
读取指定长度的字符:read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
将其存储到字符数组中。其中,cbuf 表示存储读取结果的字符数组,off 表示存储结果的起始位置,len 表示要读取的字符数。
File textFile = new File("docs/约定.md");
// 给一个 FileReader 的示例
// try-with-resources FileReader
try(FileReader reader = new FileReader(textFile);) {
// read(char[] cbuf)
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = reader.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, len));
}
}
FileReader 实现了 AutoCloseable 接口,因此可以使用 try-with-resources 语句自动关闭资源,避免了手动关闭资源的繁琐操作。
字符输出流 Writer
java.io.Writer 是字符输出流类的超类(父类),可以将指定的字符信息写入到目的地,来看它定义的一些共性方法:
- 1、
write(int c)写入单个字符。 - 2、
write(char[] cbuf)写入字符数组。 - 3、
write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)写入字符数组的一部分,off为开始索引,len为字符个数。 - 4、
write(String str)写入字符串。 - 5、
write(String str, int off, int len)写入字符串的某一部分,off 指定要写入的子串在 str 中的起始位置,len 指定要写入的子串的长度。 - 6、
flush()刷新该流的缓冲。 - 7、
close()关闭此流,但要先刷新它。
java.io.FileWriter 类是 Writer 的子类,用来将字符写入到文件。
FileWriter 构造方法
FileWriter(File file): 创建一个新的 FileWriter,参数为要读取的File对象。FileWriter(String fileName): 创建一个新的 FileWriter,参数为要读取的文件的名称。
// 第一种:使用File对象创建流对象
File file = new File("a.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
// 第二种:使用文件名称创建流对象
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.txt");
FileWriter 写入数据
写入字符:write(int b) 方法
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("output.txt");
fw.write(72); // 写入字符'H'的ASCII码
fw.write(101); // 写入字符'e'的ASCII码
fw.write(108); // 写入字符'l'的ASCII码
fw.write(108); // 写入字符'l'的ASCII码
fw.write(111); // 写入字符'o'的ASCII码
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fw != null) {
fw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
写入字符数组:write(char[] cbuf) 方法
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("output.txt");
char[] chars = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
fw.write(chars); // 将字符数组写入文件
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fw != null) {
fw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
写入指定字符数组:write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) 方法
fw = new FileWriter("output.txt");
char[] chars = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ',', ' ', 'W', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd', '!'};
fw.write(chars, 0, 5); // 将字符数组的前 5 个字符写入文件
写入字符串:write(String str) 方法
fw = new FileWriter("output.txt");
String str = "xx";
fw.write(str); // 将字符串写入文件
写入指定字符串:write(String str, int off, int len) 方法
String str = "xxxxxxx";
try (FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("output.txt")) {
fw.write(str, 0, 5); // 将字符串的前 5 个字符写入文件
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
关闭 close 和刷新 flush
因为 FileWriter 内置了缓冲区 ByteBuffer,所以如果不关闭输出流,就无法把字符写入到文件中。
flush :刷新缓冲区,流对象可以继续使用。
close :先刷新缓冲区,然后通知系统释放资源。流对象不可以再被使用了。
文本文件复制
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建输入流对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader("aa.txt");// 文件不存在会抛出java.io.FileNotFoundException
// 创建输出流对象
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("copyaa.txt");
/*创建输出流做的工作:
* 1、调用系统资源创建了一个文件
* 2、创建输出流对象
* 3、把输出流对象指向文件
* */
// 文本文件复制,一次读一个字符
copyMethod1(fr, fw);
// 文本文件复制,一次读一个字符数组
copyMethod2(fr, fw);
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
public static void copyMethod1(FileReader fr, FileWriter fw) throws IOException {
int ch;
while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) {//读数据
fw.write(ch);//写数据
}
fw.flush();
}
public static void copyMethod2(FileReader fr, FileWriter fw) throws IOException {
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) {//读数据
fw.write(chs, 0, len);//写数据
}
fw.flush();
}
}
IO 异常的处理
在学习的过程中可能习惯把异常抛出,而实际开发中建议使用try...catch...finally 代码块,处理异常部分,格式代码如下:
// 声明变量
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//创建流对象
fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");
// 写出数据
fw.write("xxx");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fw != null) {
fw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
或者直接使用 try-with-resources 的方式:
try (FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt")) {
// 写出数据
fw.write("xxx");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try-with-resources 会在 try 块执行完毕后自动关闭 FileWriter 对象 fw,不需要手动关闭流。如果在 try 块中发生了异常,也会自动关闭流并抛出异常。因此,使用 try-with-resources 可以让代码更加简洁、安全和易读。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号