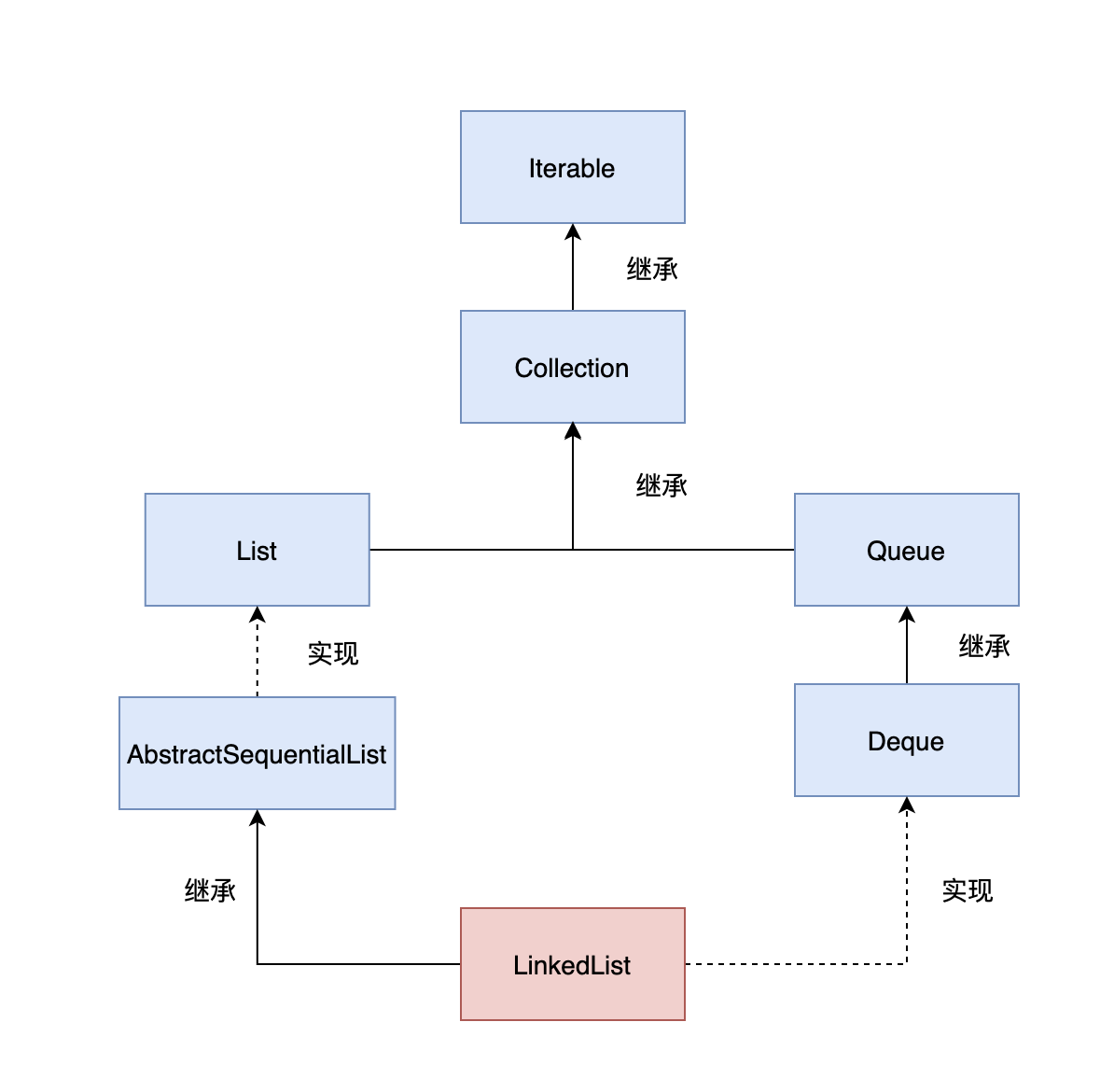
| private static class Node<E> { |
| E item; |
| |
| Node<E> next; |
| Node<E> prev; |
| |
| Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { |
| this.item = element; |
| this.next = next; |
| this.prev = prev; |
| } |
| } |
添加元素
| public boolean add(E e) { |
| linkLast(e); |
| return true; |
| } |
| public void addLast(E e) { |
| linkLast(e); |
| } |
| |
| void linkLast(E e) { |
| |
| final Node<E> l = last; |
| |
| final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); |
| |
| last = newNode; |
| if (l == null) |
| |
| first = newNode; |
| else |
| |
| l.next = newNode; |
| |
| size++; |
| modCount++; |
| } |
| public void addFirst(E e) { |
| linkFirst(e); |
| } |
| |
| private void linkFirst(E e) { |
| final Node<E> f = first; |
| final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); |
| first = newNode; |
| if (f == null) |
| last = newNode; |
| else |
| f.prev = newNode; |
| size++; |
| modCount++; |
| } |
删除元素
remove():删除第一个节点removeFirst():删除第一个节点removeLast():删除最后一个节点
| public E remove() { |
| return removeFirst(); |
| } |
| public E removeFirst() { |
| final Node<E> f = first; |
| if (f == null) |
| throw new NoSuchElementException(); |
| return unlinkFirst(f); |
| } |
| |
| private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { |
| |
| |
| final E element = f.item; |
| |
| final Node<E> next = f.next; |
| |
| f.item = null; |
| f.next = null; |
| |
| first = next; |
| if (next == null) |
| |
| last = null; |
| else |
| |
| next.prev = null; |
| |
| size--; |
| modCount++; |
| |
| return element; |
| } |
| public E remove(int index) { |
| |
| checkElementIndex(index); |
| return unlink(node(index)); |
| } |
| |
| private void checkElementIndex(int index) { |
| if (!isElementIndex(index)) |
| throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); |
| } |
| |
| private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { |
| return index >= 0 && index < size; |
| } |
| E unlink(Node<E> x) { |
| |
| final E element = x.item; |
| final Node<E> next = x.next; |
| final Node<E> prev = x.prev; |
| |
| |
| if (prev == null) { |
| first = next; |
| } else { |
| prev.next = next; |
| x.prev = null; |
| } |
| |
| |
| if (next == null) { |
| last = prev; |
| } else { |
| next.prev = prev; |
| x.next = null; |
| } |
| |
| x.item = null; |
| size--; |
| modCount++; |
| return element; |
| } |
| |
| public boolean remove(Object o) { |
| if (o == null) { |
| for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { |
| |
| if (x.item == null) { |
| unlink(x); |
| return true; |
| } |
| } |
| } else { |
| for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { |
| |
| if (o.equals(x.item)) { |
| unlink(x); |
| return true; |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| return false; |
| } |
修改元素
| public E set(int index, E element) { |
| checkElementIndex(index); |
| Node<E> x = node(index); |
| E oldVal = x.item; |
| |
| x.item = element; |
| |
| return oldVal; |
| } |
| |
| Node<E> node(int index) { |
| |
| |
| if (index < (size >> 1)) { |
| |
| Node<E> x = first; |
| for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) |
| x = x.next; |
| return x; |
| } else { |
| |
| Node<E> x = last; |
| for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) |
| x = x.prev; |
| return x; |
| } |
| } |
查找元素
indexOf(Object):查找某个元素所在的位置
| |
| public int indexOf(Object o) { |
| int index = 0; |
| if (o == null) { |
| for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { |
| if (x.item == null) |
| return index; |
| index++; |
| } |
| } else { |
| |
| for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { |
| if (o.equals(x.item)) |
| return index; |
| index++; |
| } |
| } |
| return -1; |
| } |
| public E get(int index) { |
| checkElementIndex(index); |
| return node(index).item; |
| } |
序列化
| private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) |
| throws java.io.IOException { |
| |
| |
| s.defaultWriteObject(); |
| |
| |
| |
| s.writeInt(size); |
| |
| |
| |
| for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) |
| s.writeObject(x.item); |
| } |
| private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) |
| throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { |
| |
| |
| s.defaultReadObject(); |
| |
| |
| |
| int size = s.readInt(); |
| |
| |
| for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) |
| |
| linkLast((E)s.readObject()); |
| } |
- 遍历 LinkedList 的时候,千万不要使用 for 循环,要使用迭代器。
对比ArrayList
本文作者:n1ce2cv
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sprinining/p/18300964
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步