浅拷贝深拷贝1
浅克隆
- 被复制对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,而所有的对其他对象的引用仍然指向原来的对象。即对象的浅拷贝会对“主”对象进行拷贝,但不会复制主对象里面的对象。”里面的对象“会在原来的对象和它的副本之间共享。浅拷贝仅仅复制所考虑的对象,而不复制它所引用的对象。
class Score { private int Math; private int English; private StringBuffer stringBuffer; // get、set、构造器、toString } class Student implements Cloneable { private String name; private StringBuilder stringBuilder; private int age; private Integer integer; private List<String> list; private Score score; private int[] arry; // get、set、构造器、toString @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("xixi"); list.add("haha"); list.add("enen"); List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); list2.add("嘻嘻"); list2.add("哈哈"); list2.add("嗯嗯"); StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append("jjj"); StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(); stringBuffer.append("enenen"); int[] array = {1,2,3}; Score score = new Score(11, 11, stringBuffer); Student student1 = new Student("哈哈", stringBuilder, 21, 10, list, score, array); Student student2 = (Student) student1.clone(); Student student3 = student1; // 和student1是同一个对象 System.out.println("student1.hashCode:" + student1.hashCode()); System.out.println("student2.hashCode:" + student2.hashCode()); System.out.println("student3.hashCode:" + student3.hashCode()); System.out.println("student1初始值:" + student1); System.out.println("student2初始值:" + student2); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------"); System.out.println("修改student1后:"); // String被final修饰,属于不变的引用类型,深拷贝,改变他的值就会new出新对象 student1.setName("呵呵"); System.out.println("student1.name.hashCode:" + student1.getName().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2.name.hashCode:" + student2.getName().hashCode()); // StringBuilder是可变引用类型,浅拷贝 stringBuilder.append("kkk"); System.out.println("student1.stringBuilder.hashCode:" + student1.getStringBuilder().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2.stringBuilder.hashCode:" + student2.getStringBuilder().hashCode()); student1.getScore().getStringBuffer().append("aaaa"); System.out.println("student1.score.stringBuffer.hashCode:" + student1.getScore().getStringBuffer().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2.score.stringBuffer.hashCode:" + student2.getScore().getStringBuffer().hashCode()); // 8种基本数据类型都是深拷贝 student1.setAge(99); System.out.println("student1.age:" + student1.getAge()); System.out.println("student2.age:" + student2.getAge()); /** * // integer的值是不可变的 * private final int value; * * // integer.hashCode()返回的就是integer的值 * @Override public int hashCode() { * return Integer.hashCode(value); * } * public static int hashCode(int value) { * return value; * } * * 所有的包装类型都是不变的引用类型,包装类型直接就是深克隆 */ // student1.setInteger(new Integer(99)); student1.setInteger(99); // 和new Integer(99)效果一样,都是一个新的Integer System.out.println("student1.integer.hashCode:" + student1.getInteger().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2.integer.hashCode:" + student2.getInteger().hashCode()); // student1.setList(list2); // 直接把student1的list对象换成一个新new出来的对象,hashCode不一样, student1.getList().set(0, "哦"); // 对原来的list对象修改,student2和student1共用一个list对象,student2的list也会改 student1.getList().set(1, "嗯"); student1.getList().set(2, "啊"); System.out.println("student1.list.hashCode:" + student1.getList().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2.list.hashCode:" + student2.getList().hashCode()); // 数组也是可变引用对象 student1.getArry()[0] = 9; student1.getArry()[1] = 9; student1.getArry()[2] = 9; System.out.println("student1.array.hashCode:" + student1.getArry().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2.array:hashCode:" + student2.getArry().hashCode()); // student1.setScore(new Score(99,99)); student1.getScore().setMath(99); student1.getScore().setEnglish(99); System.out.println("student1.score.hashCode:" + student1.getScore().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2.score.hashCode:" + student2.getScore().hashCode()); System.out.println(student1); System.out.println(student2); } }
- 运行结果
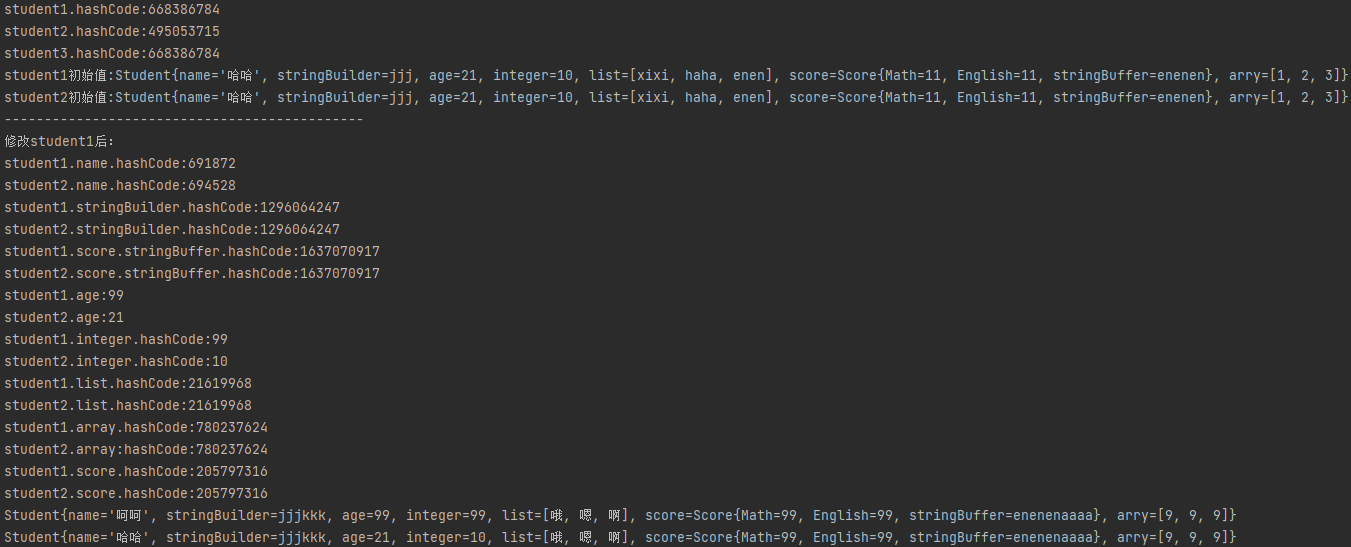
- 8种基本类型和不可变的引用类型(被final修饰的包括String,8种包装类型)都是深拷贝。改变值都是新new出一个对象。
深克隆
- 使Score实现Cloneable接口,重写clone()
@Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Score score = (Score) super.clone(); // 只需要对stringBuffer处理,int本来就是深拷贝,不用处理 score.stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(); score.stringBuffer.append(this.stringBuffer.toString()); return score; }
- 修改Student.clone()
@Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student = (Student) super.clone(); // 深拷贝stringBuilder student.stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); student.stringBuilder.append(this.stringBuilder.toString()); // 深拷贝list student.list = new ArrayList<>(); student.list.addAll(list); // 深拷贝score student.score = (Score) this.score.clone(); // 深拷贝array student.arry = new int[this.arry.length]; for (int i = 0; i < this.arry.length; i++) { student.arry[i] = this.arry[i]; } return student; }
- 运行结果
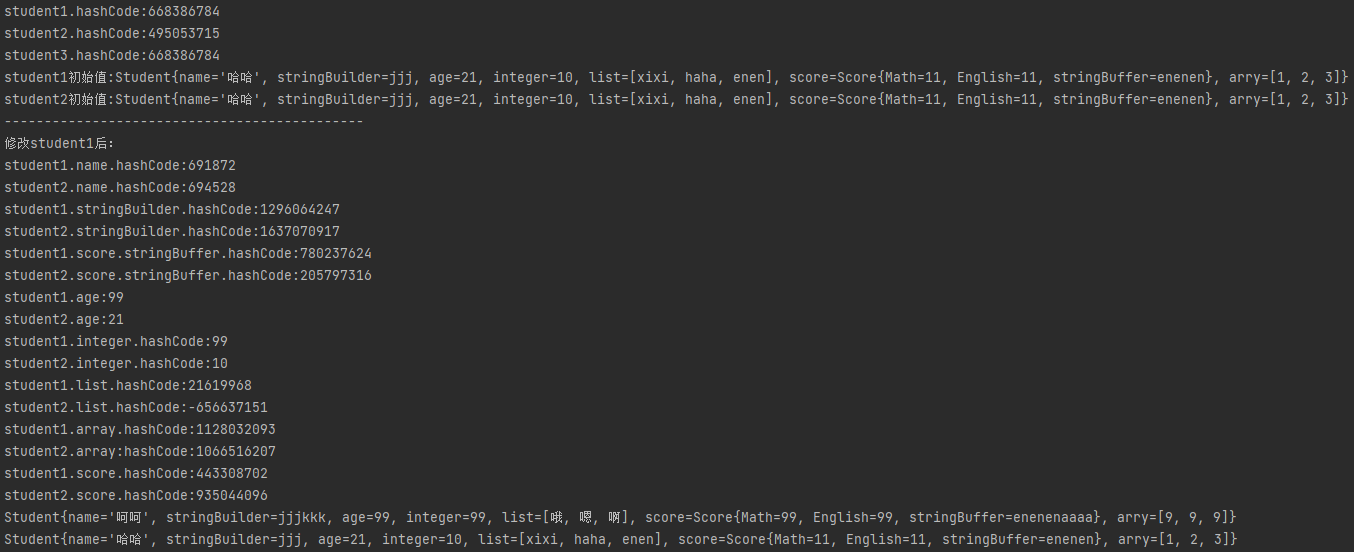
- 可变引用类型都是浅拷贝。要深拷贝这个类需要在clone()方法里对类的所有可变引用型的对员,都重新new出一个对象,把原来的值赋给新的对象,返回新对象。
本文作者:n1ce2cv
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sprinining/p/15292456.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步