C#(99):串口编程 System.IO.Ports.SerialPort类
从Microsoft .Net 2.0版本以后,就默认提供了System.IO.Ports.SerialPort类,用户可以非常简单地编写少量代码就完成串口的信息收发程序。
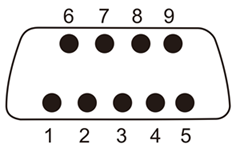
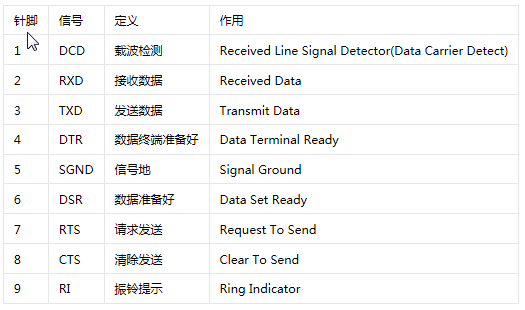
1. 串口硬件信号定义
DB9 Connector 信号定义。串口测试将2、3针脚短接即可。
2、串口端口号搜索
string[] portList = System.IO.Ports.SerialPort.GetPortNames(); for (int i = 0; i < portList.Length; i++) { string name = portList[i]; comboBox.Items.Add(name); }
还有一种通过调用API的方法来获取实现,可以获取详细的完整串口名称,对于USB-to-COM虚拟串口来说特别适用。
3、串口属性参数设置
SerialPort mySerialPort = new SerialPort("COM2");//端口 mySerialPort.BaudRate = 9600;//波特率 mySerialPort.Parity = Parity.None;//校验位 mySerialPort.StopBits = StopBits.One;//停止位 mySerialPort.DataBits = 8;//数据位 mySerialPort.Handshake = Handshake.Non; mySerialPort.ReadTimeout = 1500; mySerialPort.DtrEnable = true;//启用数据终端就绪信息 mySerialPort.Encoding = Encoding.UTF8; mySerialPort.ReceivedBytesThreshold = 1;//DataReceived触发前内部输入缓冲器的字节数 mySerialPort.DataReceived += new SerialDataReceivedEvenHandler(DataReceive_Method); mySerialPort.Open();
4、串口发送信息
- Write(Byte[], Int32, Int32) :将指定数量的字节写入串行端口
- Write(Char[], Int32, Int32) :将指定数量的字符写入串行端口
- Write(String) :将指定的字符串写入串行端口
- WriteLine(String) :将指定的字符串和NewLine值写入输出缓冲区
// Write a string port.Write("Hello World"); // Write a set of bytes port.Write(new byte[] { 0x0A, 0xE2, 0xFF }, 0, 3); // Close the port port.Close();
5. 串口接收信息
- Read(Byte[], Int32, Int32):从SerialPort输入缓冲区读取一些字节,并将那些字节写入字节数组中指定的偏移量处
- ReadByte():从SerialPort输入缓冲区中同步读取一个字节
- ReadChar(): 从SerialPort输入缓冲区中同步读取一个字符
- ReadExisting() :在编码的基础上,读取SerialPort对象的流和输入缓冲区中所有立即可用的字节
- ReadLine() :一直读取到输入缓冲区中的NewLine值
- ReadTo(String) :一直读取到输入缓冲区中的指定value的字符串
string serialReadString;
private void port_DataReceived(object sender, SerialDataReceivedEventArgs e) { serialReadString = port.ReadExisting()); this.txt1.Invoke( new MethodInvoker(delegate { this.txt1.AppendText(serialReadString); })); }
6、循环接收数据
void com_DataReceived(object sender, SerialDataReceivedEventArgs e) { // Use either the binary OR the string technique (but not both) // Buffer and process binary data while (com.BytesToRead > 0) bBuffer.Add((byte)com.ReadByte()); ProcessBuffer(bBuffer); // Buffer string data sBuffer += com.ReadExisting(); ProcessBuffer(sBuffer); } private void ProcessBuffer(string sBuffer) { // Look in the string for useful information // then remove the useful data from the buffer } private void ProcessBuffer(List<byte> bBuffer) { // Look in the byte array for useful information // then remove the useful data from the buffer }
posted on 2020-05-27 18:55 springsnow 阅读(8978) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报