常用模块及其使用
一、collctions模块
1.namedtuple
可以表示点的坐标,并且具有名称。
1 from collections import namedtuple 2 point = namedtuple('坐标',['x','y','z']) #第二个参数可以传迭代对象 3 point1 = namedtuple('坐标','x y z') #第二个参数也可以传字符串,但是中间要用空格隔开 4 p = point(1,3,5) 5 p1 = point(2,4,6) 6 print(p) 7 print(p1) 8 print(p.x) 9 print(p.y) 10 print(p.z)
2.queue
2.1 队列先进先出(FIFO)
import queue q = queue.Queue() #生成队列对象 q.put('first') #往队列中添加值 q.put('second') q.put('third') print(q.get()) #向队列要值 print(q.get()) print(q.get()) print(q.get()) #如果队列中的值取完了,程序会在原地等待,直到从队列中拿到值才停止
2.2 deque双端队列
1 from collections import deque 2 q = deque(['a','b','c']) 3 q.append(1) #从尾部插入 4 q.appendleft(2) #插入双端队列的左端 5 print(q.pop()) #从尾部弹出 6 print(q.popleft()) #从左边尾部弹出 7 print(q.popleft()) #从左边尾部弹出
3.ordererdict
1 from collections import OrderedDict 2 order_d = OrderedDict([('a',1),('b',2),('c',3)]) 3 print(order_d) 4 5 order_d1 = OrderedDict() 6 order_d1['x'] = 1 7 order_d1['y'] = 2 8 order_d1['z'] = 3 9 print(order_d1) 10 11 for i in order_d1: 12 print(order_d1[i])
4.defaultdict
习题:在列表[11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]中,将大于66的数,放入关键字k1中,小于等于66的数放入关键字k2中。
1 from collections import defaultdict 2 3 values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] 4 my_dict = defaultdict(list) #后续该字典中新建的key对应的value默认就是列表 5 for i in values: 6 if i > 66: 7 my_dict['k1'].append(i) 8 else: 9 my_dict['k2'].append(i) 10 print(my_dict)
5.counter
用来统某个字符出现的次数,这样我们在统计一个字符出现次数的时候会方便很多
1 from collections import Counter 2 s = 'asdaefqdasdawfasdw' 3 res = Counter(s) 4 print(res)
二、时间模块
1.时间戳
2.格式化时间(用来展示给人看的)
3.结构化时间
1 import time 2 3 print(time.time()) #1563447223.4735847 4 print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')) #2019-07-18 5 print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')) #2019-07-18 18:53:43 6 print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %X')) #等价于%H:%M:%S 7 print(time.strftime('%H:%M')) #18:53 8 print(time.strftime('%Y/%m')) #2019/07
1.localtime()
1 import time 2 print(time.localtime()) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2019, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=18, tm_hour=19, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=199, tm_isdst=0) 3 print(time.localtime(time.time())) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2019, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=18, tm_hour=19, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=199, tm_isdst=0) 4 res = time.localtime(time.time()) 5 print(time.mktime(res)) #1563447600.0 6 print(time.strftime('%Y-%m',time.localtime())) #2019-07 7 print(time.strptime(time.strftime('%Y-%m',time.localtime()),'%Y-%m')) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2019, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=1, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=182, tm_isdst=-1)
2.datetime()
1 import datetime 2 print(datetime.date.today()) #date>>>:年月日 3 print(datetime.datetime.today()) #datetime>>>:年月日 时分秒 4 res = datetime.date.today() 5 print(res.year) #2019 6 print(res.month) #7 7 print(res.day) #18 8 print(res.weekday()) # 0-6表示星期 0表示周一 9 print(res.isoweekday()) # 1-7表示星期 1表示周一
日期对象 = 日期对象 +/- timedelta对象
timedelta对象 = 日期对象 +/- 日期对象
1 import datetime 2 current_time = datetime.date.today() 3 timetel_t = datetime.timedelta(days=7) 4 res1 = current_time + timetel_t 5 print(current_time - timetel_t) #2019-07-11 6 print(res1-current_time) #7 days, 0:00:00
小练习:计算今天距离生日还有多少天
1 import datetime 2 birth = datetime.datetime(2019,11,24,19,25,0) 3 current_date = datetime.datetime.today() 4 print(birth-current_date)
utc时间
1 import datetime 2 3 dt_now = datetime.datetime.now() 4 dt_utcnow = datetime.datetime.utcnow() 5 print(dt_now) 6 print(dt_utcnow)
三、random模块
1 import random 2 3 print(random.randint(1,6)) #随机取一个你提供的整数范围内的数字,包含首尾 4 print(random.random()) #随机取0-1之间的小数 5 print(random.choice([1,2,3,4,5,6])) #摇号性质,随机从列表中取出一个元素 6 res = [1,2,3,4,5,6] 7 random.shuffle(res) #类似于洗牌,将列表中元素顺序打乱 8 print(res)
小练习:生成随机的验证码,5位数的随机验证码,封装成一个函数,用户想生成几位就生成几位
1 import random 2 3 def random_code(n): 4 code = '' 5 for i in range(n): 6 upper_str = chr(random.randint(65,90)) 7 lower_str = chr(random.randint(97,122)) 8 num = str(random.randint(0,9)) 9 code+= random.choice([upper_str,lower_str,num]) 10 return code 11 res = random_code(5) 12 print(res)
四、os模块
os模块:跟操作系统打交道的模块
1 import os 2 BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(__file__) 3 MOVIE_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'老师们的作品ed2k') 4 movie_list = os.listdir(MOVIE_DIR) 5 while True: 6 for i,j in enumerate(movie_list,1): 7 print(i,j) 8 choice = input('老板想看什么啊(今日top1:Rio老师)>>>') 9 if choice.isdigit(): 10 choice = int(choice) 11 if choice in range(1,len(movie_list)+1): 12 get_file = movie_list[choice-1] 13 get_path = os.path.join(MOVIE_DIR,get_file) 14 with open (get_path,'r',encoding='utf-8')as f: 15 print(f.read())
知识点补充:os.path.exist 判断文件是否存在
os.path.isfile 只能判断文件,不能判断文件夹
os.rmdir 只能删除空文件夹
os.getcwd 返回当前所在位置
os.chdir切换当前所在的目录
os.path.getsize 获取文件大小(字节大小)
五、sys模块
sys模块:跟python解释器打交道模块
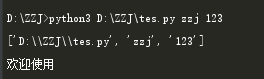
1 import sys 2 print(sys.argv) 3 if len(sys.argv) <=1 : 4 print('请输入用户名和密码') 5 else: 6 username = sys.argv[1] 7 password = sys.argv[2] 8 if username == 'zzj' and password == '123': 9 print('欢迎使用') 10 else: 11 print('用户名不存在,无法执行当前文件')
这里用终端运行:
六、序列化模块
序列:字符串
序列化:其他数据类型转换成字符串的过程
反序列化:字符串转成其他的数据类型
写入文件的数据必须是字符串
基于网络传输的必须是二进制
json模块:所有的语言都支持jason格式
支持的数据类型很少:字符串、列表、字典、整型、元组、布尔值
1 import json 2 d = {'name':'zzj'} 3 res = json.dumps(d) 4 print(res,type(res)) #{"name": "zzj"} <class 'str'> 5 res1 = json.loads(res) 6 print(res1,type(res1)) #{'name': 'zzj'} <class 'dict'>
pickle模块:只支持python
python所有的数据类型都支持
1 import pickle 2 d = {'name':'zzj'} 3 res = pickle.dumps(d) 4 print(res,type(res)) 5 res1 = pickle.loads(res) 6 print(res1,type(res1))
用pickle操作文件的时候,文件的打开模式必须是b模式
1 import pickle 2 d = {'name':'zzj'} 3 with open ('userinfo','wb')as f: 4 pickle.dump(d,f) 5 6 with open ('userinfo','rb')as f: 7 res = pickle.load(f) 8 print(res,type(res))
七、subprocess模块
sub:子
process:进程
1.用户用过网络连接上了你的这台电脑
2.用户输入相应的命令,基于网络发送给了你这台电脑上的某个程序
3.获取用户命令,里面subproces执行该用户命令
4.将执行结果再基于网络发送给用户
while True: cmd = input('cmd>>>:').strip() import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen(cmd,shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE) print(obj) print('正确命令返回的结果stdout',obj.stdout.read().decode('gbk')) print('错误命令返回的提示信息stderr',obj.stderr.read().decode('gbk'))

