Spring——AOP实现
Spring实现AOP
1、什么是 AOP
AOP (Aspect Orient Programming),直译过来就是 面向切面编程。AOP 是一种编程思想,是面向对象编程(OOP)的一种补充。面向对象编程将程序抽象成各个层次的对象,而面向切面编程是将程序抽象成各个切面。
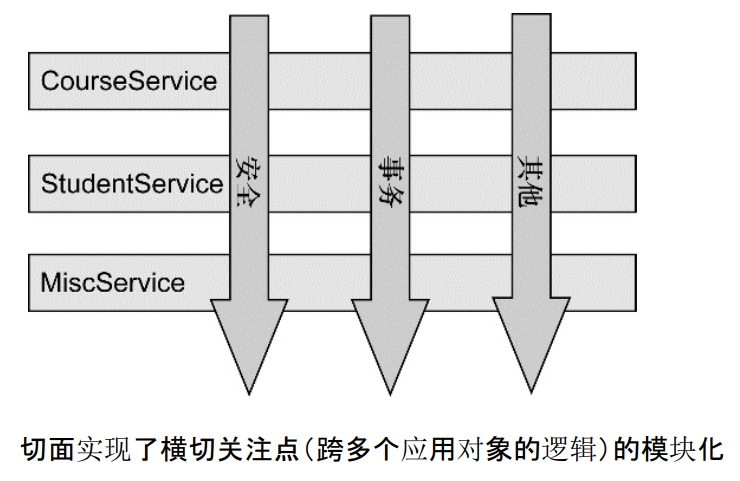
从该图可以很形象地看出,所谓切面,相当于应用对象间的横切点,我们可以将其单独抽象为单独的模块。
2、AOP的实现
【重要】:使用AOP需要导入依赖包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
方式一:使用Spring的API接口【主要SpringAPI接口实现】
-
xml配置:
<!--注册bean--> <bean id="userService" class="com.spong.demo03.UserServiceImpl"/> <bean id="logBefore" class="com.spong.demo03.LogBefore"/> <bean id="logAfter" class="com.spong.demo03.LogAfter"/> <!--方式一: 使用原生的Spring API接口--> <!--配置aop:需要导入aop的约束--> <aop:config> <!--切入点:expression:表达式,execution(要执行的位置: * * * ...)--> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.spong.demo03.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <!--执行环绕增加--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="logAfter" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="logBefore" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:config> -
需要切入的类(实现aop包下的接口MethodBeforeAdvice、AfterReturningAdvice等)
public class LogBefore implements MethodBeforeAdvice { /** * * @param method 要执行的目标对象的方法 * @param objects 方法参数 * @param o 目标对象 * @throws Throwable */ public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable { System.out.println(o.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"执行"); } }public class LogAfter implements AfterReturningAdvice { /** * * @param returnValue 方法执行后的返回值 * @param method * @param args * @param target * @throws Throwable */ public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"方法执行,返回值为"+returnValue); } }
方式二:自定义类来实现AOP【主要是切面定义】
-
自定义类:
public class Diy { public void logBefore(){ System.out.println("方法执行前"); } public void logAfter(){ System.out.println("方法执行后"); } } -
xml配置:
<!--方式二: 自定义类--> <bean id="diy" class="com.spong.demo03.Diy"/> <aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="diy"> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.spong.demo03.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <aop:before method="logBefore" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> <aop:after method="logAfter" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
方式三:使用注解实现
-
使用注解实现的切面类:
//使用注解实现AOP @Aspect //标注为一个切面 @Component //注入bean public class AnnotationPointCut { //设置切入点 @Pointcut("execution(* com.spong.demo03.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") private void pointCut(){} @Before("pointCut()") public void logBefore(){ System.out.println("方法执行前"); } @After("pointCut()") public void logAfter(){ System.out.println("方法执行后"); } @Around("pointCut()") //环绕增强,我们可以给定一个参数,代表我们要获取处理切入的点; public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { System.out.println("环绕前"); System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature()); //获得签名(调用了哪个类的哪个方法) Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕后"); } } -
xml配置:
<!--开启aop注解支持--> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <!--开启注解支持--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.spong.demo03"/> <context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config> -
测试类
public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //这里返回的是一个代理类实例,代理类也是实现了UserService接口 UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class); userService.add(); } } -
测试结果:
环绕前 void com.spong.demo03.UserService.add() 方法执行前 add 方法执行后 环绕后
切入点表达式execution (* com.sample.service..*. *(..))解析:
整个表达式可以分为五个部分:
1、execution()::表达式主体。
2、第一个*号:表示返回类型, *号表示所有的类型。
3、包名:表示需要拦截的包名,后面的两个句点表示当前包和当前包的所有子包,com.sample.service包、子孙包下所有类的方法。
4、第二个号:表示类名,号表示所有的类。
5、(..):最后这个星号表示方法名,号表示所有的方法,后面括弧里面表示方法的参数,两个句点表示任何参数
如有错误,欢迎大佬指正!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号