Krylov子空间与Arnoldi过程
一、应用背景
Krylov 子空间方法就是在Krylov子空间中寻找近似解。

二、Krylov子空间

n是原始矩阵的维度,m为降阶后矩阵的维度,通常m<<n。
三、Arnoldi 过程: 计算Km 的一组正交
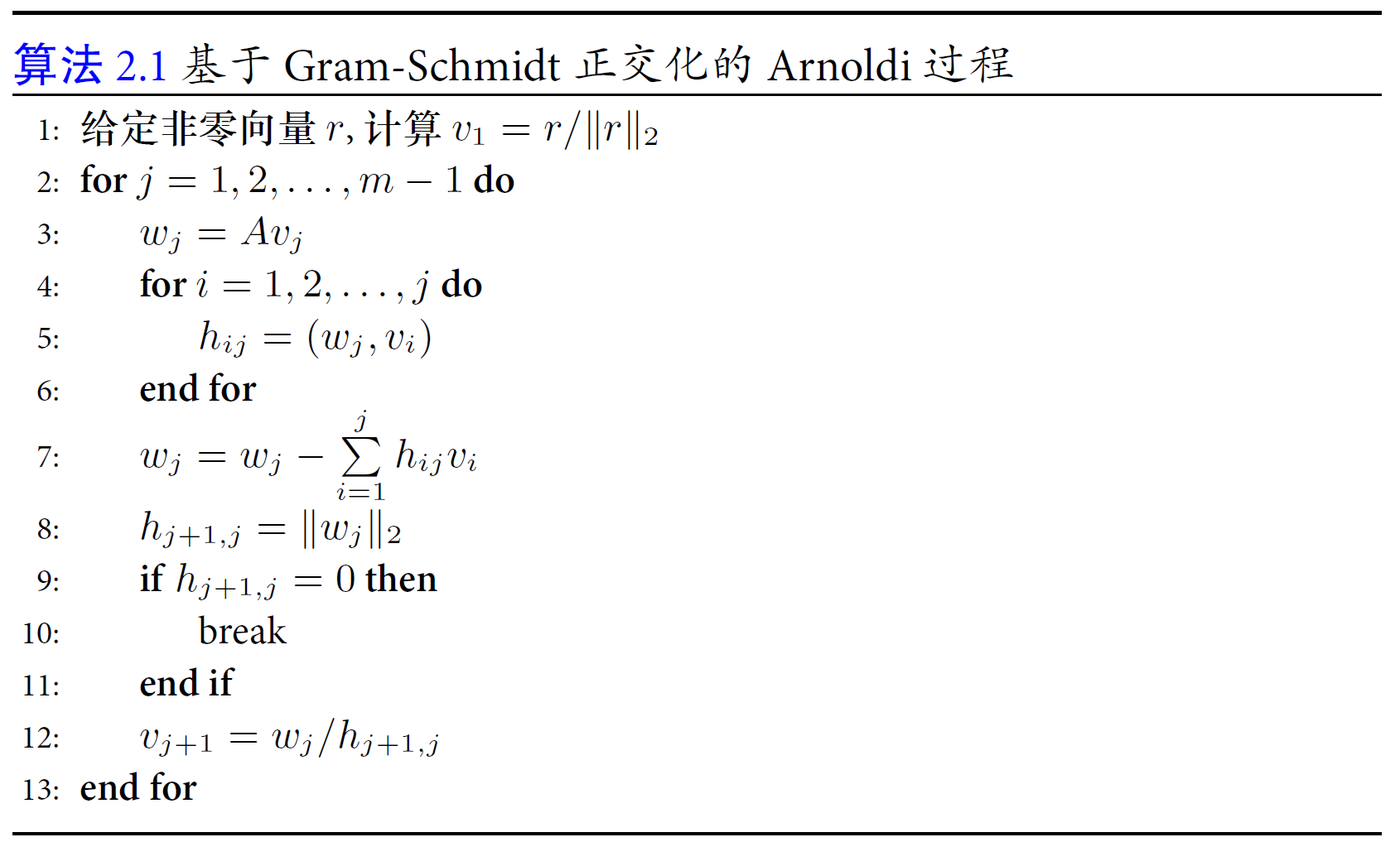
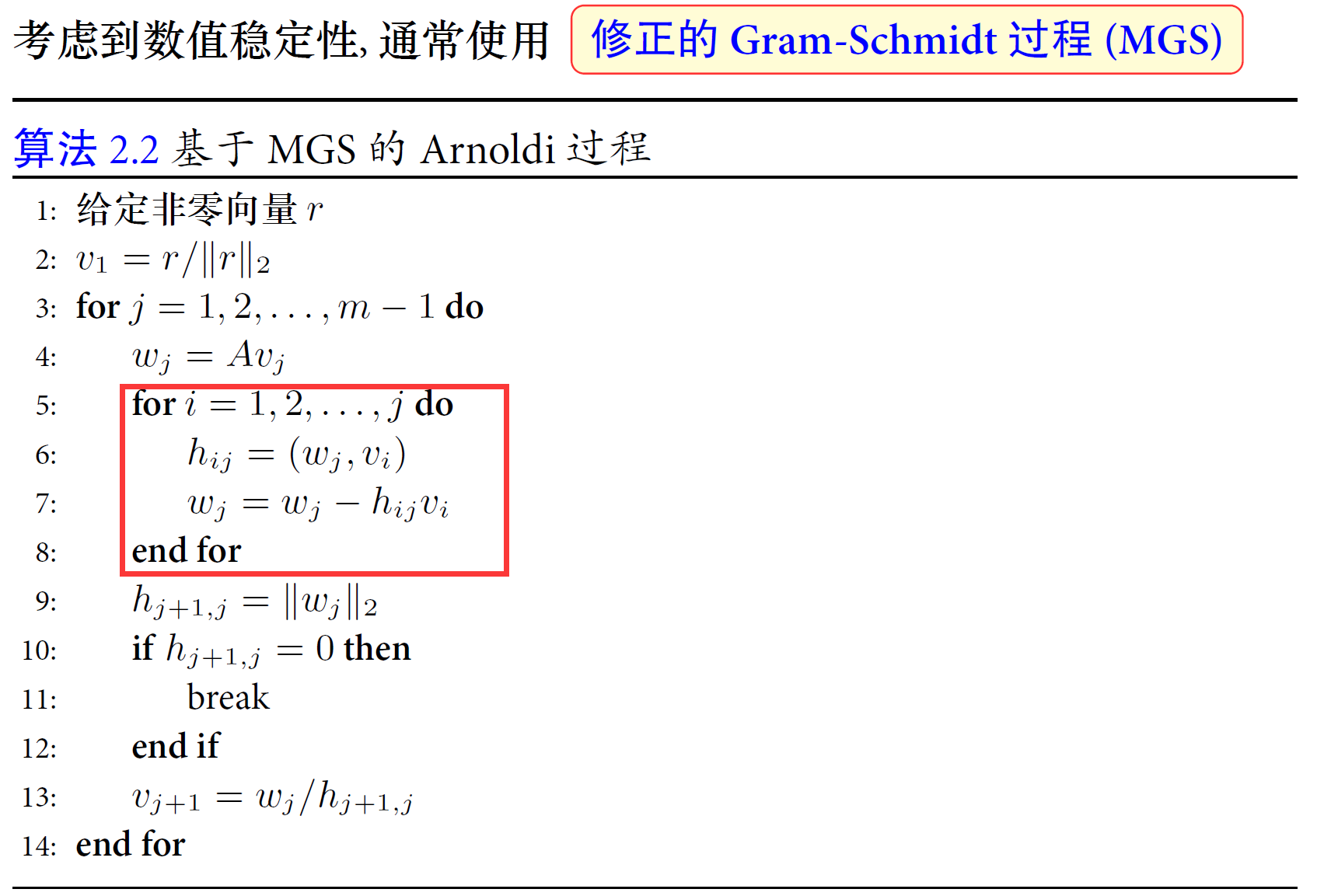

对应上述MGS过程的python代码:
import numpy as np
def arnoldi_iteration(A, b, n: int):
"""Compute a basis of the (n + 1)-Krylov subspace of the matrix A.
This is the space spanned by the vectors {b, Ab, ..., A^n b}.
Parameters
----------
A : array_like
An m × m array.
b : array_like
Initial vector (length m).
n : int
One less than the dimension of the Krylov subspace, or equivalently the *degree* of the Krylov space. Must be >= 1.
Returns
-------
Q : numpy.array
An m x (n + 1) array, where the columns are an orthonormal basis of the Krylov subspace.
h : numpy.array
An (n + 1) x n array. A on basis Q. It is upper Hessenberg.
"""
eps = 1e-12
h = np.zeros((n + 1, n))
Q = np.zeros((A.shape[0], n + 1))
# Normalize the input vector
Q[:, 0] = b / np.linalg.norm(b, 2) # Use it as the first Krylov vector
for k in range(1, n + 1):
v = np.dot(A, Q[:, k - 1]) # Generate a new candidate vector
for j in range(k): # Subtract the projections on previous vectors
h[j, k - 1] = np.dot(Q[:, j].conj(), v)
v = v - h[j, k - 1] * Q[:, j]
h[k, k - 1] = np.linalg.norm(v, 2)
if h[k, k - 1] > eps: # Add the produced vector to the list, unless
Q[:, k] = v / h[k, k - 1]
else: # If that happens, stop iterating.
return Q, h
return Q, h
四、重要性质
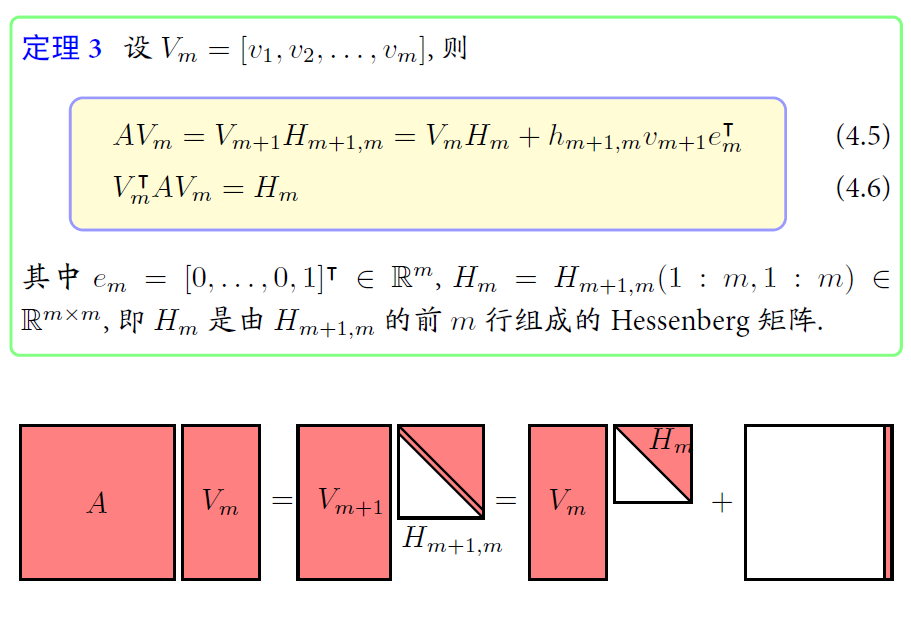
(4.5)和(4.6)这两个式子在指数积分方法(krylov法)中会有应用。





