骑士巡游问题
问题概述
骑士巡游问题对国际象棋爱好者来说是较有意思的难题之一。这个问题是:称为骑士的棋子在一个空的棋盘上行进,能否在64个方格棋盘上的每个方格都走一次且只走一次。
在国际象棋中,骑士的移动路线是L形的(在一个方向上走两格,在垂直方向上走一格)。因此在一个空棋盘中间的方格上,其实可以有8种不同的移动方式(从0到7编号),如下图所示:
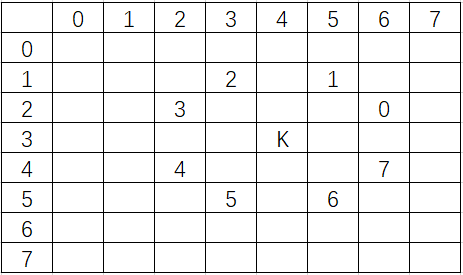
可达性试探法
算法思想
根据每个方格的可到达程度将它们分类,然后总是把骑士移动到最难到达的那个方格(即可达性数字最小的方格,贪心算法的感觉)。我们给一个二维array对象access填上数,这些数表示每个方格周围有多少个可到达的方格。在一个空棋盘上,每个中心方格定为8,每个角落定为2,其他的方格为3、4或6,如下所示:
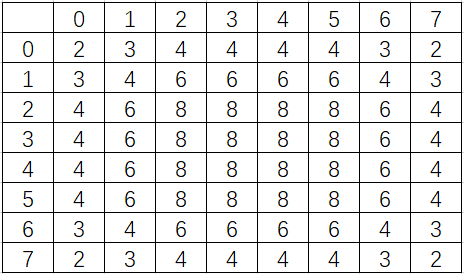
在任何时候,骑士都应该移动到具有最低可达数的方格。如果满足此条件的方格不止一个,骑士可以选择移动到其中的任何一个方格。因此,骑士巡游可以从任何一个角落开始。需要注意的是:随着骑士在棋盘上的移动,越来越多的方格被占用,因此应该随之减少可达数。这样,在巡游的任何时刻,每个有效方格的可达数与该方格可到达的确切方格数保持相等。
C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 8;
// 检测当前选择的位置是否有效
bool vaildWay(int col, int row, int board[][SIZE]) {
return (col >= 0 && col < SIZE && row >= 0
&& row < SIZE && !board[row][col]);
}
int main() {
int board[SIZE][SIZE] = { 0 }; // 初始化棋盘数组
int access[SIZE][SIZE] = { 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 3, 2,
3, 4, 6, 6, 6, 6, 4, 3,
4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 8, 6, 4,
4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 8, 6, 4,
4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 8, 6, 4,
4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 8, 6, 4,
3, 4, 6, 6, 6, 6, 4, 3,
2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 3, 2 }; // 可达性数组
int horizontal[SIZE] = { 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2 }; // 水平位移
int vertical[SIZE] = { -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1 }; // 垂直位移
int currentCol, currentRow; // 当前位置
int testCol, testRow; // 测试位置
int moveSteps = 0; // 移动步伐
srand(time(0));
currentCol = rand() % 8; // 随机选择起始位置
currentRow = rand() % 8;
board[currentRow][currentCol] = ++moveSteps; // 标记起始位置
bool done = false;
while (!done) {
int miniWay = 9; // 挑选最小的可达性位置
int direction = -1; // 记录方向
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i) { // 扫描8个方向
testCol = currentCol + horizontal[i];
testRow = currentRow + vertical[i];
if (vaildWay(testCol, testRow, board)) {
if (access[testRow][testCol] < miniWay) {
miniWay = access[testRow][testCol];
direction = i;
}
--access[testRow][testCol]; // 更新可达性数组
}
}
if (direction == -1) // 如果没有合适的方向
done = true;
else { // 更新当前位置
currentCol += horizontal[direction];
currentRow += vertical[direction];
board[currentRow][currentCol] = ++moveSteps;
}
}
if (moveSteps == 64) // 如果遍历到所有的方格位置
cout << " successful!!\n\n";
else
cout << " failed\n\n";
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i) { // 输出棋盘数据
for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; ++j)
cout << setw(3) << board[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
暴力方法
算法思想
所谓暴力方法,就是不断试错,不断的使用随机数进行测试,直到完成需要的目标或者达到目的次数为止。需要注意的是,暴力解法可能在有限次内不会成功的找到正确的解法,我们保存其中走的最远的次数进行输出。
C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 8;
const int MAXTIMES = 10000; // 最大尝试次数
// 检测当前选择的位置是否有效
bool vaildWay(int col, int row, int board[][SIZE]) {
return (col >= 0 && col < SIZE && row >= 0
&& row < SIZE && !board[row][col]);
}
int main() {
int board[SIZE][SIZE] = { 0 }; // 初始化棋盘数组
int horizontal[SIZE] = { 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2 }; // 水平位移
int vertical[SIZE] = { -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1 }; // 垂直位移
int currentCol, currentRow; // 当前位置
int testCol, testRow; // 测试位置
int moveSteps = 0; // 移动步伐
int tryTimes = 0; // 尝试的次数
int bestSteps = 0; // 最佳的选择的步伐数
srand(time(0));
while (moveSteps != 64 && tryTimes < MAXTIMES) {
++tryTimes; // 记录尝试次数
// 初始化相关的参数
memset(board, 0, sizeof(board)); // 清空棋盘数组的数据
moveSteps = 0;
currentCol = rand() % 8;
currentRow = rand() % 8;
board[currentRow][currentCol] = ++moveSteps;
bool done = false;
// 开始进行暴力解法
while (!done) {
int direction = rand() % 8; // 随机选择一个方向
testCol = currentCol + horizontal[direction];
testRow = currentRow + vertical[direction];
if (!vaildWay(testCol, testRow, board)) { // 如果当前方向无效,则扫描剩余的7个方向
for (int i = 1; i < SIZE; ++i) {
direction = (direction + 1) % SIZE;
testCol = currentCol + horizontal[direction];
testRow = currentRow + vertical[direction];
if (vaildWay(testCol, testRow, board))
break;
}
}
if (vaildWay(testCol, testRow, board)) { // 找到有效方向,更新数据
currentCol = testCol;
currentRow = testRow;
board[currentRow][currentCol] = ++moveSteps;
}
else
done = true;
}
//cout << moveSteps << endl; // 输出当前测试能够达到的步伐数
if (moveSteps > bestSteps)
bestSteps = moveSteps;
}
if (moveSteps == 64) {
cout << "After " << tryTimes << " times, successful!!\n\n";
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i) { // 输出棋盘数据
for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; ++j)
cout << setw(3) << board[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
}
else
cout << "After " << tryTimes
<< " times, failed!!\nThe maximum number of step is "
<< bestSteps << ".\n\n";
return 0;
}
附加问题
问题概述
基本的骑士巡游中,骑士移动64次并且经过了棋盘中每个方格一次且只有一次时,才是一个完整的巡游。而在这基础上,如果骑士的第65次移动能够回到出发点的巡游,被称为封闭巡游。在上面问题的基础上,修改算法,测试一个完整的巡游是否是一个封闭巡游。
算法思想
只需要在可达性算法的基础上进行添加即可,在确保已经完成了一次完整巡游的前提下,再进行一次8个方向的扫描,如果能够扫描到起始点,则说明在第65次移动回到出发点,完成封闭巡游,否则,则不能。
C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 8;
// 检测当前选择的位置是否有效
bool vaildWay(int col, int row, int board[][SIZE]) {
return (col >= 0 && col < SIZE&& row >= 0
&& row < SIZE && !board[row][col]);
}
int main() {
int board[SIZE][SIZE] = { 0 }; // 初始化棋盘数组
int access[SIZE][SIZE] = { 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 3, 2,
3, 4, 6, 6, 6, 6, 4, 3,
4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 8, 6, 4,
4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 8, 6, 4,
4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 8, 6, 4,
4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 8, 6, 4,
3, 4, 6, 6, 6, 6, 4, 3,
2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 3, 2 }; // 可达性数组
int horizontal[SIZE] = { 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2 }; // 水平位移
int vertical[SIZE] = { -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1 }; // 垂直位移
int currentCol, currentRow; // 当前位置
int testCol, testRow; // 测试位置
int moveSteps = 0; // 移动步伐
srand(0);
currentCol = rand() % 8; // 随机选择起始位置
currentRow = rand() % 8;
board[currentRow][currentCol] = ++moveSteps; // 标记起始位置
bool done = false;
while (!done) {
int miniWay = 9; // 挑选最小的可达性位置
int direction = -1; // 记录方向
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i) { // 扫描8个方向
testCol = currentCol + horizontal[i];
testRow = currentRow + vertical[i];
if (vaildWay(testCol, testRow, board)) {
if (access[testRow][testCol] < miniWay) {
miniWay = access[testRow][testCol];
direction = i;
}
--access[testRow][testCol]; // 更新可达性数组
}
}
if (direction == -1) // 如果没有合适的方向
done = true;
else { // 更新当前位置
currentCol += horizontal[direction];
currentRow += vertical[direction];
board[currentRow][currentCol] = ++moveSteps;
}
}
if (moveSteps == 64) { // 如果遍历到所有的方格位置
cout << " successful!!\n\n";
// 进行封闭巡游的测试
bool closedFlag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i) { // 扫描8个方向
testCol = currentCol + horizontal[i];
testRow = currentRow + vertical[i];
if (board[testRow][testCol] == 1) { // 如果检测到起点则成功
closedFlag = true;
break;
}
}
if (closedFlag)
cout << "It is closed!" << "\n\n";
else
cout << "It is not closed." << "\n\n";
}
else
cout << " failed\n\n";
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i) { // 输出棋盘数据
for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; ++j)
cout << setw(3) << board[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}


