Abp Vnext 动态(静态)API客户端源码解析
根据以往的经验,通过接口远程调用服务的原理大致如下:
- 服务端:根据接口定义方法的签名生成路由,并暴露Api。
- 客户端:根据接口定义方法的签名生成请求,通过HTTPClient调用。
这种经验可以用来理解ABP VNext自动API的方式,但如果不使用自动API并且控制器定义了路由的情况下,远程调用的路由地址就有可能跟服务端暴露的路由不一致,预料的结果应该会返回404,但是Abp vnext却能够正常工作。那么客户端在使用远程调用时,是如何知道实际调用方法的路由地址呢?下面我们来探究一下源码。
一.动态API客户端
下面是注册动态API客户端的源码,AddHttpClientProxies 方法传入两个参数:接口层程序集和远程服务名称。该方法主要是遍历所有继承 IRemoteService 接口的类型,并为它们注册动态代理。同时,将每个类型的实例与远程服务名称关联起来,以便在进行远程调用时能够根据类型获取到对应的远程配置。需要注意的是,如果配置不存在对应的远程服务名称,则采用默认配置。
context.Services.AddHttpClientProxies(
typeof(IdentityApplicationContractsModule).Assembly, //接口层程序集
RemoteServiceName //远程服务名称
);
public static IServiceCollection AddHttpClientProxy(this IServiceCollection services, Type type, string remoteServiceConfigurationName = "Default", bool asDefaultService = true)
{
/*省略一些代码...*/
Type type2 = typeof(DynamicHttpProxyInterceptor<>).MakeGenericType(type); //拦截器
services.AddTransient(type2);
Type interceptorAdapterType = typeof(AbpAsyncDeterminationInterceptor<>).MakeGenericType(type2);
Type validationInterceptorAdapterType = typeof(AbpAsyncDeterminationInterceptor<>).MakeGenericType(typeof(ValidationInterceptor));
if (asDefaultService)
{
//生成代理,依赖注入到容器
services.AddTransient(type, (IServiceProvider serviceProvider) => ProxyGeneratorInstance.CreateInterfaceProxyWithoutTarget(type, (IInterceptor)serviceProvider.GetRequiredService(validationInterceptorAdapterType), (IInterceptor)serviceProvider.GetRequiredService(interceptorAdapterType)));
}
services.AddTransient(typeof(IHttpClientProxy<>).MakeGenericType(type), delegate (IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
//生成代理,通过HttpClientProxy封装,依赖注入到容器
object obj = ProxyGeneratorInstance.CreateInterfaceProxyWithoutTarget(type, (IInterceptor)serviceProvider.GetRequiredService(validationInterceptorAdapterType), (IInterceptor)serviceProvider.GetRequiredService(interceptorAdapterType));
return Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(HttpClientProxy<>).MakeGenericType(type), obj);
});
return services;
}
通过动态代理实例调用方法的时候,会先进入拦截器 DynamicHttpProxyInterceptor 的 InterceptAsync 方法。
public override async Task InterceptAsync(IAbpMethodInvocation invocation)
{
var context = new ClientProxyRequestContext(
await GetActionApiDescriptionModel(invocation), //获取Api描述信息
invocation.ArgumentsDictionary,
typeof(TService));
if (invocation.Method.ReturnType.GenericTypeArguments.IsNullOrEmpty())
{
await InterceptorClientProxy.CallRequestAsync(context);
}
else
{
var returnType = invocation.Method.ReturnType.GenericTypeArguments[0];
var result = (Task)CallRequestAsyncMethod
.MakeGenericMethod(returnType)
.Invoke(this, new object[] { context });
invocation.ReturnValue = await GetResultAsync(result, returnType); //调用CallRequestAsync泛型方法
}
}先通过 GetActionApiDescriptionModel 方法获取到Api描述信息,将其封装进远程调用的上下文。接着调用 CallRequestAsync 方法真正进行远程请求。如果是泛型,则调用 CallRequestAsync 的泛型方法。让我们先来看看 GetActionApiDescriptionModel 方法是如何获取到Api描述信息的。
protected virtual async Task<ActionApiDescriptionModel> GetActionApiDescriptionModel(IAbpMethodInvocation invocation)
{
var clientConfig = ClientOptions.HttpClientProxies.GetOrDefault(typeof(TService)) ?? //获取远程服务名称
throw new AbpException($"Could not get DynamicHttpClientProxyConfig for {typeof(TService).FullName}.");
var remoteServiceConfig = await RemoteServiceConfigurationProvider.GetConfigurationOrDefaultAsync(clientConfig.RemoteServiceName);//获取远程服务端点配置
var client = HttpClientFactory.Create(clientConfig.RemoteServiceName); //创建HttpClient
return await ApiDescriptionFinder.FindActionAsync(
client,
remoteServiceConfig.BaseUrl, //远程服务地址
typeof(TService),
invocation.Method
);
}远程服务端点配置例如:
"RemoteServices": {
"Default": {
"BaseUrl": "http://localhost:44388"
},
"XXXDemo":{
"BaseUrl": "http://localhost:44345"
}
},根据接口类型获取到远程服务名称,再根据名称获取到服务端点配置。ApiDescriptionFinder 是 IApiDescriptionFinder 的实例,默认实现是 ApiDescriptionFinder。
public async Task<ActionApiDescriptionModel> FindActionAsync(
HttpClient client,
string baseUrl,
Type serviceType,
MethodInfo method)
{
var apiDescription = await GetApiDescriptionAsync(client, baseUrl); //获取Api描述信息并缓存结果
//TODO: Cache finding?
var methodParameters = method.GetParameters().ToArray();
foreach (var module in apiDescription.Modules.Values)
{
foreach (var controller in module.Controllers.Values)
{
if (!controller.Implements(serviceType)) //不继承接口跳过,所以写控制器为什么需要要继承服务接口的作用之一便在于此
{
continue;
}
foreach (var action in controller.Actions.Values)
{
if (action.Name == method.Name && action.ParametersOnMethod.Count == methodParameters.Length) //签名是否匹配
{
/*省略部分代码 */
}
}
}
}
throw new AbpException($"Could not found remote action for method: {method} on the URL: {baseUrl}");
}
public virtual async Task<ApplicationApiDescriptionModel> GetApiDescriptionAsync(HttpClient client, string baseUrl)
{
return await Cache.GetAsync(baseUrl, () => GetApiDescriptionFromServerAsync(client, baseUrl)); //缓存结果
}
protected virtual async Task<ApplicationApiDescriptionModel> GetApiDescriptionFromServerAsync(
HttpClient client,
string baseUrl)
{
//构造请求信息
var requestMessage = new HttpRequestMessage(
HttpMethod.Get,
baseUrl.EnsureEndsWith('/') + "api/abp/api-definition"
);
AddHeaders(requestMessage); //添加请求头
var response = await client.SendAsync( //发送请求并获取响应结果
requestMessage,
CancellationTokenProvider.Token
);
if (!response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
throw new AbpException("Remote service returns error! StatusCode = " + response.StatusCode);
}
var content = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
var result = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<ApplicationApiDescriptionModel>(content, DeserializeOptions);
return result;
}GetApiDescriptionAsync 方法包装了缓存,GetApiDescriptionFromServerAsync 才是真正去获取Api描述信息的方法,它传递了两个参数,一个是httpclient(作用无需多说),另一个是baseurl即远程服务端点地址。通过Get请求方式调用远程服务的 "api/abp/api-definition" 接口,获取到该服务所有API描述信息,然后根据远程调用服务类型跟方法签名找到对应的API描述信息。API描述信息包含了端点的实际路由,支持版本号,是否允许匿名访问等信息。到此API描述信息已经获取到,回过头来看看 CallRequestAsync 方法的实现。
public virtual async Task<T> CallRequestAsync<T>(ClientProxyRequestContext requestContext)
{
return await base.RequestAsync<T>(requestContext);
}
public virtual async Task<HttpContent> CallRequestAsync(ClientProxyRequestContext requestContext)
{
return await base.RequestAsync(requestContext);
}
protected virtual async Task<HttpContent> RequestAsync(ClientProxyRequestContext requestContext)
{
//获取远程服务名称
var clientConfig = ClientOptions.Value.HttpClientProxies.GetOrDefault(requestContext.ServiceType) ?? throw new AbpException($"Could not get HttpClientProxyConfig for {requestContext.ServiceType.FullName}.");
//获取远程服务端点配置
var remoteServiceConfig = await RemoteServiceConfigurationProvider.GetConfigurationOrDefaultAsync(clientConfig.RemoteServiceName);
var client = HttpClientFactory.Create(clientConfig.RemoteServiceName);
var apiVersion = await GetApiVersionInfoAsync(requestContext); //获取API版本
var url = remoteServiceConfig.BaseUrl.EnsureEndsWith('/') + await GetUrlWithParametersAsync(requestContext, apiVersion); //拼接完整的url
var requestMessage = new HttpRequestMessage(requestContext.Action.GetHttpMethod(), url) //构造HTTP请求信息
{
Content = await ClientProxyRequestPayloadBuilder.BuildContentAsync(requestContext.Action, requestContext.Arguments, JsonSerializer, apiVersion)
};
AddHeaders(requestContext.Arguments, requestContext.Action, requestMessage, apiVersion); //添加请求头
if (requestContext.Action.AllowAnonymous != true) //是否需要认证
{
await ClientAuthenticator.Authenticate( //认证
new RemoteServiceHttpClientAuthenticateContext(
client,
requestMessage,
remoteServiceConfig,
clientConfig.RemoteServiceName
)
);
}
HttpResponseMessage response;
try
{
response = await client.SendAsync( //发送请求
requestMessage,
HttpCompletionOption.ResponseHeadersRead /*this will buffer only the headers, the content will be used as a stream*/,
GetCancellationToken(requestContext.Arguments)
);
}
return response.Content;
}GetUrlWithParametersAsync 方法是根据API描述信息跟调用参数值拼接出完整的路由地址,比如user/{id}/?name=xxxxx,接着构造出HTTP请求信息,添加请求头,如果需要身份认证,则调用 ClientAuthenticator.Authenticate 方法,ClientAuthenticator 是 IRemoteServiceHttpClientAuthenticator 的实例,它的实现有多种,有【Volo.Abp.Http.Client.IdentityModel】模块的 IdentityModelRemoteServiceHttpClientAuthenticator 类,它是使用OAuth 2.0协议直接调用接口获取访问令牌。 有 【Volo.Abp.Http.Client.IdentityModel.Web】 模块的 HttpContextIdentityModelRemoteServiceHttpClientAuthenticator 类,它是从当前请求上下文获取到当前登录用户的访问令牌。
public override async Task Authenticate(RemoteServiceHttpClientAuthenticateContext context)
{
if (context.RemoteService.GetUseCurrentAccessToken() != false)
{
var accessToken = await GetAccessTokenFromHttpContextOrNullAsync(); //获取当前登录用户Token
if (accessToken != null)
{
context.Request.SetBearerToken(accessToken);
return;
}
}
await base.Authenticate(context);
}如果远程调用需要传递当前登录用户令牌则可以引用 【Volo.Abp.Http.Client.IdentityModel.Web】模块
[DependsOn(typeof(AbpHttpClientIdentityModelWebModule))]端点配置例如:
"RemoteServices": {
"AbpMvcClient": {
"BaseUrl": "http://localhost:44388",
"UseCurrentAccessToken": "true"
}
}AddHeaders 方法,请求头添加租户等信息
protected virtual void AddHeaders(
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, object> argumentsDictionary,
ActionApiDescriptionModel action,
HttpRequestMessage requestMessage,
ApiVersionInfo apiVersion)
{
/*省略代码/*
//TenantId
if (CurrentTenant.Id.HasValue)
{
//TODO: Use AbpAspNetCoreMultiTenancyOptions to get the key
requestMessage.Headers.Add(TenantResolverConsts.DefaultTenantKey, CurrentTenant.Id.Value.ToString());
}
/*省略代码/*
}要点
1.控制器要继承服务接口
2.如果采用内部网关, api/abp/api-definition 将会转发到某一个服务,所以就需要将所有微服务的Api层引用到该服务上(或者在内部网关),这样才能通过 api/abp/api-definition 接口获取到对应服务的API描述信息。否则就不能直接通过内部网关调用,需要配置不同的远程服务名称指向相应的服务上才能获取到API描述信息。
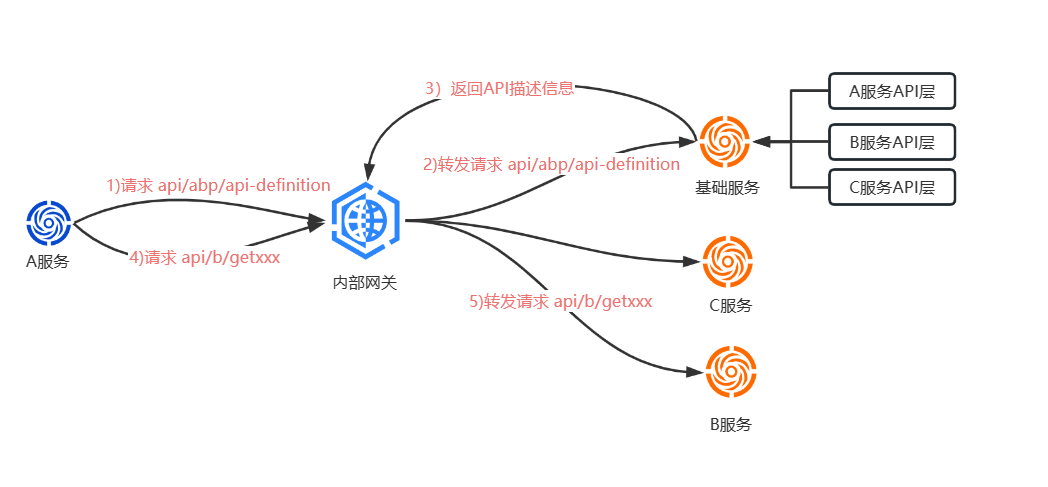
二.静态API客户端
静态API客户端跟动态API客户端不一样,静态API客户端是通过abp cli工具提前生成好调用类跟API描述文件,在生成的时候同样遵守动态API客户端获取API描述信息的规则(注意要点1,2)
生成后ClientProxies目录包含调用类跟 *generate-proxy.json 文件,*generate-proxy.json 文件包含了API描述信息。
生成的调用类如下:
[Dependency(ReplaceServices = true)]
[ExposeServices(typeof(IIdentityRoleAppService), typeof(IdentityRoleClientProxy))]
public partial class IdentityRoleClientProxy : ClientProxyBase<IIdentityRoleAppService>, IIdentityRoleAppService
{
public virtual async Task<ListResultDto<IdentityRoleDto>> GetAllListAsync()
{
return await RequestAsync<ListResultDto<IdentityRoleDto>>(nameof(GetAllListAsync));
}
}
protected virtual async Task RequestAsync(string methodName, ClientProxyRequestTypeValue arguments = null)
{
await RequestAsync(BuildHttpProxyClientProxyContext(methodName, arguments));
}
protected virtual ClientProxyRequestContext BuildHttpProxyClientProxyContext(string methodName, ClientProxyRequestTypeValue arguments = null)
{
if (arguments == null)
{
arguments = new ClientProxyRequestTypeValue();
}
var methodUniqueName = $"{typeof(TService).FullName}.{methodName}.{string.Join("-", arguments.Values.Select(x => TypeHelper.GetFullNameHandlingNullableAndGenerics(x.Key)))}";
var action = ClientProxyApiDescriptionFinder.FindAction(methodUniqueName); //获取调用方法的API描述信息
if (action == null)
{
throw new AbpException($"The API description of the {typeof(TService).FullName}.{methodName} method was not found!");
}
var actionArguments = action.Parameters.GroupBy(x => x.NameOnMethod).ToList();
if (action.SupportedVersions.Any())
{
//TODO: make names configurable
actionArguments.RemoveAll(x => x.Key == "api-version" || x.Key == "apiVersion");
}
return new ClientProxyRequestContext( //封装未远程调用上下文
action,
actionArguments
.Select((x, i) => new KeyValuePair<string, object>(x.Key, arguments.Values[i].Value))
.ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Value),
typeof(TService));
}ClientProxyApiDescriptionFinder 是 IClientProxyApiDescriptionFinder 的实例。默认实现是 ClientProxyApiDescriptionFinder 。
该实例初始化时调用 GetApplicationApiDescriptionModel 方法从虚拟文件系统中读取所有的 *generate-proxy.json 文件获取到API描述信息。
private ApplicationApiDescriptionModel GetApplicationApiDescriptionModel()
{
var applicationApiDescription = ApplicationApiDescriptionModel.Create();
var fileInfoList = new List<IFileInfo>();
GetGenerateProxyFileInfos(fileInfoList);
foreach (var fileInfo in fileInfoList)
{
using (var streamReader = new StreamReader(fileInfo.CreateReadStream()))
{
var content = streamReader.ReadToEnd();
var subApplicationApiDescription = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<ApplicationApiDescriptionModel>(content);
foreach (var module in subApplicationApiDescription.Modules)
{
if (!applicationApiDescription.Modules.ContainsKey(module.Key))
{
applicationApiDescription.AddModule(module.Value);
}
}
}
}
return applicationApiDescription;
}
private void GetGenerateProxyFileInfos(List<IFileInfo> fileInfoList, string path = "")
{
foreach (var directoryContent in VirtualFileProvider.GetDirectoryContents(path))
{
if (directoryContent.IsDirectory)
{
GetGenerateProxyFileInfos(fileInfoList, directoryContent.PhysicalPath);
}
else
{
if (directoryContent.Name.EndsWith("generate-proxy.json"))
{
fileInfoList.Add(VirtualFileProvider.GetFileInfo(directoryContent.GetVirtualOrPhysicalPathOrNull()));
}
}
}
}后面 RequestAsync 方法就跟动态API客户端一样了。
要点
1.因为已经事先生成好API描述文件,所以避免了动态API客户端要点2的问题。但是在生成时也需要遵循要点2。
总结
动态API客户端
1.注册动态代理传入的接口层程序集和远程服务名称,可以实现将远程调用类型与远程服务名称绑定在一起的作用。这样,在使用具体的服务类型进行远程调用时,就能够根据远程服务名称快速找到对应的服务地址。
2.在远程调用时,首先会调用相应服务的 api/abp/api-definition 接口获取到该服务的所有API描述信息,后将其封装成远程调用上下文,接着拼接完整的Url,添加请求头与认证信息(不允许匿名访问)就可以进行http请求了。
静态API客户端
1.通过abp cli工具生成调用类跟API描述文件,在远程调用时,通过*generate-proxy.json 文件获取到相应接口的API描述信息,往后跟动态API客户端流程一样。
最后
写到最后,文章开头的疑问应该解决了吗?
ABPVNEXT框架 QQ交流群:655362692
分类:
Abp源码解析





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)