C++中strncpy函数和strncpy_s函数的使用及注意事项
https://blog.csdn.net/leowinbow/article/details/82745016
在掌握了strcpy函数和strcpy_s函数之后,我们不可避免地会谈到strncpy函数和strncpy_s函数,其实这四个函数的功能几乎一致,就是对两个字符串数组进行复制和赋值,但是具体实现有一点点区别。
首先来说一下strncpy函数。该函数依然还是存在于标准名称空间std内,出现的目的很简单,对于strcpy函数,只能将两个字符串进行完整的复制和赋值,这里就会产生一个实际应用时的问题,如果我们只需要复制某个字符串的前几个字符呢?
其实对于这个问题,我们首先可能会想到使用strcpy_s函数,因为该函数有一个长度,我们在安全函数的基础上将长度表示成我们希望复制的长度,但是实际运行时这样写会出现问题,举例如下:
-
// strncpy_s.cpp
-
//
-
-
-
-
-
-
int main()
-
{
-
using namespace std;
-
-
char str1[100];
-
char str2[5];
-
cout << "Please enter your favorite lines (Warning: No longer than 100!):\n";
-
cin.getline(str1, 100);
-
strcpy_s(str2, 5, str1);
-
cout << "str1 is " << endl << str1 << endl;
-
cout << "while str2 is " << endl << str2 << endl;
-
-
system("pause");
-
return 0;
-
}
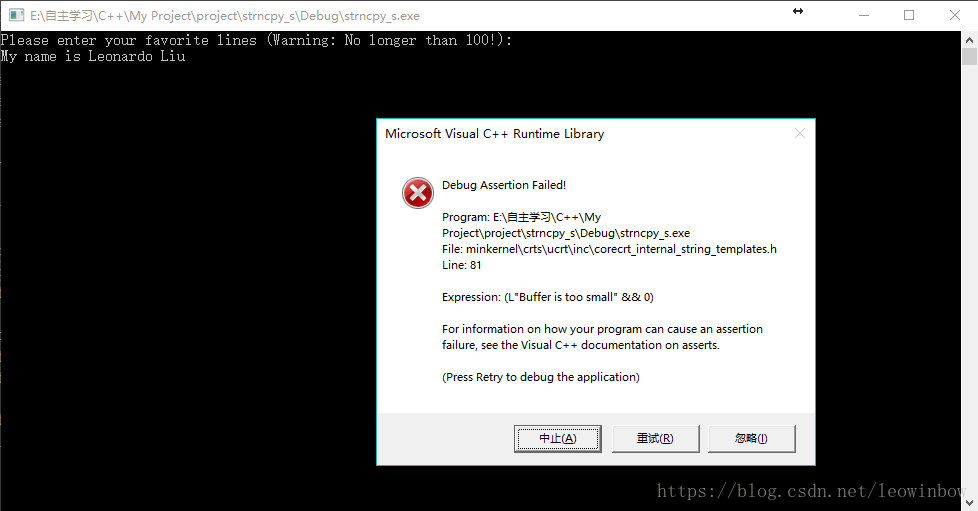
对于以上代码,运行结果如下图所示:
由运行结果可知,Buffer is too small,即告诉我们安全函数之所以安全,就是不可以这样操作,不可以把一个长度超过x的字符串数组复制并赋值给长度为x的字符串数组。
于是由此,strncpy函数应运而生。
由于我使用的IDE是Visual Studio 2017,所以只要使用strncpy函数就会报错并提示使用安全版本,所以这里对于基础版本的strncpy函数只做理论介绍。
strncpy函数的原型如下所示:
char * strncpy(char * str2, char * str1, int size);
功能就是复制str1中的内容,赋进str2中,复制的长度由size的数值决定,size的类型不一定是Int,但我们一般来说遇到的长度都是整数,所以这里用int比较简单。
比如说以下语句:
-
char str1[5] = "abcd";
-
char str2[10] = "leonardo";
-
strncpy(str2, str1, 3);
因为IDE不支持基础版本函数,所以我没法看运行结果,就文字描述一下。
以上代码运行之后,strncpy函数会将str1的前3个字符的内容复制,赋到str2里,于是str2就变成了‘a’'b'‘c’。
那么对于strncpy_s函数,原型如下所示:
strncpy_s(char * str2, int size2, char * str1, int size1);
这里多了一个长度,就是被复制的str2的长度,我们可以用sizeof(str2)来表示这个长度。
那么改成使用strncpy_s函数之后,上面的代码就可以正确运行了。
-
// strncpy_s.cpp
-
//
-
-
-
-
-
-
int main()
-
{
-
using namespace std;
-
-
char str1[5] = "abcd";
-
char str2[10] = "leonardo";
-
cout << "str1 is " << endl << str1 << endl;
-
cout << "str2 is " << endl << str2 << endl;
-
strncpy_s(str2, sizeof(str2), str1, 3);
-
cout << "after the copy str2 is " << endl << str2 << endl;
-
-
system("pause");
-
return 0;
-
}
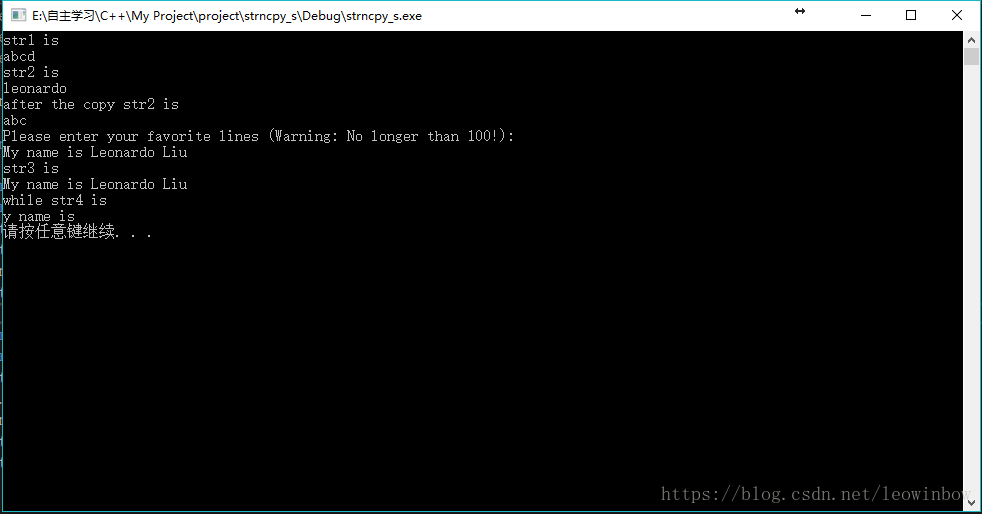
运行结果如下图所示:
于是回到我们最早那个代码,稍作修改使用strncpy_s函数,修改后代码如下:
-
// strncpy_s.cpp
-
//
-
-
-
-
-
-
int main()
-
{
-
using namespace std;
-
-
char str1[5] = "abcd";
-
char str2[10] = "leonardo";
-
cout << "str1 is " << endl << str1 << endl;
-
cout << "str2 is " << endl << str2 << endl;
-
strncpy_s(str2, sizeof(str2), str1, 3);
-
cout << "after the copy str2 is " << endl << str2 << endl;
-
-
char str3[100];
-
char str4[10];
-
cout << "Please enter your favorite lines (Warning: No longer than 100!):\n";
-
cin.getline(str3, 100);
-
strncpy_s(str4, sizeof(str4), str3, 10);
-
cout << "str3 is " << endl << str3 << endl;
-
cout << "while str4 is " << endl << str4 << endl;
-
-
system("pause");
-
return 0;
-
}
对于str3,它本身的长度是100,用户输入可以输入小于100的任意长度的字符,但是str4没有这么长,它的长度只有10,所以只能把str3的前10个字符内容复制给str3。
但是上面这样写还是有点问题,那就是字符串数组的最后一位一定是‘\0',如果直接复制10位,无法赋进str4,因为这样就把它最后一位的'\0'给覆盖了,就会报错,所以我们修改上面代码的strncpy_s()函数那里,改为
strncpy_s(str4, sizeof(str4), str3, 9);这样就正确了。
运行结果如下图所示:
于是就完成了我们之前所说的,希望只复制某个字符串数组的一部分给另一个字符串数组的功能了。
其实这个功能还可以延伸,假如说,我们希望复制的字段并不是原字符串最开始的字符怎么办呢,其实也很简单,只需要在strncpy_s函数的第三个参数处进行操作就可以了。
比如说我们希望从第2个字符开始复制,那么第3个参数就由"str3"改写为"str3+1"即可。因为str3是数组,数组名直接使用而不带标号,即是表示地址,所以“str3+1”即是表示str3[1]的地址了,同理"str3+5"即是表示str[5]的地址。
于是我们把上述程序的第23行,即strncpy_s()函数赋值那一句改成如下所示:
strncpy_s(str4, sizeof(str4), str3 + 1, 9);运行结果如下图:
从图中可以看出,确实是从第2个字符开始复制的。
那么接下来我们就要考虑,如果希望复制的不是连续的字符,而是分散的,比如说str3[2],str3[5],str3[8]和str3[9]这种呢?
这种情况就需要多个strncpy_s语句了,因为每一句只能进行一次复制和赋值,多次才能完成上述任务。
此时我们就需要去操作第1个参数了,即str4,因为str4也是一个数组名表示地址,所以我们这样分散复制时,后面几次复制就需要从str4的str4[2]开始赋值了。
我们来看一下完整代码:
-
// strncpy_s.cpp
-
//
-
-
-
-
-
-
int main()
-
{
-
using namespace std;
-
-
char str1[5] = "abcd";
-
char str2[10] = "leonardo";
-
cout << "str1 is " << endl << str1 << endl;
-
cout << "str2 is " << endl << str2 << endl;
-
strncpy_s(str2, sizeof(str2), str1, 3);
-
cout << "after the copy str2 is " << endl << str2 << endl;
-
cout << endl;
-
-
char str3[100];
-
char str4[10];
-
cout << "Please enter your favorite lines (Warning: No longer than 100!):\n";
-
cin.getline(str3, 100);
-
cout << endl;
-
strncpy_s(str4, sizeof(str4), str3 + 2, 1);
-
strncpy_s(str4 + 1, sizeof(str4) - 1, str3 + 5, 1);
-
strncpy_s(str4 + 2, sizeof(str4) - 2, str3 + 8, 2);
-
cout << "str3 is " << endl << str3 << endl;
-
cout << "while str4 is " << endl << str4 << endl;
-
-
system("pause");
-
return 0;
-
}
上述代码的第25,26,27三行都是在进行strncpy_s函数的复制,可以看到我们分了3次复制,因为str3[2],str3[5]都只能单独复制,因为不连续,而str3[8]和str3[9]可以联合复制,因为连续。
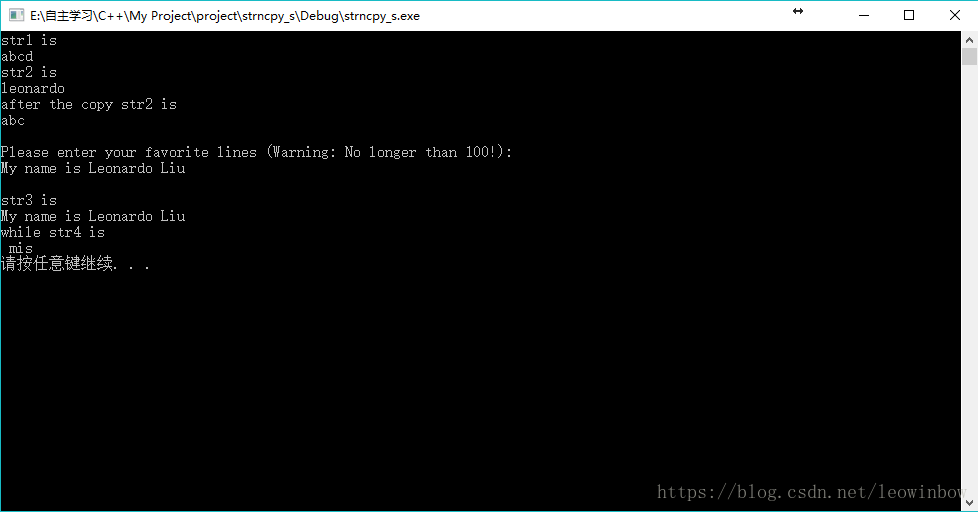
上述代码运行结果如下图所示:
从图中可以看到,str3[2]是‘ ’,str3[5]是'm',str3[8]是'i',str3[9]是's'。
所以这样我们就完成了分散复制的功能了。
目前我掌握的有关strncpy函数和strncpy_s函数的使用及注意事项就是这样,以后继续学习遇到新的知识了会持续补充。