使用Truffle 部署智能合约
使用Truffle 部署智能合约
之前我们使用Geth,原生的以太坊Golang工具,分析了创世区块的参数内容,在本地创建了私有以太坊区块链,并使用两个账户进行了挖矿和转账操作,对以太坊有了基本了解。
该篇章开始使用一个新的平台Truffle Suite,学习部署示例的智能合约,和一个稍微复杂一些的实用智能合约,学习Solidity语言的基本语法和智能合约的使用。
本文绝大多数参考资料来源于Solidity官方文档和Truffle官方文档。
1. 安装Truffle
Truffle Suite套件包括三个组件:
- Truffle:命令行工具,用来部署智能合约
- Ganache:GUI工具,用来可视化查看区块、账户、合约、交易等内容
- drizzle:Javascript库,用于前端开发
虽然Truffle套件在全平台通用,但在Windows上可能会出现莫名其妙的命名空间冲突问题,本次全部使用Ubuntu进行操作。
使用npm即可安装Truffle:(如何安装npm,换源等问题不在本篇的讨论范围内)
npm install -g truffle
后续使用Ganache做可视化浏览,Ganache为Linux提供了Appimage打包,下载后记得为其赋予可执行属性才能打开:
下载地址:https://github.com/trufflesuite/ganache/releases
chmod +x ganache-<Version>-linux-x86_64.AppImage
2. 学习示例智能合约 MetaCoin
2.1 准备
Truffle作为集成平台,提供了类似npm的功能,使用truffle unbox <projectname>,可以下载其他人发布的智能合约。
Metacoin是一个非常简单的智能合约,他设计了一种新货币Metacoin(下文可能称其为代币),其汇率为 1 Metacoin = 2 ETH,使用Metacoin智能合约可以进行Metacoin转账等操作。
新建文件夹Metacoin,打开终端输入:
truffle unbox metacoin
如果执行unbox命令时提示 RequestError: Error: connect ECONNREFUSED 错误,可以尝试使用export https_proxy为bash设置代理,加快访问速度
下载成功后,会看到文件夹内多出了一下内容:

其中contracts文件夹内有三个sol文件,是Solidity语言编写的只能合约文件;
migrations文件夹中的两个js文件是truffle部署智能合约时的部署文件,用来管理和升级智能合约,而且这些文件执行是有顺序的,必须以数字为开头;
test文件夹中是测试文件,可以使用js或者solidity语言编写测试脚本;
truffle-config.js 是truffle 的配置文件,包含truffle使用什么版本的编译器,在什么端口开放区块链的rpc协议等;
LICENSE为该代码的许可证。
2.2 交互
我们首先演示一下这个智能合约的实际效果,之后观察代码思考其运行的方法。
要部署智能合约,我们首先需要生成一条区块链。Truffle 可以快速帮我们生成开发环境的区块链,并构造出10个账户:
truffle develop

可以看到,一条新的区块链已经生成,并在9545端口打开了http服务(rpc服务),并预先生成了10个账户,每个账户中默认存有100个ETH,当前的控制台使用的是默认的第0个账户。
在truffle控制台可以使用Web3进行交互,例如:
truffle(develop)> web3.eth.getAccounts()
[ '0xB836A85f25f9Ab41290f2a63D1Ee83AEa9F53b94',
'0x0fC57BdDf263df2C70A5468B15b6fD620a366Cb4',
'0x9A2219312B49cd833650067427874204dC5e261c',
'0xfB440A02DCE4Aea19374902b57bEDEb23342d38f',
'0x78d551ECe5749D3453960460D337b283F6315174',
'0x737173efe01E9B720A310535fa513a23099d6fa2',
'0x39313f35e7549aEE9Df037936190a923a897B437',
'0x6F12D8eaC6996ba70Ca12e44E47669FEEDFD7ED7',
'0xDbe225FAc5F4CA0f74466af1b0625d2d7a4C7c75',
'0x56c467638B135C8584d871b1F468B8bb2363Db1a' ]
truffle(develop)> web3.eth.getBalance('0xB836A85f25f9Ab41290f2a63D1Ee83AEa9F53b94')
'100000000000000000000'
部署智能合约之前,需要编译sol文件:
truffle(develop)> compile
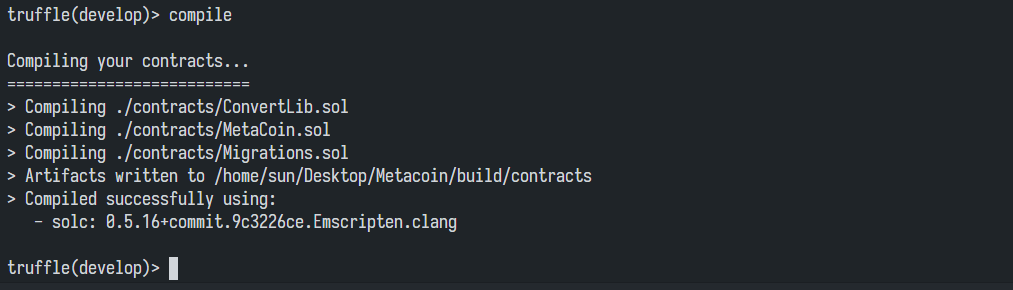
同时我们会看到Metacoin文件夹内多出来一个build文件夹,其中存放了编译好的智能合约。使用migrate命令部署之恩那个合约:
truffle(develop)> migrate
结果如下:
truffle(develop)> migrate
Compiling your contracts...
===========================
> Everything is up to date, there is nothing to compile.
Starting migrations...
======================
> Network name: 'develop'
> Network id: 5777
> Block gas limit: 6721975 (0x6691b7)
1_initial_migration.js
======================
Deploying 'Migrations'
----------------------
> transaction hash: 0x9d236e01303e2fc44c0717733120fe28669d5f2dacdd2b66561170331e72ff35
> Blocks: 0 Seconds: 0
> contract address: 0x65ae7471c845a10049053a15Be43EE86E76cF1F5
> block number: 1
> block timestamp: 1611852614
> account: 0xB836A85f25f9Ab41290f2a63D1Ee83AEa9F53b94
> balance: 99.9967165
> gas used: 164175 (0x2814f)
> gas price: 20 gwei
> value sent: 0 ETH
> total cost: 0.0032835 ETH
> Saving migration to chain.
> Saving artifacts
-------------------------------------
> Total cost: 0.0032835 ETH
2_deploy_contracts.js
=====================
Deploying 'ConvertLib'
----------------------
> transaction hash: 0xb2e3678a744446e6d3d98a43f3195994666b0e948f87b24eb5612ab20dcf08f9
> Blocks: 0 Seconds: 0
> contract address: 0xb59dBD1609f0982B0f7d64d3592D8390092442C7
> block number: 3
> block timestamp: 1611852614
> account: 0xB836A85f25f9Ab41290f2a63D1Ee83AEa9F53b94
> balance: 99.99396028
> gas used: 95470 (0x174ee)
> gas price: 20 gwei
> value sent: 0 ETH
> total cost: 0.0019094 ETH
Linking
-------
* Contract: MetaCoin <--> Library: ConvertLib (at address: 0xb59dBD1609f0982B0f7d64d3592D8390092442C7)
Deploying 'MetaCoin'
--------------------
> transaction hash: 0xf9b71d6dca179dddeac7bc1fba8d52f0b1ba430ac6c623aa4aeb7ea5ece09110
> Blocks: 0 Seconds: 0
> contract address: 0x8Baf7f61EEBb19eB22cC165AC9291338bF857522
> block number: 4
> block timestamp: 1611852614
> account: 0xB836A85f25f9Ab41290f2a63D1Ee83AEa9F53b94
> balance: 99.98822922
> gas used: 286553 (0x45f59)
> gas price: 20 gwei
> value sent: 0 ETH
> total cost: 0.00573106 ETH
> Saving migration to chain.
> Saving artifacts
-------------------------------------
> Total cost: 0.00764046 ETH
Summary
=======
> Total deployments: 3
> Final cost: 0.01092396 ETH
可以看到,由于刚刚编译过sol文件,部署时跳过了编译,直接使用1_initial_migration.js和2_deploy_contracts.js部署智能合约,最终消耗了0.01092396 ETH
truffle(develop)> web3.eth.getBalance('0xB836A85f25f9Ab41290f2a63D1Ee83AEa9F53b94')
'99987682400000000000'
Truffle控制台支持async/await 方法,我们新建变量时更加方便了。新建一个变量instance,为刚刚部署的合约的实例。
truffle(development)> let instance = await MetaCoin.deployed()
查看账户余额(代币的余额,即Metacoin的余额):
truffle(develop)> let balance = await instance.getBalance('0xB836A85f25f9Ab41290f2a63D1Ee83AEa9F53b94')
undefined
truffle(develop)> balance.toNumber()
10000
查看以太坊汇率转换后的余额:
truffle(develop)> let ether = await instance.getBalanceInEth('0xB836A85f25f9Ab41290f2a63D1Ee83AEa9F53b94')
undefined
truffle(develop)> ether.toNumber()
20000
向第1个账户发送一些代币:
truffle(develop)> instance.sendCoin('0x0fC57BdDf263df2C70A5468B15b6fD620a366Cb4', 500)
查看其余额:
truffle(development)> let received = await instance.getBalance('0x0fC57BdDf263df2C70A5468B15b6fD620a366Cb4')
undefined
truffle(development)> received.toNumber()
500
2.3 解析
接下来我们详细分析三个sol文件:
-
Migrations.sol
Migrations文件是使用truffle部署智能合约时必要的文件,其内容一般不会变。
-
MetaCoin.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity >=0.4.25 <0.7.0;
// 第一行声明了solidity的编译器版本
import "./ConvertLib.sol";
// 表示引用了当前目录下的库文件ConvertLib.sol
// 定义了一个合约,名为MetaCoin
contract MetaCoin {
// 变量balances本身时一个address类型,但被映射为无符号整型
mapping (address => uint) balances;
// 事件用来记录日志
event Transfer(address indexed _from, address indexed _to, uint256 _value);
// constructor函数为构造函数,在合约部署时运行
// tx.origin 是一个特殊的全局变量,意味最初调用合约的账户地址
// 向部署调用合约的人的余额添加10000个代币
constructor() public {
balances[tx.origin] = 10000;
}
// sendCoin函数接收两个参数(收件人和代币数量),返回布尔值
function sendCoin(address receiver, uint amount) public returns(bool sufficient) {
// 首先判断调用合约的人(发件人)的余额,如果余额小于要发送的代币数量,则返回false
// msg.sender是一个特殊的变量,意味调用合约的账户的地址
if (balances[msg.sender] < amount) return false;
// 修改发件人和收件人的余额
balances[msg.sender] -= amount;
balances[receiver] += amount;
// 记录这个event
emit Transfer(msg.sender, receiver, amount);
// 最终返回 true
return true;
}
// 查看代币转换为以太币后的价值
function getBalanceInEth(address addr) public view returns(uint){
// 调用了ConvertLib中的汇率转换函数
return ConvertLib.convert(getBalance(addr),2);
}
// 查看代币的数量
function getBalance(address addr) public view returns(uint) {
return balances[addr];
}
}
- ConvertLib.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity >=0.4.25 <0.7.0;
library ConvertLib{
// convert函数接受两个参数:amount和conversionRate,即货币数量和汇率,返回uint转换后的货币数量
// 该文件主要是为我们演示了如何在Solidity中引用Library
function convert(uint amount,uint conversionRate) public pure returns (uint convertedAmount)
{
return amount * conversionRate;
}
}
convert函数接受两个参数:amount和conversionRate,即货币数量和汇率,返回uint转换后的货币数量
该文件主要是为我们演示了如何在Solidity中引用Library
深入理解Truffle部署配置
上述三个文件完成了智能合约内容的编写,要部署合约,需要使用migrations中的两个js文件:
//TODO: 有关合约迁移的具体内容,会在后续补充
- 1_initial_migration.js
const Migrations = artifacts.require("Migrations");
module.exports = function(deployer) {
deployer.deploy(Migrations);
};
- 2_deploy_constracts.js
const ConvertLib = artifacts.require("ConvertLib");
const MetaCoin = artifacts.require("MetaCoin");
module.exports = function(deployer) {
deployer.deploy(ConvertLib);
deployer.link(ConvertLib, MetaCoin);
deployer.deploy(MetaCoin);
};
最后来看一下truffle-config.js 文件:
module.exports = {
// Uncommenting the defaults below
// provides for an easier quick-start with Ganache.
// You can also follow this format for other networks;
// see <http://truffleframework.com/docs/advanced/configuration>
// for more details on how to specify configuration options!
//
//networks: {
// development: {
// host: "127.0.0.1",
// port: 7545,
// network_id: "*"
// },
// test: {
// host: "127.0.0.1",
// port: 7545,
// network_id: "*"
// }
//}
//
};
MetaCoin的truffle-config.js文件是一个简陋版本,只定义了两种network(development和test),并且默认时被注释掉的。
默认情况下,使用truffle develop会开放一个9545端口,我们也可以在配置文件中写好配置并在使用时指定:
truffle develop --network <network_config_name>
实际上完整的truffle-config.js文件应该长这样:
/**
* Use this file to configure your truffle project. It's seeded with some
* common settings for different networks and features like migrations,
* compilation and testing. Uncomment the ones you need or modify
* them to suit your project as necessary.
*
* More information about configuration can be found at:
*
* trufflesuite.com/docs/advanced/configuration
*
* To deploy via Infura you'll need a wallet provider (like @truffle/hdwallet-provider)
* to sign your transactions before they're sent to a remote public node. Infura accounts
* are available for free at: infura.io/register.
*
* You'll also need a mnemonic - the twelve word phrase the wallet uses to generate
* public/private key pairs. If you're publishing your code to GitHub make sure you load this
* phrase from a file you've .gitignored so it doesn't accidentally become public.
*
*/
// const HDWalletProvider = require('@truffle/hdwallet-provider');
// const infuraKey = "fj4jll3k.....";
//
// const fs = require('fs');
// const mnemonic = fs.readFileSync(".secret").toString().trim();
module.exports = {
/**
* Networks define how you connect to your ethereum client and let you set the
* defaults web3 uses to send transactions. If you don't specify one truffle
* will spin up a development blockchain for you on port 9545 when you
* run `develop` or `test`. You can ask a truffle command to use a specific
* network from the command line, e.g
*
* $ truffle test --network <network-name>
*/
networks: {
// Useful for testing. The `development` name is special - truffle uses it by default
// if it's defined here and no other network is specified at the command line.
// You should run a client (like ganache-cli, geth or parity) in a separate terminal
// tab if you use this network and you must also set the `host`, `port` and `network_id`
// options below to some value.
//
development: {
host: "127.0.0.1", // Localhost (default: none)
port: 7545, // Standard Ethereum port (default: none)
network_id: "*", // Any network (default: none)
},
// Another network with more advanced options...
// advanced: {
// port: 8777, // Custom port
// network_id: 1342, // Custom network
// gas: 8500000, // Gas sent with each transaction (default: ~6700000)
// gasPrice: 20000000000, // 20 gwei (in wei) (default: 100 gwei)
// from: <address>, // Account to send txs from (default: accounts[0])
// websocket: true // Enable EventEmitter interface for web3 (default: false)
// },
// Useful for deploying to a public network.
// NB: It's important to wrap the provider as a function.
// ropsten: {
// provider: () => new HDWalletProvider(mnemonic, `https://ropsten.infura.io/v3/YOUR-PROJECT-ID`),
// network_id: 3, // Ropsten's id
// gas: 5500000, // Ropsten has a lower block limit than mainnet
// confirmations: 2, // # of confs to wait between deployments. (default: 0)
// timeoutBlocks: 200, // # of blocks before a deployment times out (minimum/default: 50)
// skipDryRun: true // Skip dry run before migrations? (default: false for public nets )
// },
// Useful for private networks
// private: {
// provider: () => new HDWalletProvider(mnemonic, `https://network.io`),
// network_id: 2111, // This network is yours, in the cloud.
// production: true // Treats this network as if it was a public net. (default: false)
// }
},
// Set default mocha options here, use special reporters etc.
mocha: {
// timeout: 100000
},
// Configure your compilers
compilers: {
solc: {
version: "0.7.1", // Fetch exact version from solc-bin (default: truffle's version)
// docker: true, // Use "0.5.1" you've installed locally with docker (default: false)
// settings: { // See the solidity docs for advice about optimization and evmVersion
// optimizer: {
// enabled: false,
// runs: 200
// },
// evmVersion: "byzantium"
// }
}
}
};
我们还可以定义构造区块链时的gasLimit,使用from字段定义使用的账户(默认使用第0个账户),在compilers中,还可以指定编译器版本。
学习另一个实用智能合约 Ballot
在 Solidity 的文档中给出了一个实现投票的智能合约,请注意,这个 sol 文件需要 0.7.0 以上的编译器版本才能编译:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
pragma solidity >=0.7.0 <0.9.0;
// 请注意,这个sol文件需要0.7.0以上的编译器版本才能编译
/// @title Voting with delegation.
contract Ballot {
// This declares a new complex type which will
// be used for variables later.
// It will represent a single voter.
struct Voter {
uint weight; // weight is accumulated by delegation
bool voted; // if true, that person already voted
address delegate; // person delegated to
uint vote; // index of the voted proposal
}
// This is a type for a single proposal.
struct Proposal {
bytes32 name; // short name (up to 32 bytes)
uint voteCount; // number of accumulated votes
}
address public chairperson;
// This declares a state variable that
// stores a `Voter` struct for each possible address.
mapping(address => Voter) public voters;
// A dynamically-sized array of `Proposal` structs.
Proposal[] public proposals;
/// Create a new ballot to choose one of `proposalNames`.
constructor(bytes32[] memory proposalNames) {
chairperson = msg.sender;
voters[chairperson].weight = 1;
// For each of the provided proposal names,
// create a new proposal object and add it
// to the end of the array.
for (uint i = 0; i < proposalNames.length; i++) {
// `Proposal({...})` creates a temporary
// Proposal object and `proposals.push(...)`
// appends it to the end of `proposals`.
proposals.push(Proposal({
name: proposalNames[i],
voteCount: 0
}));
}
}
// Give `voter` the right to vote on this ballot.
// May only be called by `chairperson`.
function giveRightToVote(address voter) public {
// If the first argument of `require` evaluates
// to `false`, execution terminates and all
// changes to the state and to Ether balances
// are reverted.
// This used to consume all gas in old EVM versions, but
// not anymore.
// It is often a good idea to use `require` to check if
// functions are called correctly.
// As a second argument, you can also provide an
// explanation about what went wrong.
require(
msg.sender == chairperson,
"Only chairperson can give right to vote."
);
require(
!voters[voter].voted,
"The voter already voted."
);
require(voters[voter].weight == 0);
voters[voter].weight = 1;
}
/// Delegate your vote to the voter `to`.
function delegate(address to) public {
// assigns reference
Voter storage sender = voters[msg.sender];
require(!sender.voted, "You already voted.");
require(to != msg.sender, "Self-delegation is disallowed.");
// Forward the delegation as long as
// `to` also delegated.
// In general, such loops are very dangerous,
// because if they run too long, they might
// need more gas than is available in a block.
// In this case, the delegation will not be executed,
// but in other situations, such loops might
// cause a contract to get "stuck" completely.
while (voters[to].delegate != address(0)) {
to = voters[to].delegate;
// We found a loop in the delegation, not allowed.
require(to != msg.sender, "Found loop in delegation.");
}
// Since `sender` is a reference, this
// modifies `voters[msg.sender].voted`
sender.voted = true;
sender.delegate = to;
Voter storage delegate_ = voters[to];
if (delegate_.voted) {
// If the delegate already voted,
// directly add to the number of votes
proposals[delegate_.vote].voteCount += sender.weight;
} else {
// If the delegate did not vote yet,
// add to her weight.
delegate_.weight += sender.weight;
}
}
/// Give your vote (including votes delegated to you)
/// to proposal `proposals[proposal].name`.
function vote(uint proposal) public {
Voter storage sender = voters[msg.sender];
require(sender.weight != 0, "Has no right to vote");
require(!sender.voted, "Already voted.");
sender.voted = true;
sender.vote = proposal;
// If `proposal` is out of the range of the array,
// this will throw automatically and revert all
// changes.
proposals[proposal].voteCount += sender.weight;
}
/// @dev Computes the winning proposal taking all
/// previous votes into account.
function winningProposal() public view
returns (uint winningProposal_)
{
uint winningVoteCount = 0;
for (uint p = 0; p < proposals.length; p++) {
if (proposals[p].voteCount > winningVoteCount) {
winningVoteCount = proposals[p].voteCount;
winningProposal_ = p;
}
}
}
// Calls winningProposal() function to get the index
// of the winner contained in the proposals array and then
// returns the name of the winner
function winnerName() public view
returns (bytes32 winnerName_)
{
winnerName_ = proposals[winningProposal()].name;
}
// 以下为作者新添加的两个函数
function getProposalName(uint index) public view returns (bytes32) {
require(index < proposals.length, "No This Proposal");
require(index >= 0, "Not a positive Number");
return proposals[index].name;
}
function getProposalVoteCount(uint index) public view returns (uint) {
require(index < proposals.length, "No this Proposal");
require(index >= 0, "Not a positive Number");
return proposals[index].voteCount;
}
}
这个智能合约实现了基本的投票功能,分析构造函数,我们知道该合约部署时需要传入一个bytes32[]参数,是一个由被选举人构成的列表,构造函数还将msg.sender设置为新变量chairperson;
结构体Voter代表一个投票人,其中包含权重、是否已投票、该投票人的委托投票人,以及投票投给了谁;
结构体Proposal代表一个被选举人,包含名字、得票数量;
函数giveRightToVote只能被 chairperson 调用,接受一个参数 voter,如果这个 voter 还没有投过票,并且这个 voter 还没有投票权,则赋予其投票权;
函数delegate是一个委托投票权的函数,允许投票人将自己的投票权委托给另一个人;
函数vote 是投票函数,拥有投票权的投票人可以为被选举人投票;
函数winningProposal 计算得票数最高的被选举人,返回其编号;
函数winnerName通过上个函数的编号,返回被选举人的名字;
函数getProposalName 和getProposalVoteCount 返回被选举人的名字和其当前得票数量。
3.1 准备
新建一个Vote文件夹,要创建一个空的truffle项目,在终端内运行:
truffle init
可以看到文件夹内产生了一些变化:
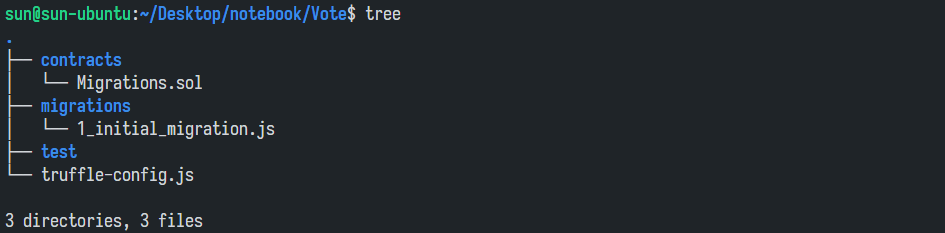
我们在contracts文件夹内新建Ballot.sol,复制上述的投票智能合约代码;
在migrations文件夹内新建2_deploy_contracts.js文件:
const Ballot = artifacts.require("Ballot");
module.exports = function(deployer) {
deployer.deploy(
Ballot,
[
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000",
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001",
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002",
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003"
]
);
};
部署Ballot智能合约时,其构造函数需要传入一个bytes32[] 类型的参数,代表被选举人。Truffle会在部署智能合约时为其传入这个参数。
打开truffle-config.js文件,修改配置,接下来我们使用可视化工具Ganache观察区块链变化。首先设置网络,新建一个ganache网络,为了与之后的Ganache做适配:
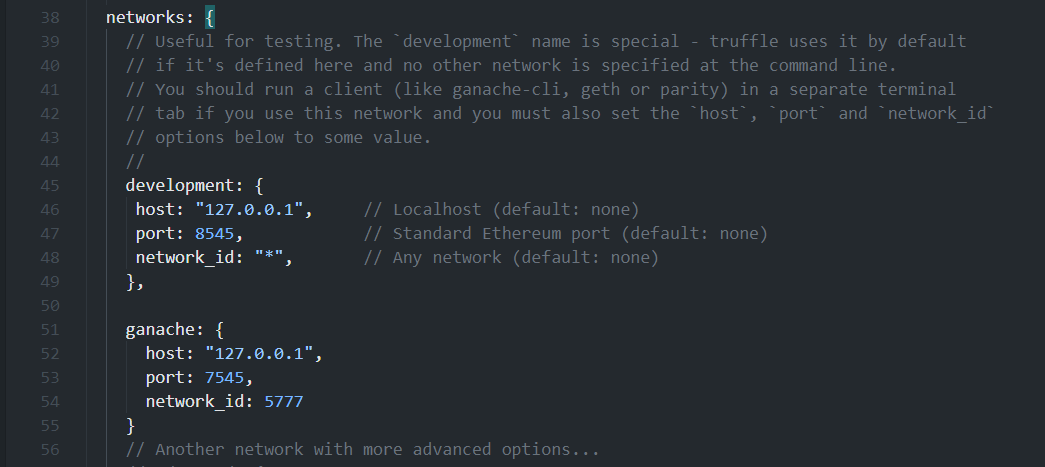
同时为了匹配0.7.0以上的编译器版本,修改compiler字段:
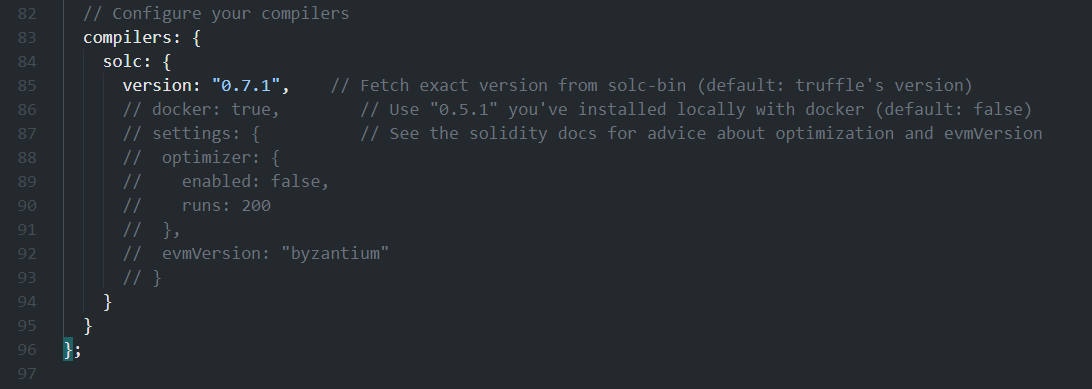
最后的目录长这样:

3.2 交互
打开 Ganache,选 Quickstart,可以看到 Ganache 也会帮我们生成一条区块链,并预先设置 10 个账户,每个账户内含 100 ETH。
我们点击右上角的齿轮按钮进入设置:
点击ADD PROJECT,选择truffle-config.js 文件,加载我们的Truffle项目
在 Server 菜单中,可以看到 Ganache 生成的区块链的地址、开放的 RPC 端口,NetworkID 等,这些值与我们刚刚创建好的 Ganache 网络配置匹配,稍后可以使用 truffle 命令部署智能合约:
点击SAVE AND RESTART 保存更改。在 CONTRACTS 菜单中,提示我们需要使用 Truffle 部署智能合约:
打开终端,输入以下命令:
truffle migrate --network ganache
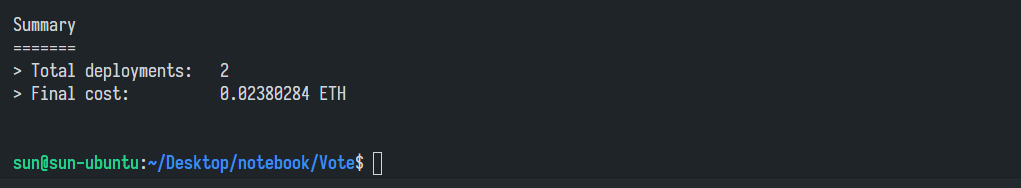
合约成功部署:
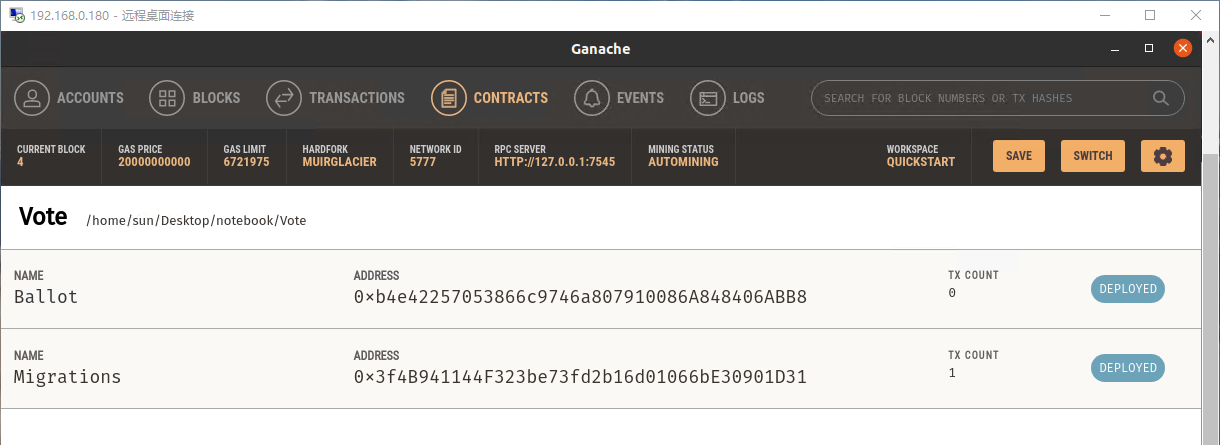
部署合约需要消耗 ETH,查看ACCOUNTS可以看到默认的第 0 个账户消耗掉 0.02380284 个 ETH:
BLOCK 和 TRANSACTIONS 记录了区块链和交易,可以查看学习。
Ganache 本身不具备 web3 交互,因此要使用合约,还需要进入 Truffle 控制台进行操作:
truffle console --network ganache
第一步依然是获得刚刚部署过的智能合约的实例:
truffle(ganache)> let instance = await Ballot.deployed()
undefined
truffle(ganache)> instance.address
'0xb4e42257053866c9746a807910086A848406ABB8'
可以看到这个智能合约实例地址与 Ganache 显示的地址是一致的。
由于目前第0个账户是部署合约的账户,因此 chairperson 的地址应该为第0个账户的地址。同时,由于我们在进入控制台之前没有设置使用的账户,因此默认控制台正在使用的也是第0个账户。
现在我们有权利为其他账户赋予投票权利,我们当然可以直接在 Ganache 内抄下某个账户地址,也可以使用 web3 获得账户地址:
truffle(ganache)> let allAccounts = web3.eth.getAccounts()
undefined
truffle(ganache)> allAccounts
[ '0x78087a3fDd3Ad30Dc23dF8a80eA6fE81Db1b7fbb',
'0xB7D53a71a1a8A45C9F1DF152cf6DB0F5805261B6',
'0x605227a90d1566EEeC77AE2e36Ad48dcAe5d6CD4',
'0x8c4491074a1623A96D62288FCA0aFeD73Ab710e3',
'0xaB750d95277e2Cd67bA1Effd00d2cb8319170620',
'0xd619b30e8f019569D59fe6aD557e52E5302F227f',
'0x5BB81474c351a28507DD5317F4023088b8912f41',
'0xb5528106D4c92262C3da2d3E29282fd1687eAAA6',
'0xf79a3C4a0881F879Ddf5D18beB37e5B5767aEFED',
'0xf3e67be6A334CB438282BCB09A57d7A92eacE03f' ]
将投票权赋予账户'0xB7D53a71a1a8A45C9F1DF152cf6DB0F5805261B6':
instance.giveRightToVote('0xB7D53a71a1a8A45C9F1DF152cf6DB0F5805261B6')
此时发生了一笔交易,在Ganache内也可以同步查看:
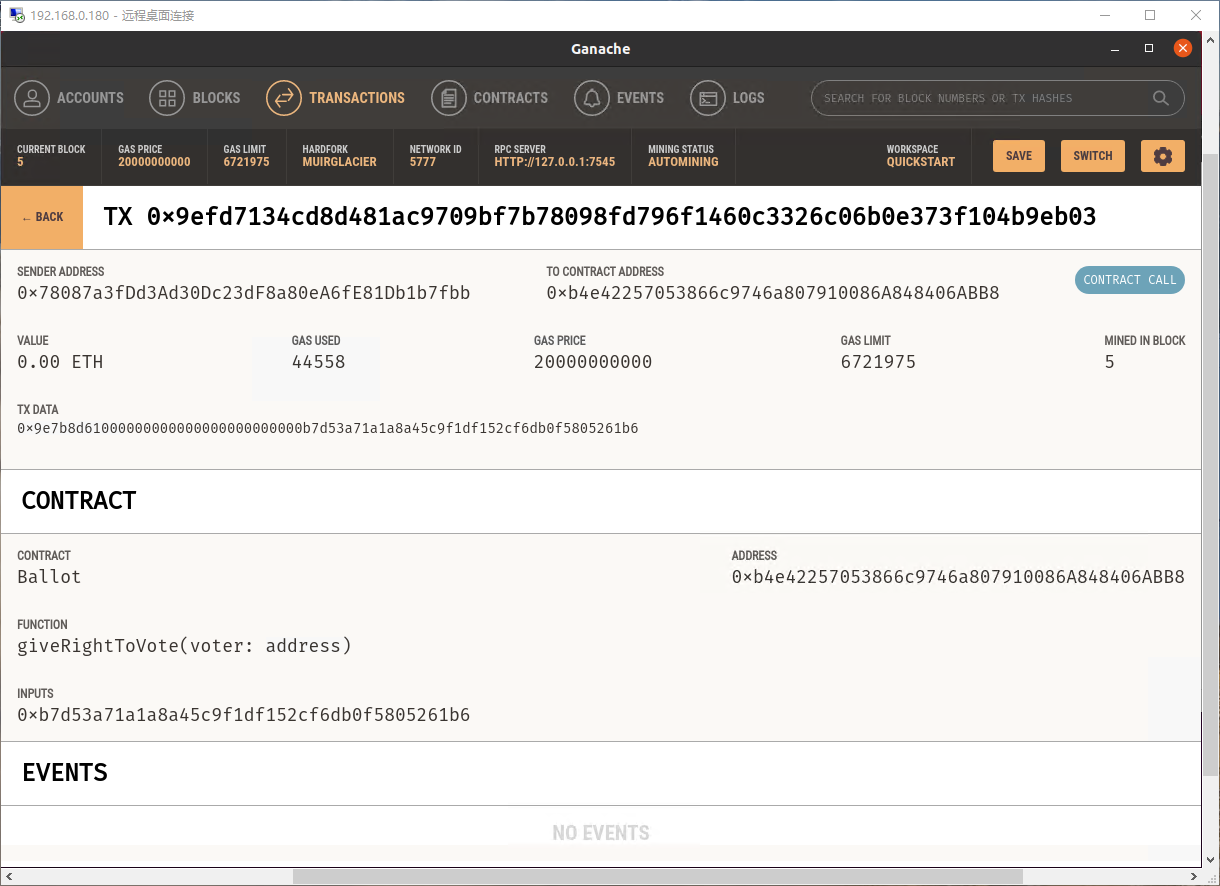
目前账户 '0xB7D53a71a1a8A45C9F1DF152cf6DB0F5805261B6' 获得了投票权,现在怎么使用该账户为某个被选举人投票呢?
刚才我们提到,默认进入truffle控制台会使用第0个账户,要切换账户,需要修改网络配置文件。我们首先退出目前的控制台,修改truffle-config.js文件:
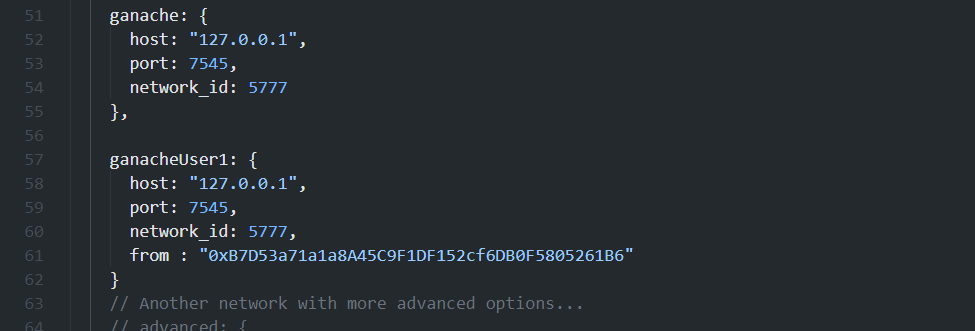
新建一个 ganacheUser1 配置,指定 from 地址,使用此网络配置文件重新进入控制台:
truffle console --network ganacheUser1
使用投票函数 vote,为某个被选举人投票,当然首先还是需要获得智能合约实例:
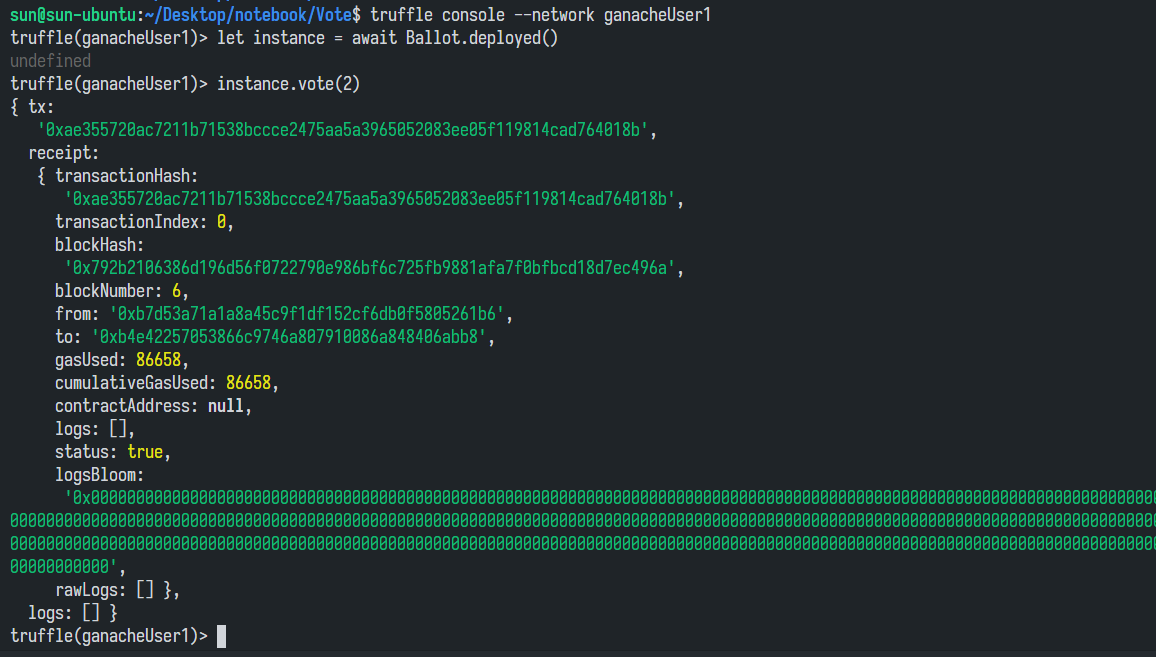
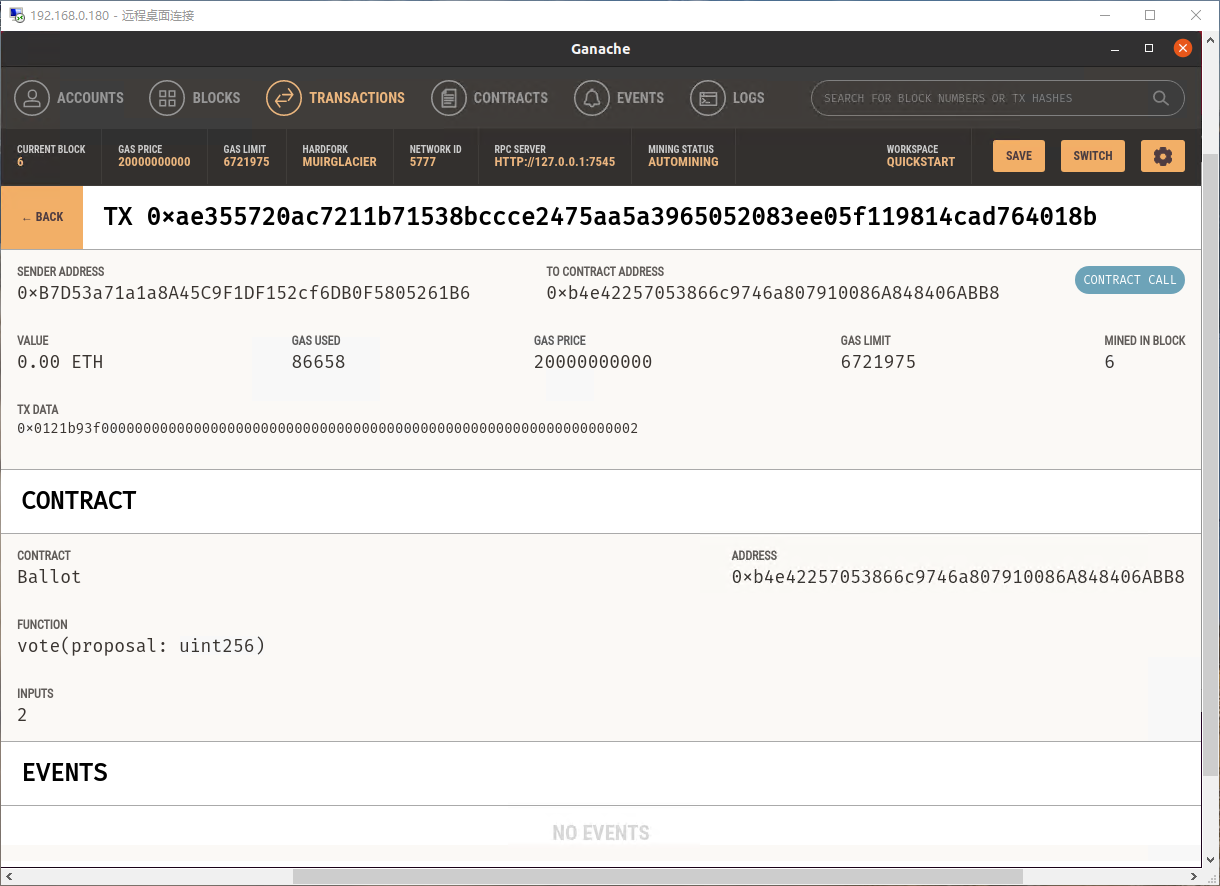
投票成功了。我们同时可以在 Ganache 内看到交易信息和区块信息:
使用 winnerName 函数查看得票数最高的被选举人:
truffle(ganacheUser1)> instance.winnerName()
'0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002'
总结
相比于Remin编辑器,Truffle套件为我们提供了完整的以太坊区块链智能合约开发系统,其自带的develop模块可以直接生成容易上手的区块链,比geth更加简单。Ganache是Truffle套件内的可视化应用程序,帮助我们直观地查看交易和区块变化。
通过亲自部署智能合约,与智能合约进行交互,可以快速理解Solidity语言的用法。
📖其他参考文档:
详解 Solidity 事件Event - 完全搞懂事件的使用 - Tiny熊 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
testrpc - truffle always says ".my_function is not a function" - Ethereum Stack Exchange
智能合约概述 — Solidity develop 文档 (solidity-cn.readthedocs.io)
Solidity by Example — Solidity 0.8.1 documentation (soliditylang.org)
快速入门 Truffle | Truffle 中文文档 - DApp 开发框架 | 深入浅出区块链 (learnblockchain.cn)
How to switch account from default in testrpc - Ethereum Stack Exchange


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号