设计模式:适配器模式
一:适配器模式的定义
适配器模式:将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另一个接口。适配器模式让那些接口不兼容的类可以一起工作
Adapter Pattern:Convert the interface of a class into another interface clients expect.Adapter lets classes work together that couldn't otherwise because of incompatible interface.
适配器模式的别名为包装器(Wrapper)模式,它既可以作为类结构型模式,也可以作为对象结构型模式。在适配器模式定义中所提及的接口是指广义的接口,它可以表示一个方法或者方法的集合。
二:适配器模式的结构
类适配器模式结构图:

对象适配器结构图:
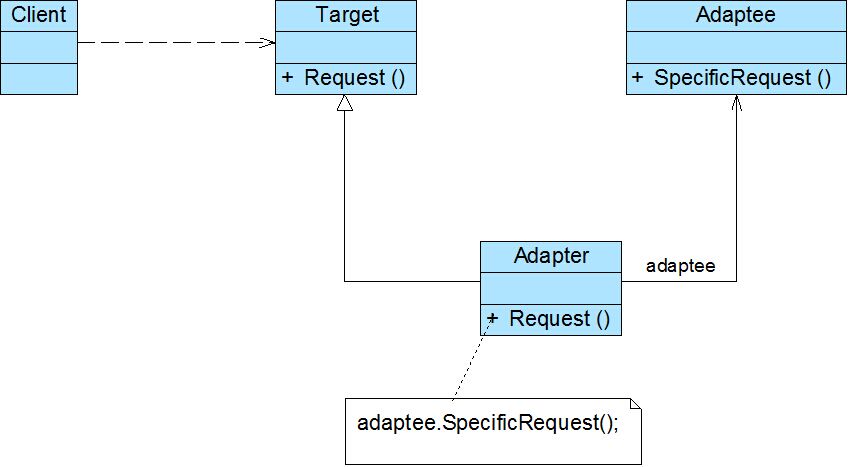
由图可知适配器模式包含一下三个角色:
1:Target(目标抽象类):目标抽象类定义客户所需的接口,可以是一个抽象类或接口,也可以是具体类。在类适配器中,由于C#语言不支持多重继承,所以它只能是接口。
2:Adapter(适配器类):它可以调用另一个接口,作为一个转换器,对Adaptee和Target进行适配。它是适配器模式的核心。
3:Adaptee(适配者类):适配者即被适配的角色,它定义了一个已经存在的接口,这个接口需要适配,适配者类包好了客户希望的业务方法。
三:适配器模式的实现
1:类适配器
class Adapter : Adaptee, Target { public void Request() { base.SpecificRequest(); } }
2:对象适配器
class Adapter : Target { private Adaptee adaptee; //维持一个对适配者对象的引用 public Adapter(Adaptee adaptee) { this.adaptee = adaptee; } public void Request() { adaptee.SpecificRequest();//转发调用 } }
注意:在实际开发中对象适配器的使用频率更高。
四:适配器模式的应用
在为某学校开发教务管理系统时,开发人员发现需要对学生成绩进行排序和查找,该系统的设计人员已经开发了一个成绩操作接口ScoreOperation,在该接口中声明了排序方法Sort(int[]) 和查找方法Search(int[], int),为了提高排序和查找的效率,开发人员决定重用现有算法库中的快速排序算法类QuickSortClass和二分查找算法类BinarySearchClass,其中QuickSortClass的QuickSort(int[])方法实现了快速排序,BinarySearchClass的BinarySearch (int[], int)方法实现了二分查找。
由于某些原因,开发人员已经找不到该算法库的源代码,无法直接通过复制和粘贴操作来重用其中的代码;而且部分开发人员已经针对ScoreOperation接口编程,如果再要求对该接口进行修改或要求大家直接使用QuickSortClass类和BinarySearchClass类将导致大量代码需要修改。
现使用适配器模式设计一个系统,在不修改已有代码的前提下将类QuickSortClass和类BinarySearchClass的相关方法适配到ScoreOperation接口中。
结构如下图所示:
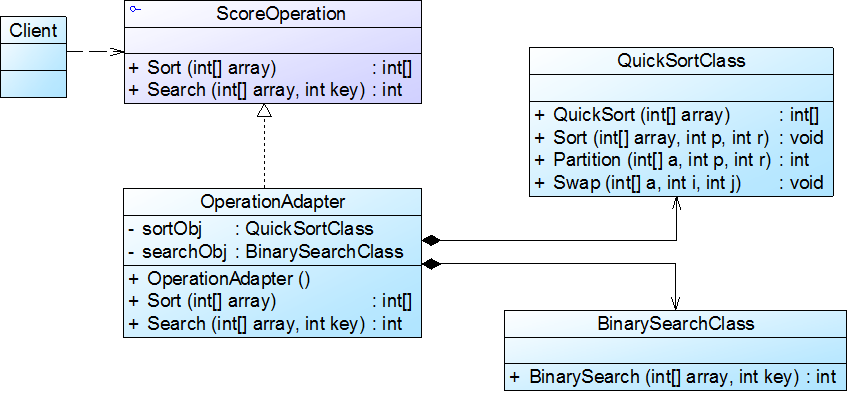
ScoreOperation接口充当抽象目标,QuickScortClass和BinarySearchClass充当适配者,OperationAdapter充当适配器。
(1)ScoreOperation:抽象成绩操作类,充当目标接口
public interface ScoreOperation { int[] Sort(int[] array); //成绩排序 int Search(int[] array, int key); //成绩查找 }
(2)QuickSortClass:快速排序类,充当适配者
public class QuickSortClass { public int[] QuickSort(int[] array) { Sort(array, 0, array.Length - 1); return array; } public void Sort(int[] array, int p, int r) { int q = 0; if(p < r) { q = Partition(array, p, r); Sort(array, p, q - 1); Sort(array, q + 1, r); } } public int Partition(int[] array, int p, int r) { int x = array[r]; int j = p - 1; for (int i = p; i <= r - 1; i++) { if(array[i] <= x) { j++; Swap(array, j, i); } } Swap(array, j + 1, r); return j + 1; } public void Swap(int[] array, int i, int j) { int t = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = t; } }
(3)BinarySearchClass:二分查找类,充当适配者
public class BinarySearchClass { public int BinarySearch(int[] array, int key) { int low = 0; int high = array.Length - 1; while (low <= high) { int mid = (low + high) / 2; int midVal = array[mid]; if (midVal < key) low = mid + 1; else if (midVal > key) high = mid - 1; else return 1; //找到元素返回1 } return -1; //未找到元素返回-1 } }
(4)OperationAdapter:操作适配器,充当适配器
public class OperationAdapter : ScoreOperation { //定义适配者QuickSortClass对象 private QuickSortClass sortObj; //定义适配者BinarySearchClass对象 private BinarySearchClass searchObj; public OperationAdapter() { sortObj = new QuickSortClass(); searchObj = new BinarySearchClass(); } public int Search(int[] array, int key) { return searchObj.BinarySearch(array, key); } public int[] Sort(int[] array) { return sortObj.QuickSort(array); } }
(5)配置文件App.config:在配置文件中存储了适配器类的类名
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <configuration> <startup> <supportedRuntime version="v4.0" sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.5.2" /> </startup> <appSettings> <add key="adapter" value="Model.AdapterSample.OperationAdapter"/> </appSettings> </configuration>
(6)Program:客户端测试类
static void Main(string[] args) { ScoreOperation operation; //读取配置文件 string adapterType = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["adapter"]; //通过反射生成对象 operation = (ScoreOperation)Assembly.Load("Model.AdapterSample").CreateInstance(adapterType); int[] socres = { 84,76, 50, 69, 90, 92, 88, 86 }; int[] result; int score; Console.WriteLine("程序的排序结果是:"); result = operation.Sort(socres); //遍历输出成绩 foreach (var item in result) Console.Write(item+","); Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("查找成绩90:"); score = operation.Search(result, 90); if(score!=-1) Console.WriteLine("找到成绩90."); else Console.WriteLine("没有找到成绩90。"); Console.WriteLine("查找成绩92:"); score = operation.Search(result, 920); if(score!=-1) Console.WriteLine("找到成绩92."); else Console.WriteLine("没有找到成绩92。"); Console.ReadKey(); }
五:适配器模式的优缺点
优点:
1:将目标类和适配者类解耦,通过引入一个适配器类来重用现有的适配者类,无需修改原有结构。
2:增加了类的透明性和复用性,将具体的业务实现过程封装在适配者类中,对于客户端类而言是透明的,而且提高了适配者的复用性,同一适配者类可以在多个不同的系统中复用。
3:灵活性和扩展性都非常好,通过使用配置文件,可以很方便的更换适配器,也可以在不修改原有代码的基础上 增加新的适配器,完全复合开闭原则。
缺点:
1:一次最多只能适配一个适配者类,不能同时适配多个适配者。
2:适配者类不能为最终类,在C#中不能为sealed类
3:目标抽象类只能为接口,不能为类,其使用有一定的局限性。
六:适配器模式的适用环境
系统需要使用一些现有的类,而这些类的接口不符合系统的需要,甚至没有这些类的源代码
创建一个可以重复使用的类,用于和一些彼此之间没有太大关联的类,包括一些可能在将来引进的类一起工作
七:缺醒适配器模式
缺醒适配器模式(Default Adapter Pattern):当不需要实现一个接口所提供的所有方法时,可先设计一个抽象类实现该接口,并为接口中的每个方法提供一个默认实现(空方法),那么该抽象类可以有选择性的覆盖父类的某些方法来实现需求,它适用于不想使用一个接口中的所有方法的情况,又称为单接口适配器模式。
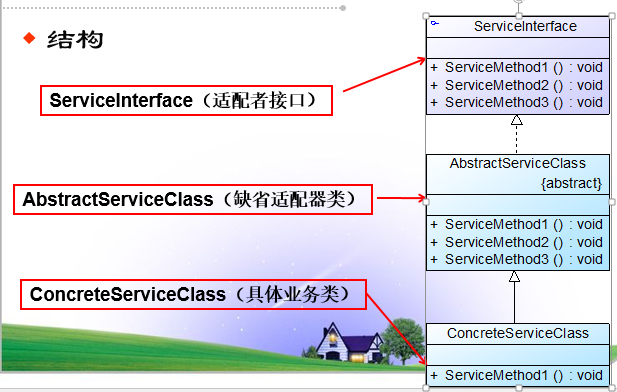
由图可知,在缺醒适配器模式中,包含以下三个角色:
1:ServiceInsterface(适配者接口):它是一个接口,通常在该接口中声明了大量的方法
2:AbstractServiceClass(缺醒适配器类):它是缺醒适配器模式的核心类,使用空方法的形式实现了ServiceInterface接口中声明的方法。通常将它定义为抽象类,因为对它进行实例化也没有任何意义。
3:ConcreteServiceClass(具体业务类):它是缺醒适配器的子类,在没有引入适配器之前,它需要实现适配者接口,因此需要实现在适配者接口中生命的所有方法,而对于一些无需使用的方法不得不提供空实现。有了缺醒适配器之后,可以直接继承该适配器类,根据需要有选择性的覆盖配置器类中定义的方法。
八:双向适配器
在对象适配器中如果同时包含目标类和适配者类的引用,适配者可以通过它调用目标类中的方法,目标类也可以通过它调用适配者类中的方法,那么该适配器就是一个双向适配器。
双向适配器结构示意图:
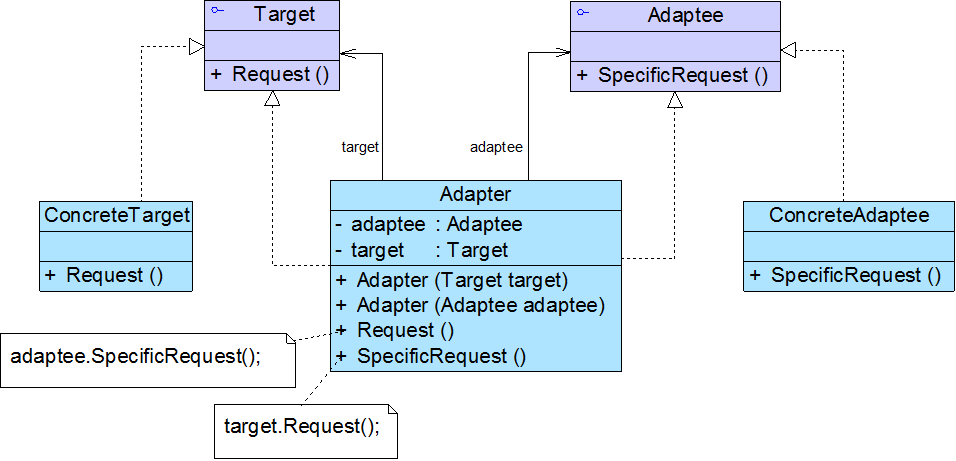
示意代码:
public class Adapter:Target,Adaptee { //同时维持对抽象目标类和适配者类的引用 private Target target; private Adaptee adaptee; public Adapter(Target target) { this.target = target; } public Adapter(Adaptee adatee) { this.adaptee = adatee; } public void Reqeust() { this.adaptee.SpecificRequest(); } public void SpecificRequest() { this.target.Request(); } }
posted on 2015-09-13 23:40 Sunshine 阅读(57810) 评论(1) 编辑 收藏 举报



