Vue基础学习笔记
文章目录
- 🚙Vue基础🚙
- 一、Vue入门
- 二、Vue列表展示
- 三、Vue计数器
- 四、Vue的MVVM
- 五、options选项
- 六、Vue的生命周期🛴
- 七、vue的template
- 八、Mustache插值语法
- 九、v-once
- 十、v-html
- 十一、v-text
- 十二、v-pre
- 十三、v-cloak
- 十四、v-bind基本使用🚜
- 十五、v-bind动态绑定class属性(对象语法)🚜
- 十六、v-bind动态绑定class属性(数组语法)🚜
- 十七、作业
- 十八.v-bind(style对象属性)
- 十九.v-bind(style数组属性)
- 二十.计算属性
- 二十一.计算属性的复杂操作
- 二十二.计算属性getter、setter
- 二十三.计算属性computed和methods的对比
- 二十四.es6语法
- 二十五.v-on
- 二十六.v-on参数
- 二十七.v-on修饰符
- 二十八.v-if、v-else-if、v-else
- 二十九.案例(切换)
- 三十.input复用(问题)
- 三十一.v-show
- 三十二.v-for
- 三十三.组件的key属性
- 三十四.数组方法
- 三十五.图书购物车
- 三十六.v-model
- 三十七.v-model结合radio
- 三十八.v-model结合checkbox
- 三十九.v-model结合select
- 四十.值绑定
- 四十一.修饰符
- 推荐Vscode编译器、vue官网:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/installation.html
🚙Vue基础🚙
一、Vue入门
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{message}}
{{name}}
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// let(变量)/const(常量)
//声明式编程
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: "你好啊,李银河!",
name: "codewhy"
}
})
//原始js的做法(命令式编程)
// 1. 创建div元素,设置id属性
// 2.定义一个变量message
// 3.将message变量放在前面的div元素中显示
// 4.修改message的数据:今天天气不错
// 5.将修改后的数据再次替换到div
</script>
</body>
</html>

二、Vue列表展示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in movies">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: "你好啊!",
movies: ['星际穿越','大话西游','少年派','盗梦空间']
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
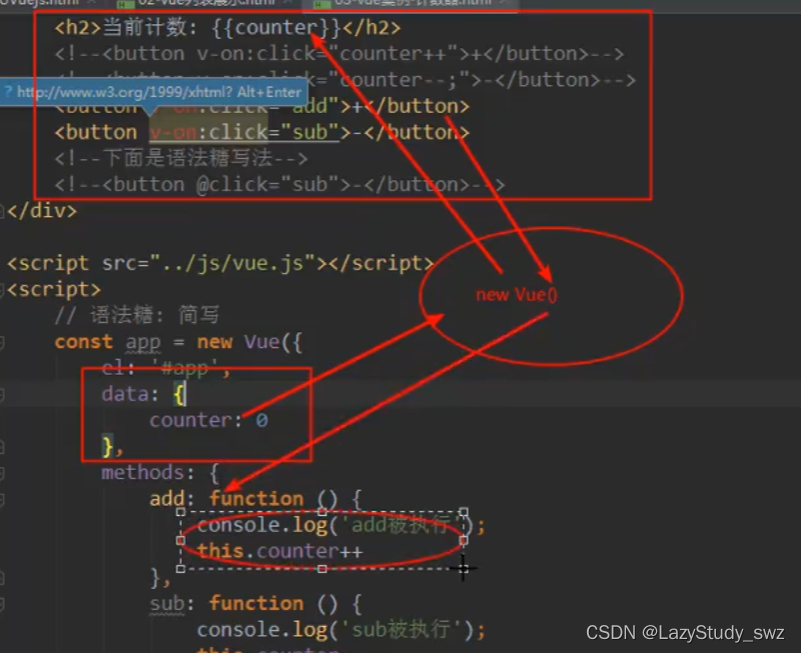
三、Vue计数器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>当前计数:{{counter}}</h2>
<!-- 1.简单的可以这样写 -->
<!-- <button v-on:click="counter++">+</button>
<button v-on:click="counter--">-</button> -->
<!-- 2.复杂的监听这样写 -->
<button v-on:click="add">+</button>
<button v-on:click="sub">-</button>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
counter: 0
},
methods:{
add:function(){
this.counter++;
console.log("add被执行");
},
sub:function(){
this.counter--;
console.log("sub被执行");
}
}
})
//以前:
//1.拿button
//2.添加监听
</script>
</body>
</html>

- 语法糖:v-on:click === @click
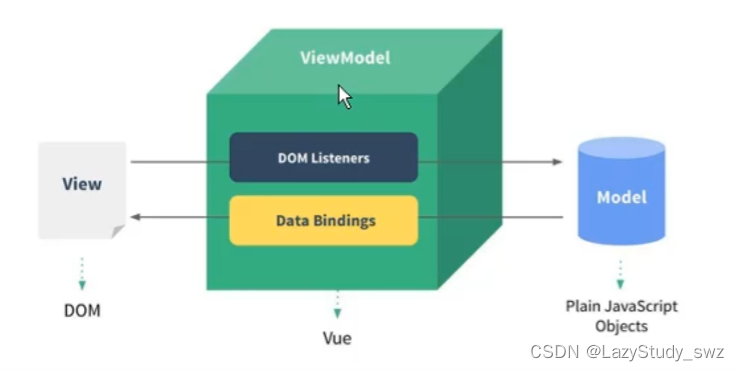
四、Vue的MVVM
五、options选项

注:开发中什么时候称之为方法,什么时候称之为 函数?
- 方法—定义在类中;函数—定义在外面
六、Vue的生命周期🛴
- 生命周期:事务从诞生到消亡的整个过程
- 源码下载:https://github.com/vuejs/vue/tree/v2.6.14
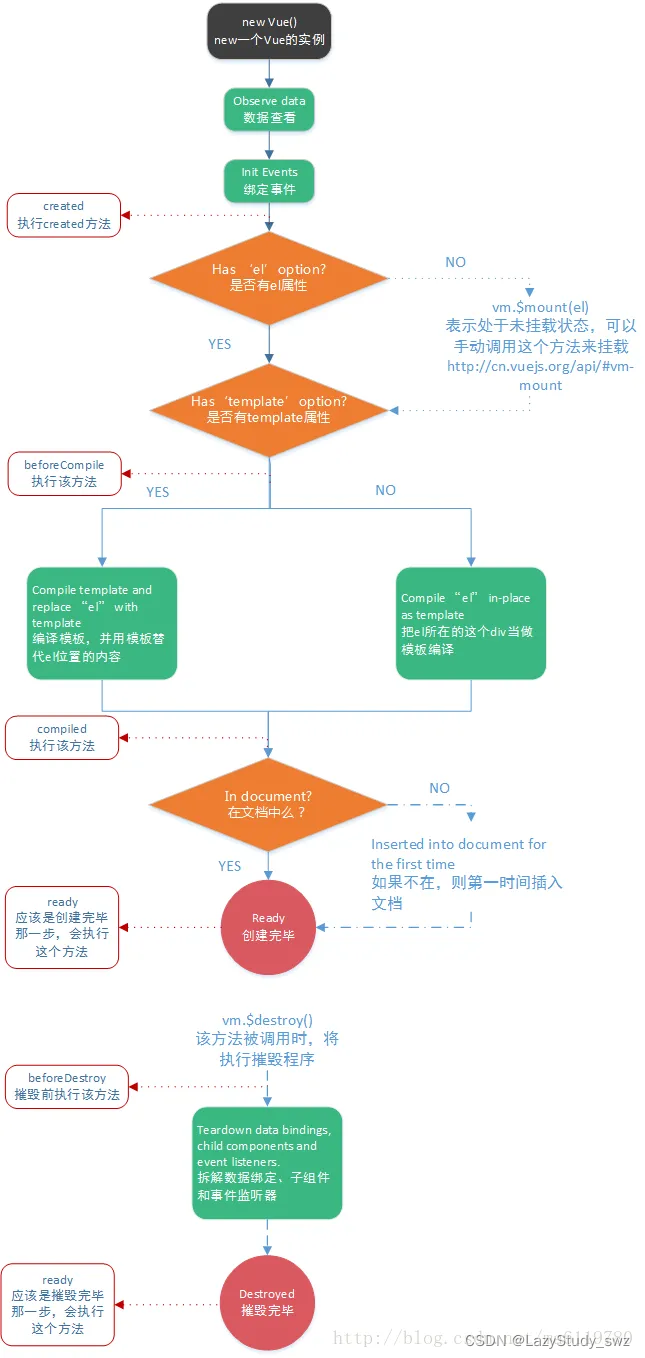
- 注:在生命周期中,我们可以自己根据的需要求,编写回调函数。
七、vue的template
前端代码规范:缩进两个空格
打开:文件—首选项—用户片段—新建
{
// Place your 全局 snippets here. Each snippet is defined under a snippet name and has a scope, prefix, body and
// description. Add comma separated ids of the languages where the snippet is applicable in the scope field. If scope
// is left empty or omitted, the snippet gets applied to all languages. The prefix is what is
// used to trigger the snippet and the body will be expanded and inserted. Possible variables are:
// $1, $2 for tab stops, $0 for the final cursor position, and ${1:label}, ${2:another} for placeholders.
// Placeholders with the same ids are connected.
// Example:
// "Print to console": {
// "scope": "javascript,typescript",
// "prefix": "log",
// "body": [
// "console.log('$1');",
// "$2"
// ],
// "description": "Log output to console"
// }
"vue": {
"prefix": "vue",
"body": [
"<!DOCTYPE html>",
"<html lang='en'>",
"<head>",
" <meta charset='UTF-8'>",
" <meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>",
" <title>Document</title>",
"</head>",
"<body>",
"<div id='app'>",
" {{message}}",
"</div>",
"<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>",
"<script>",
" const app = new Vue({",
" el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素",
" data:{ //定义数据",
" message: '你好啊,李银河!',",
" name: 'codewhy'",
" }",
" })",
"</script>",
"</body>",
"</html>",
],
"description": "vue实例对象"
}
}
使用:直接输入prefix的值,回车即可。
八、Mustache插值语法
注:大括号插值法{{message}}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- mustache语法,不仅仅可以直接写变量,也可以写简单的表达式 -->
{{firstname + " "+ lastname}}
{{counter * 2}}
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
firstname: 'codewhy',
lastname: 'byy',
counter: 100
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
九、v-once
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<h2>{{message}}</h2>
<h2 v-once>{{message}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
注:只在第一次渲染,后面不会渲染。
十、v-html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<h2 >{{url}}</h2>
<h2 v-html="url"></h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
url: '<a href="www.baidu.com">百度一下</a>'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
注:解析标签
十一、v-text
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<h2 v-text="message"></h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
注:不推荐,不灵活,不如Mustache
十二、v-pre
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<h2 v-pre>{{message}}</h2>
<h2>{{message}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
注:原封不动的显示,不解析数据
十三、v-cloak
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
[v-cloak]{
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app' v-cloak>
{{message}}
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
//在vue解析之前,div中有一个属性v-cloak
//在vue解析之后,div中没有一个属性v-cloak
setTimeout(function(){
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy'
}
})
},1000)
</script>
</body>
</html>
注:因为html从头到尾渲染,为了避免某些数据来不及渲染,我们可以通过v-cloak来设置style属性,没有渲染成功之前,显示为空,而不是直接是{{message}}。
十四、v-bind基本使用🚜

注:前面主要针对模板的内容,属性需要v-bind
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- 这里是错误的,不可以使用mustache语法 -->
<!-- <img src="{{imgurl}}" alt=""> -->
<!-- 正确做法 -->
<img v-bind:src="imgurl" alt="">
<a v-bind:href="aHref" >百度一下</a>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
imgurl: "https://pic4.zhimg.com/v2-589b604591675be07573676ddcab2ff4_720w.jpg?source=d6434cab",
aHref: 'https://www.baidu.com'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 语法糖:直接写
:
十五、v-bind动态绑定class属性(对象语法)🚜
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.active{
color:red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- 字符串没有意义 -->
<!-- <h2 class="active">{{message}}</h2>
<h2 :class="active">{{message}}</h2> -->
<!-- 对象绑定,有意义 -->
<!-- <h2 :class="{类名1:boolean,类名2:boolean}">{{message}}</h2> -->
<h2 class="title" :class="{active:isActive,line:isLine}">{{message}}</h2>
<button v-on:click="btnClick">按钮</button>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
isActive: true,
isLine: true,
},
methods:{
btnClick:function(){
this.isActive = !this.isActive
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
简化:当class属性太长的时候
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.active{
color:red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- 字符串没有意义 -->
<!-- <h2 class="active">{{message}}</h2>
<h2 :class="active">{{message}}</h2> -->
<!-- 对象绑定,有意义 -->
<!-- <h2 :class="{类名1:boolean,类名2:boolean}">{{message}}</h2> -->
<h2 class="title" :class="getClasses()">{{message}}</h2>
<button v-on:click="btnClick">按钮</button>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
isActive: true,
isLine: true,
},
methods:{
btnClick:function(){
this.isActive = !this.isActive
},
getClasses:function(){
return {active:this.isActive,line:this.isLine}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
十六、v-bind动态绑定class属性(数组语法)🚜
意义不大,原始的class即可完成,有时候变量可能需要。
十七、作业
注:点击变色
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.active{
color:red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<ul>
<li :class="{active:isActive==index}" v-on:click="colorChoose(index)" v-for="(item,index) in movies">
{{index}}--------- {{item}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
movies: ['夏洛特烦恼','大话西游','桃姐','人世间'],
isActive: 0
},
methods:{
colorChoose:function(index){
this.isActive = index;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
十八.v-bind(style对象属性)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- <h2 :style="{key(属性值):value(属性值)}">{{message}}</h2> -->
<h2 :style="{fontSize:finalSize,color:finalColor}">{{message}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
finalSize: '50px',
finalColor: 'red'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
函数方法改进:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- <h2 :style="{key(属性值):value(属性值)}">{{message}}</h2> -->
<h2 :style="getStyles()">{{message}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
finalSize: '50px',
finalColor: 'red'
},
methods:{
getStyles:function(){
return {fontSize:this.finalSize,color:this.finalColor};
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
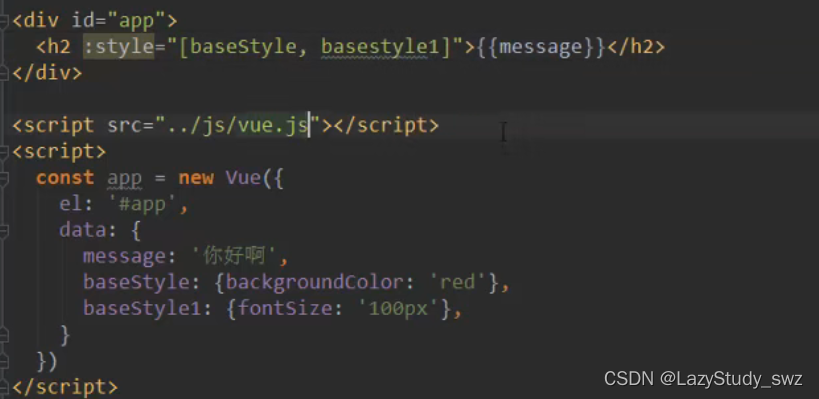
十九.v-bind(style数组属性)
了解即可
二十.计算属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<h2>{{firstname}}{{lastname}}</h2>
<h2>{{getFullName()}}</h2>
<h2>{{fullName}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
firstname: 'a',
lastname: 'b',
},
methods:{
getFullName(){
return this.firstname + this.lastname;
}
},
//计算属性
computed: {
fullName:function(){
return this.firstname + this.lastname;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
二十一.计算属性的复杂操作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<h2>总价:{{totalPrice}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
books: [
{id:110,name:'Unix',price:119},
{id:111,name:'代码大全',price:201},
{id:112,name:'深入理解计算机原理',price:52}
]
},
//有缓存,方法没有
computed: {
totalPrice:function(){
let result = 0;
for(let i =0;i<this.books.length;i++){
result += this.books[i].price;
}
return result;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
二十二.计算属性getter、setter
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
{{message}}
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
firstname: 'a',
lastname: 'b',
},
computed: {
// fullName:function(){
// return this.firstname + this.lastname;
// }
//属性fullName,一般只实现get方法,所以一般可以简写为上面的写法
fullName :{
set:function(newValue){
console.log(newValue);
const names = newValue.split(" ");
this.firstname = names[0];
this.lastname = names[1];
},
get:function(){
return this.firstname + this.lastname;
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
二十三.计算属性computed和methods的对比
- 计算属性:一次计算,多次使用,有缓存
- methods:多次计算,多次使用,无缓存
二十四.es6语法
24.1 let/var
注:let有闭包,var没有,推荐使用let
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button>按钮1</button>
<button>按钮2</button>
<button>按钮3</button>
<button>按钮4</button>
<button>按钮5</button>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
//ES5之前因为 if、for没有块级作用域的概念,所以很多时候需要借鉴function的作用域
//1.变量作用域:变量在什么范围内是可用
{
var name = 'why';
console.log(name);
}
console.log(name);//var没有块级作用域
//2.没有块级作用域引起的问题 if
var func;
if(true){
var name = 'why';
func = function(){
console.log(name);
}
//func();
}
name = 'modify';
func();
//3.没有块级作用域引起的问题 for
//为什么闭包可以解决问题:函数是一个作用域
// var btns = document.getElementsByTagName('button')
// for(var i = 0;i<btns.length;i++){
// (function(i){ //0
// btns[i].addEventListener('click',function(){
// console.log('第' + i + '个按钮被点击');
// })
// })(i)
// }
// 4.es6
const btns = document.getElementsByTagName('button')
for(let i = 0;i<btns.length;i++){
btns[i].addEventListener('click',function(){
console.log('第' + i + '个按钮被点击');
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
24.2 const

24.3 对象字面量增强

二十五.v-on
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<h2>{{counter}}</h2>
<!-- <button v-on:click="counter++">+</button>
<button v-on:click="counter--">-</button> -->
<button @click="add">+</button>
<button v-on:click="sub">-</button>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
counter: 0
},
methods:{
add(){
this.counter++;
},
sub(){
this.counter--;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
语法糖:@click
二十六.v-on参数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- 不需要参数的时候,不需要括号 -->
<button @click="btn1Click">按钮1</button>
<button @click="btn1Click">按钮1</button>
<!-- 需要参数的时候,默认传入event参数,不需要括号 -->
<button @click="btn2Click">按钮2</button>
<button @click="btn2Click">按钮2</button>
<!-- 需要参数的时候,并且需要event参数,-->
<button @click="btn3Click(123,$event)">按钮3</button>
<button @click="btn3Click">按钮3</button>
<!-- 需要参数的时候,并且需要event参数,-->
<button @click="btn3Click(123,$event)">按钮3</button>
<button @click="btn3Click">按钮3</button>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy'
},methods: {
btn1Click(){
console.log(123);
},
btn2Click(event){
console.log(event);
},
btn3Click(first,event){
console.log(first);
console.log(event);
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
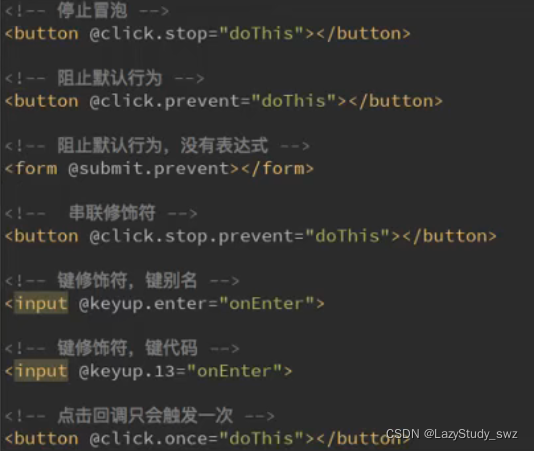
二十七.v-on修饰符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- 1.stop修饰符的使用(停止冒泡) -->
<div @click="divClick">
<button @click.stop='btnClick'>
按钮
</button>
</div>
<br>
<!-- 2.prevent修饰符的使用(阻止默认行为) -->
<form action="baidu">
<input type="submit" value="提交" @click.prevent="submitClick">
</form>
<!-- 3.监听某个键盘的键帽 -->
<input type="text" @keyup.enter="keyUp">
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy'
},
methods: {
btnClick(){
console.log("btnClick");
},
divClick(){
console.log("divClick");
},
submitClick(){
console.log("submitClick");
},
keyUp(){
console.log("keyup");
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
二十八.v-if、v-else-if、v-else

二十九.案例(切换)

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<span v-if="isShow">
<label for="" >邮箱登录:</label>
<input type="text">
</span>
<span v-else>
<label for="" >账号登录:</label>
<input type="text">
</span>
<button @click="toggleButton">切换</button>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
isShow: true
},
methods: {
toggleButton(){
this.isShow = !this.isShow;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
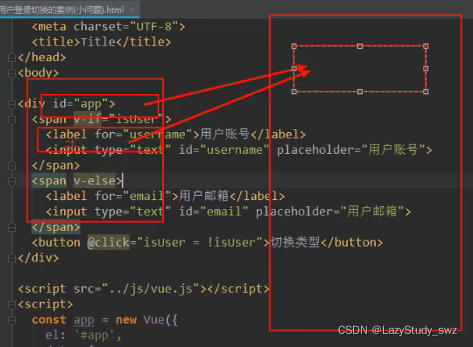
三十.input复用(问题)
注:上面的切换,会有input复用的问题

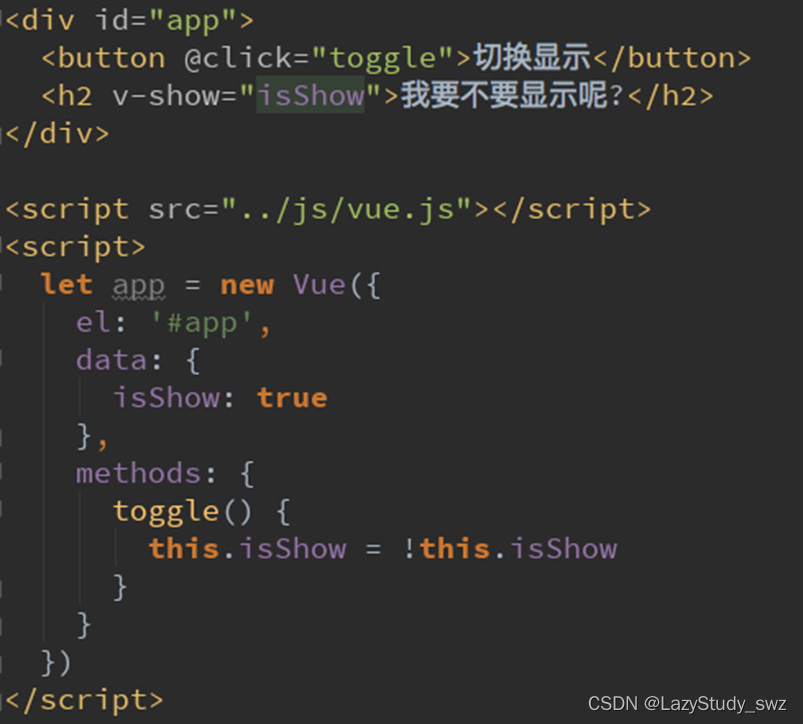
三十一.v-show

三十二.v-for
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in movies">
{{item}}
</li>
--------------
<li v-for="(item,index) in movies">
{{index}} {{item}}
</li>
-------------
<li v-for="(value,key,index) in info">
{{index}}-{{key}}-{{value}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
movies:['a','b','c'],
info:{
name:'123',
age:18,
height:180
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
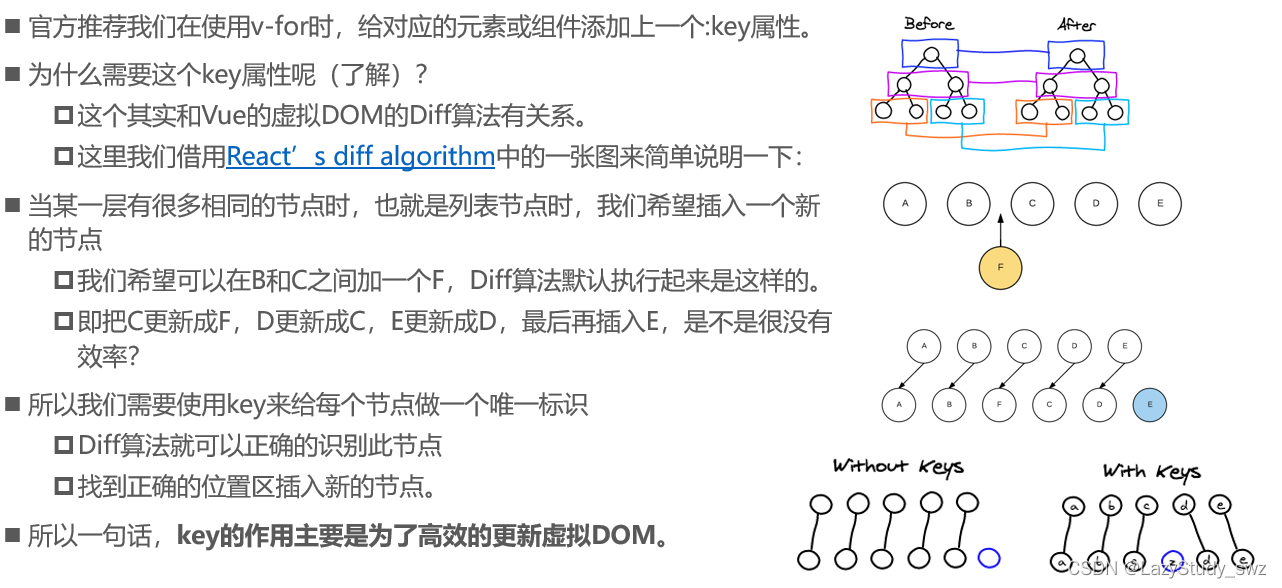
三十三.组件的key属性
三十四.数组方法
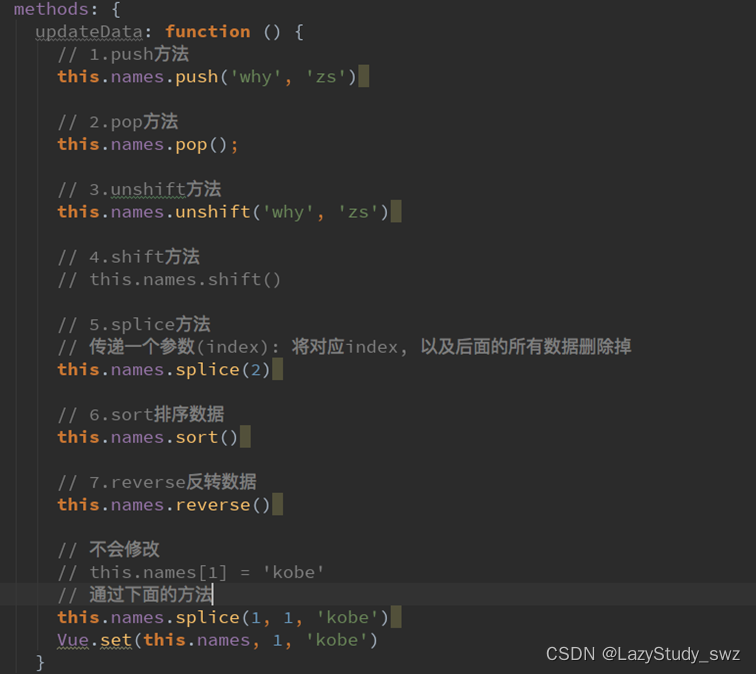
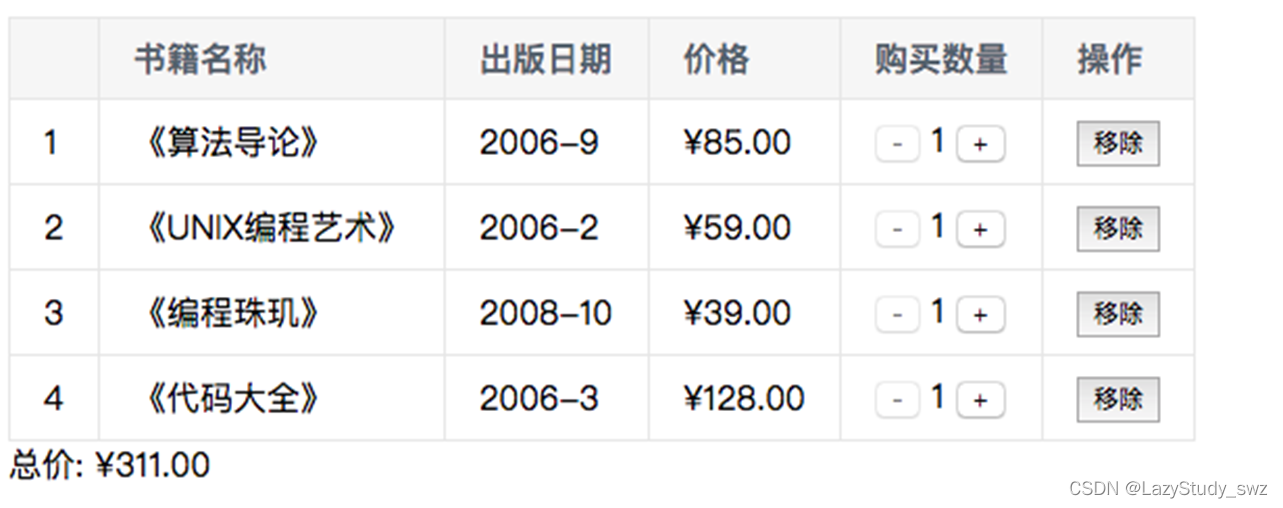
三十五.图书购物车
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
table{
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
}
th,td{
padding: 8px 16px;
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
text-align: left;
}
th{
background-color:#f7f7f7;
color:#5c6b77;
font-weight: 600;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<div v-if="list.length">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>书籍名称</th>
<th>日期</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>购买数量</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(item,index) in list" :key="item.id">
<td >{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.data}}</td>
<td>{{item.prize | showPrice}}</td>
<td>
<button @click="sub(index)">-</button>
{{item.count}}
<button @click="add(index)">+</button>
</td>
<td>
<button @click="handleRemove(index)">移除</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div>
总价:{{totalPrice | showPrice}}
</div>
</div>
<div v-else>
购物车为空
</div>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
list:[
{
id:1,
name:"a",
data:"2006-10",
prize:88.5,
count:1
},
{
id:2,
name:"a",
data:"2007-10",
prize:88.5,
count:1
},
{
id:3,
name:"a",
data:"2008-10",
prize:88.555,
count:1
},
{
id:4,
name:"a",
data:"2009-10",
prize:48.00,
count:1
}
]
},computed: {
totalPrice(){
let total = 0
for(let i =0;i<this.list.length;i++){
let item = this.list[i];
total += item.prize * item.count;
}
return total;
}
},methods: {
sub(index){
this.list[index].count--;
},
add(index){
this.list[index].count++;
},
handleRemove(index){
this.list.splice(index,1);
}
},filters:{//过滤器
showPrice(prize){
return "¥" + prize.toFixed(2);
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
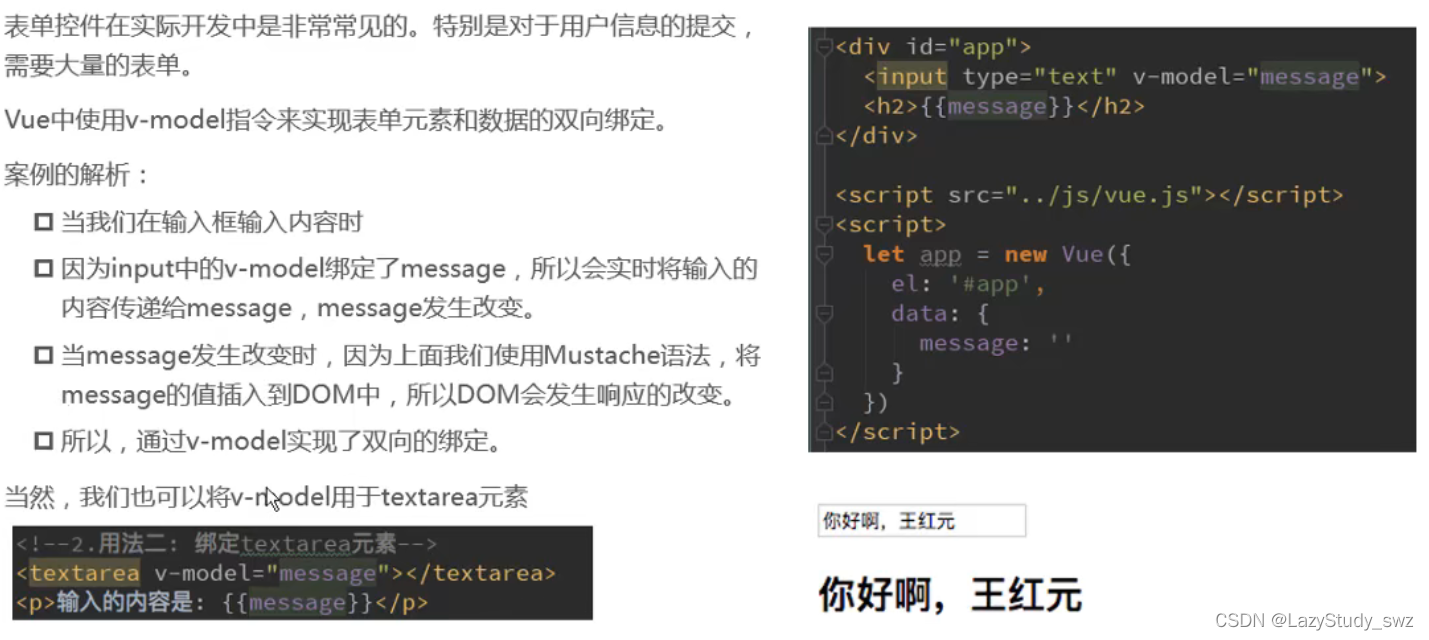
三十六.v-model
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- <input type="text" v-model="message"> -->
<!-- 等价 -->
<!-- <h2>{{message}}</h2>
<input type="text" :value = "message" v-on:input="valueChange"> -->
<!-- 等价2 -->
<h2>{{message}}</h2>
<input type="text" :value = "message" v-on:input="message = $event.target.value">
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy'
},methods:{
valueChange(event){
console.log('---');
this.message = event.target.value;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
三十七.v-model结合radio
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<label for="">
<input type="radio" id="male" name="sex" value="男" v-model="sex">男
</label>
<label for="">
<input type="radio" id="womale" name="sex" value ="女" v-model="sex">女
</label>
<h2>您选择的性别是:{{sex}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
sex: '男'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
三十八.v-model结合checkbox
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- checkbox单选框 -->
<!-- label的作用就是让你选择文字的时候选上 -->
<label for="agree">
<input type="checkbox" id="agree" v-model="agree">同意协议
</label>
<h2>您的选择:{{agree}}</h2>
<button :disabled="!agree">下一步</button>
<!-- checkbox多选框 -->
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="篮球">篮球
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="足球">足球
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="羽毛球">羽毛球
<h2>你的爱好是:{{hobbies}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
agree: false,
hobbies: []
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
三十九.v-model结合select

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- 选择一个 -->
<select name="" id="" v-model="fruit">
<option value="苹果">苹果</option>
<option value="香蕉">香蕉</option>
<option value="草莓">草莓</option>
<option value="梨">梨</option>
<option value="西瓜">西瓜</option>
</select>
<h2>
{{fruit}}
</h2>
<!-- 选择多个 -->
<select name="" id="" v-model="fruits" multiple>
<option value="苹果">苹果</option>
<option value="香蕉">香蕉</option>
<option value="草莓">草莓</option>
<option value="梨">梨</option>
<option value="西瓜">西瓜</option>
</select>
<h2>
{{fruits}}
</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
fruit: '苹果',
fruits: []
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
四十.值绑定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- checkbox单选框 -->
<!-- label的作用就是让你选择文字的时候选上 -->
<label for="agree">
<input type="checkbox" id="agree" v-model="agree">同意协议
</label>
<h2>您的选择:{{agree}}</h2>
<button :disabled="!agree">下一步</button>
<!-- checkbox多选框 -->
<!-- <input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="篮球">篮球
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="足球">足球
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="羽毛球">羽毛球 -->
<label for="" v-for="item in originHobbies">
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" :value="item">{{item}}
</label>
<h2>你的爱好是:{{hobbies}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
agree: false,
hobbies: [],
originHobbies :['篮球','足球','羽毛球']
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

四十一.修饰符

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<meta charset='UTF-8'>
<meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='app'>
<!-- 1.修饰符:lazy -->
<!-- 失去焦点,防抖 -->
<input type="text" v-model.lazy="message">
<h2>{{message}}</h2>
<!-- 2.number -->
<input type="text" v-model.number="age">
<h2>{{typeof(age)}}</h2>
<!-- 3.trim -->
<input type="text" v-model.trim="name">
<h2>{{name}}</h2>
</div>
<script src='../js/vue.js'></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app', //用于挂载要管理的元素
data:{ //定义数据
message: '你好啊,李银河!',
name: 'codewhy',
age: 0,
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
分类:
前端





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具