第四周总结 and 实验二
一、课堂笔记总览
1.String类两种实例方法
区别
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "hello";
String str3 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1 == str3);
String str2 = "hello";
String str3 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1 == str3);
output:
true
false
true
false
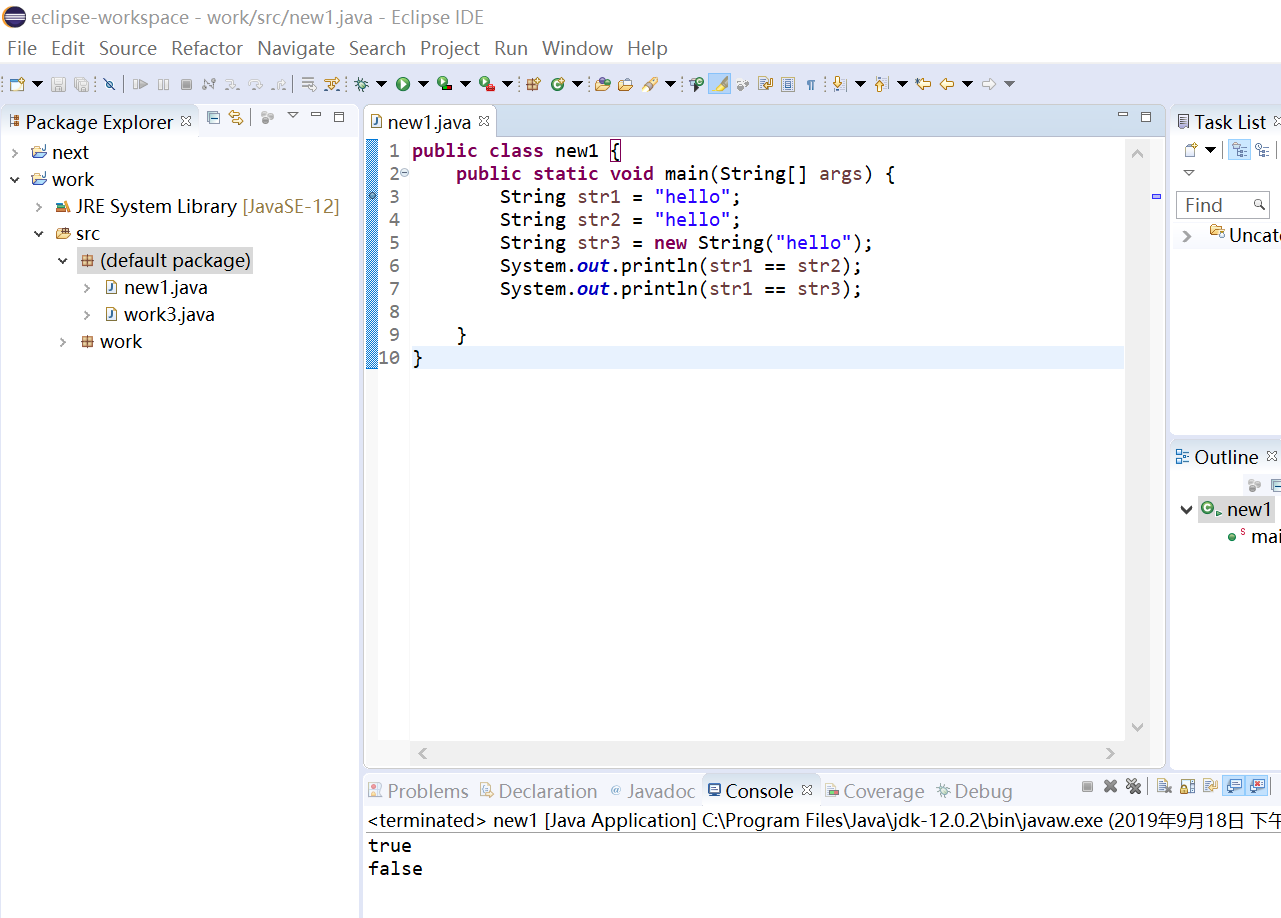
String str1 = “hello”;会将字符串数据放入对象池,下次再实例化该对象时可以直接使用
用new进行实例化,该字符串常量不会保存到对象池(可以使用intern()操作入池),另外还会产生额外垃圾空间,不建议使用。
用new进行实例化,该字符串常量不会保存到对象池(可以使用intern()操作入池),另外还会产生额外垃圾空间,不建议使用。
StringBuffer类
String类是字符串常量,是不可更改的常量。而StringBuffer是字符串变量,它的对象是可以扩充和修改的。
newString
凡是new 的都在在堆中开辟内存的
rt 你定义的是一个静态一维数组 里面是空的(因为你带了{ } 号)
不过也有内存 他的内存空间是在堆中的
String str[ ] = new String[10]; 像这样 是一个 动态的
它在堆中开辟了10 个空间 且他们的地址是连续的 空间大小都是一致的
rt 你定义的是一个静态一维数组 里面是空的(因为你带了{ } 号)
不过也有内存 他的内存空间是在堆中的
String str[ ] = new String[10]; 像这样 是一个 动态的
它在堆中开辟了10 个空间 且他们的地址是连续的 空间大小都是一致的
String类操作例(查找单个字符)
在String中使用indexOf()方法,可以返回指定的字符串的位置,如果不存在则返回-1.
public class StringAPIDemo05{
public static void main(String[]args){
String str1 ="abcdefgsjh";
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("c"));
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("c",3));
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("x"));
}
}

程序输出结果
2
-1 //没有查到
-1
foreach操作
oreach 并不是 Java 中的关键字,是 for 语句的特殊简化版本,在遍历数组、集合时, foreach 更简单便捷。从英文字面意思理解 foreach 也就是“ for 每一个”的意思,当使用foreach循环基本类型时变量时不能修改集合中的元素的值,遍历对象时可以修改对象的属性的值,但是不能修改对象的引用
修改基本类型的值(原集合中的值没有变化,因为str是集合中变量的一个副本)
在String中使用indexOf()方法,可以返回指定的字符串的位置,如果不存在则返回-1.
public class StringAPIDemo05{
public static void main(String[]args){
String str 1 ="abcdefgsjh";
System.out.println(str1.indexof("c"));
System.out.println(str1.indexof("c",3));
System.out.println(str1.indexof("x"));
}
}
String类操作例(split切割字符串操作)
String str="This is a test of Java" ;
int count=0;
String[] s=str .split("");
for(String e:s){
if(e.equals("is")){
count++ ;
}
}
System.out.printIn(count);
使用replace删除字符串
public class Test{
public static void mian(String[]args){
String str ="This is a test of java";
str=str.replace(" test", "");
System.out.println(str);
}
}
- 实验目的
- 掌握类的定义,熟悉属性、构造函数、方法的作用,掌握用类作为类型声明变量和方法返回值;
- 理解类和对象的区别,掌握构造函数的使用,熟悉通过对象名引用实例的方法和属性;
- 理解static修饰付对类、类成员变量及类方法的影响。
- 实验内容
- 写一个名为Rectangle的类表示矩形。其属性包括宽width、高height和颜色color,width和height都是double型的,而color则是String类型的。要求该类具有:
(1) 使用构造函数完成各属性的初始赋值
(2) 使用get…()和set…()的形式完成属性的访问及修改
(3) 提供计算面积的getArea()方法和计算周长的getLength()方法
额等信息。
1.实验源码
package Rextangle;
public class Rextangle { private String color; 书5.13 构造方法重载
private double width; //private封装属性 width
private double height; //private封装属性 height
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color=color; //this调用本类属性color
}
public void setWidth(double width) { //定义构造方法为width赋值
this.width=width;
}
public void setHeight(double height) { //定义构造方法为height赋值
this.height=height;
}
public String getColor() { //取得color
return color;
}
public double getWidth() { //取得 width
return width;
}
public double getHeight() { //取得高
return height;
}
public double getArea() { //取得面积
return width*height;
}
public double getLength() {
return 2*(width+height);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Rextangle r=new Rextangle(); //我们调用一个参数的构造
r.setWidth(30); //s输入Rextangle矩形的宽
r.setHeight(22); //s输入Rextangle矩形的高
System.out.println(r.getArea());
System.out.println(r.getLength()); 输出周长getLength
}
}
private double width; //private封装属性 width
private double height; //private封装属性 height
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color=color; //this调用本类属性color
}
public void setWidth(double width) { //定义构造方法为width赋值
this.width=width;
}
public void setHeight(double height) { //定义构造方法为height赋值
this.height=height;
}
public String getColor() { //取得color
return color;
}
public double getWidth() { //取得 width
return width;
}
public double getHeight() { //取得高
return height;
}
public double getArea() { //取得面积
return width*height;
}
public double getLength() {
return 2*(width+height);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Rextangle r=new Rextangle(); //我们调用一个参数的构造
r.setWidth(30); //s输入Rextangle矩形的宽
r.setHeight(22); //s输入Rextangle矩形的高
System.out.println(r.getArea());
System.out.println(r.getLength()); 输出周长getLength
}
}
实验
结果

- 银行的账户记录Account有账户的唯一性标识(11个长度的字符和数字的组合),用户的姓名,开户日期,账户密码(六位的数字,可以用0开头),当前的余额。银行规定新开一个账户时,银行方面提供一个标识符、账户初始密码123456,客户提供姓名,开户时客户可以直接存入一笔初始账户金额,不提供时初始余额为0。定义该类,并要求该类提供如下方法:存款、取款、变更密码、可以分别查询账户的标识、姓名、开户日期、当前余额等信息。





