类型转换函数
1. 转换构造函数
类的构造函数可以定义不同类型的参数,当参数满足下列条件时,就可称其为转换构造函数。
- 函数仅有一个参数
- 参数是基本类型或者其他类类型
其中,有一种特殊情形,也可构成转换构造函数。
- 函数有多个参数,但除了第一个参数外,其余都是默认参数
- 第一个参数是基本类型或者其他类类型
- 函数调用时只使用一个参数
C++编译器在进行编译工作时,会尽力尝试让源码通过编译,因此如果碰到了这样的代码Test t = 100,编译器不会立即报错,而是进行以下尝试:
- 查找类中是否有定义转换构造函数
- 如果定义了Test(int i),则先调用Test(100)将int类型隐式转换为Test类型,再赋值给t,编译通过
- 如果没有定义,编译才报错
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test()
{
mValue = 0;
}
//转换构造函数
Test(int i)
{
mValue = i;
}
//当仅以第一个参数调用时,该函数等价于Test(int i),也是转换构造函数
/*Test(int i, int j = 0, int k = 0)
{
mValue = i;
}*/
Test operator + (const Test &p)
{
Test ret(mValue + p.mValue);
return ret;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
};
int main()
{
Test t = 5; // Test t = Test(5);
Test r = t + 10; // Test r = t + Test(10);
cout << "t.value = " << t.value() << endl;
cout << "r.value = " << r.value() << endl;
return 0;
}
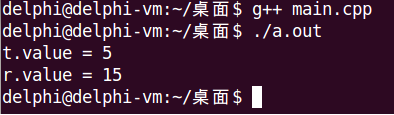
可以看到,当定义了转换构造函数时,编译器尽力尝试的结果是隐式类型转换,而隐式类型转换
- 有可能会让程序以意想不到的方式工作
- 是工程中BUG的重要来源,应该尽力避免
2. explicit关键字
- 在工程中可以使用explicit关键字修饰转换构造函数,从而杜绝编译器的转换尝试
- 转换构造函数被explicit修饰时只能使用显式的强制类型转换
- 作为编程的一般性原则,建议给所有的构造函数都加上explicit关键字
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
explicit Test()
{
mValue = 0;
}
explicit Test(int i)
{
mValue = i;
}
//当仅以第一个参数调用时, 该函数等价于Test(int i), 也是转换构造函数, explicit有效且有必要
/*explicit Test(int i, int j = 0, int k = 0)
{
mValue = i;
}*/
Test operator + (const Test &p)
{
Test ret(mValue + p.mValue);
return ret;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
};
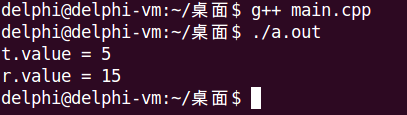
int main()
{
//Test t = 5; // Error
//Test r = t + 10; // Error
Test t = static_cast<Test>(5);
Test r = t + static_cast<Test>(10);
cout << "t.value = " << t.value() << endl;
cout << "r.value = " << r.value() << endl;
return 0;
}
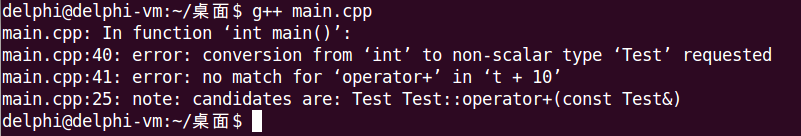
当使用了explicit关键字后,如果main()使用40-41行替换43-44行,编译会直接报错
3. 类型转换函数
转换构造函数可以将其他类型转换为类类型,而类型转换函数则可以将类类型转换到其他类型,包括普通类型和其他类类型。
- 类型转换函数是转换构造函数的逆过程,它们具有同等的地位
- 编译器也能够使用类型转换函数进行隐式转换,从而尽力让源码通过编译
- 当目标类型是其他类类型时,类型转换函数可能与转换构造函数冲突
定义类型转换函数需要用到operator关键字,其语法规则为
operator TargetType ()
{
TargetType ret;
//......
return ret;
}
当编译器遇到Test t(1); int i = t;这样的代码时,不会立即报错,而是进行以下尝试
- 查看Test类中是否有定义类型转换函数
operator int () - 如果有定义,则进行隐式转换,先调用类型转换函数将t转换为int,再赋值给i,编译通过
- 如果没有定义,编译才报错
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test;
class Value
{
int mValue;
public:
Value(int i = 0)
{
mValue = i;
}
//如果不加explicit,会与Test中的operator Value ()冲突,产生二义性
explicit Value(Test &t)
{
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
};
class Test
{
private:
int mValue;
public:
Test(int i = 0)
{
mValue = i;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
operator int ()
{
return mValue;
}
operator Value ()
{
Value ret(mValue);
return ret;
}
};
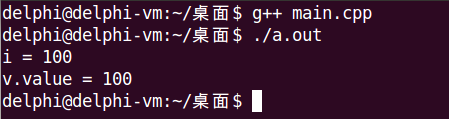
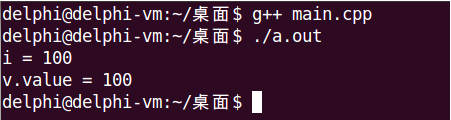
int main()
{
Test t(100);
int i = t;
Value v = t;
cout << "i = " << i << endl;
cout << "v.value = " << v.value() << endl;
return 0;
}
和转换构造函数不同,类型转换函数没有类似explicit这种杜绝机制,也就是说,只要定义了类型转换函数,我们就无法抑制编译器的隐式调用。
因此,在工程中,通常不会使用类型转换函数,而是以toType()的public成员函数来代替类型转换函数。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test;
class Value
{
int mValue;
public:
Value(int i = 0)
{
mValue = i;
}
//如果不加explicit,会与Test中的operator Value ()冲突,产生二义性
explicit Value(Test &t)
{
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
};
class Test
{
private:
int mValue;
public:
Test(int i = 0)
{
mValue = i;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
/*
* 工程中不用且不推荐的方式
*/
/*operator int ()
{
return mValue;
}
operator Value ()
{
Value ret(mValue);
return ret;
}*/
/*
* 工程中常用且推荐的方式:提供toType()的public成员函数
*/
int toInt()
{
return mValue;
}
Value toValue()
{
Value ret(mValue);
return ret;
}
};
int main()
{
Test t(100);
int i = t.toInt();
Value v = t.toValue();
cout << "i = " << i << endl;
cout << "v.value = " << v.value() << endl;
return 0;
}