【Golang】go语言设计模式
介绍
go语言不是一个纯面向对象的编程语言,但是go语言可以进行面向对象编程。
go语言可以使用结构体来模拟类与对象。
一. 工厂模式
工厂模式属于创建型模式,又叫做静态工厂方法。
特点:
在简单工厂模式中,可以根据参数的不同来返回不同的类实例。简单工厂模式会专门定义一个类来负责创建其他类的对象。
factory.go
package main //实现一个抽象的产品 type Product interface{ SetName(name string) GetName() string } //实现具体的产品:产品1 type Product1 struct { name string } func (p1 *Product1) SetName(name string) { p1.name = name } func (p1 *Product1) GetName() string { return "产品1的name" + p1.name } //实现具体的产品:产品2 type Product2 struct { name string } func (p2 *Product2) SetName(name string) { p2.name = name } func (p2 *Product2) GetName() string { return "产品1的name" + p2.name } type productType int const ( p1 productType = iota p2 ) //实现简单工厂类 type productFactory struct { } func (pf productFactory) Create(productType productType) Product { if productType == p1 { return &Product1{} } if productType == p2 { return &Product2{} } return nil }
factory_test.go
package main import ( "fmt" "testing" ) //通过传统方式创建对象 func TestProduct_Create(t *testing.T) { product1 := &Product1{} product1.SetName("p1") fmt.Println(product1.GetName()) product2 := &Product1{} product2.SetName("p2") fmt.Println(product2.GetName()) } //通过工厂方式创建对象 func TestProductFactory_Create(t *testing.T) { productFactory := productFactory{} product1 := productFactory.Create(p1) product1.SetName("p1") fmt.Println(product1.GetName()) product2 := productFactory.Create(p2) product2.SetName("p2") fmt.Println(product2.GetName()) }
案例:用简单工厂模式实现redis和memcache的创建
package main import ( "errors" ) //定义一个Cache接口 type Cache interface{ Set(key, value string) Get(key string) string } //实现具体的Cache redis type RedisCache struct { data map[string]string } func (redis *RedisCache) Set(key, value string) { redis.data[key] = value } func (redis *RedisCache) Get(key string) string { return "redis:" + redis.data[key] } //实现具体的Cache redis type MemcacheCache struct { data map[string]string } func (mem *MemcacheCache) Set(key, value string) { mem.data[key] = value } func (mem *MemcacheCache) Get(key string) string { return "Memcache:" + mem.data[key] } type cacheType int const ( redis cacheType = iota mem ) //实现cache简单工厂类 type cacheFactory struct { } func (cache cacheFactory) Create(cacheType cacheType) (Cache, error) { if cacheType == redis { return &RedisCache{ data : map[string]string{}, }, nil } if cacheType == mem { return &MemcacheCache{ data : map[string]string{}, }, nil } return nil, errors.New("error cache type") }
测试
package main import ( "fmt" "testing" ) func TestCacheFactory_Create(t *testing.T) { cacheFactory := cacheFactory{} redis, error := cacheFactory.Create(redis) if error != nil { t.Error(error) } redis.Set("redis_k1", "redis_v1") fmt.Println(redis.Get("redis_k1")) }
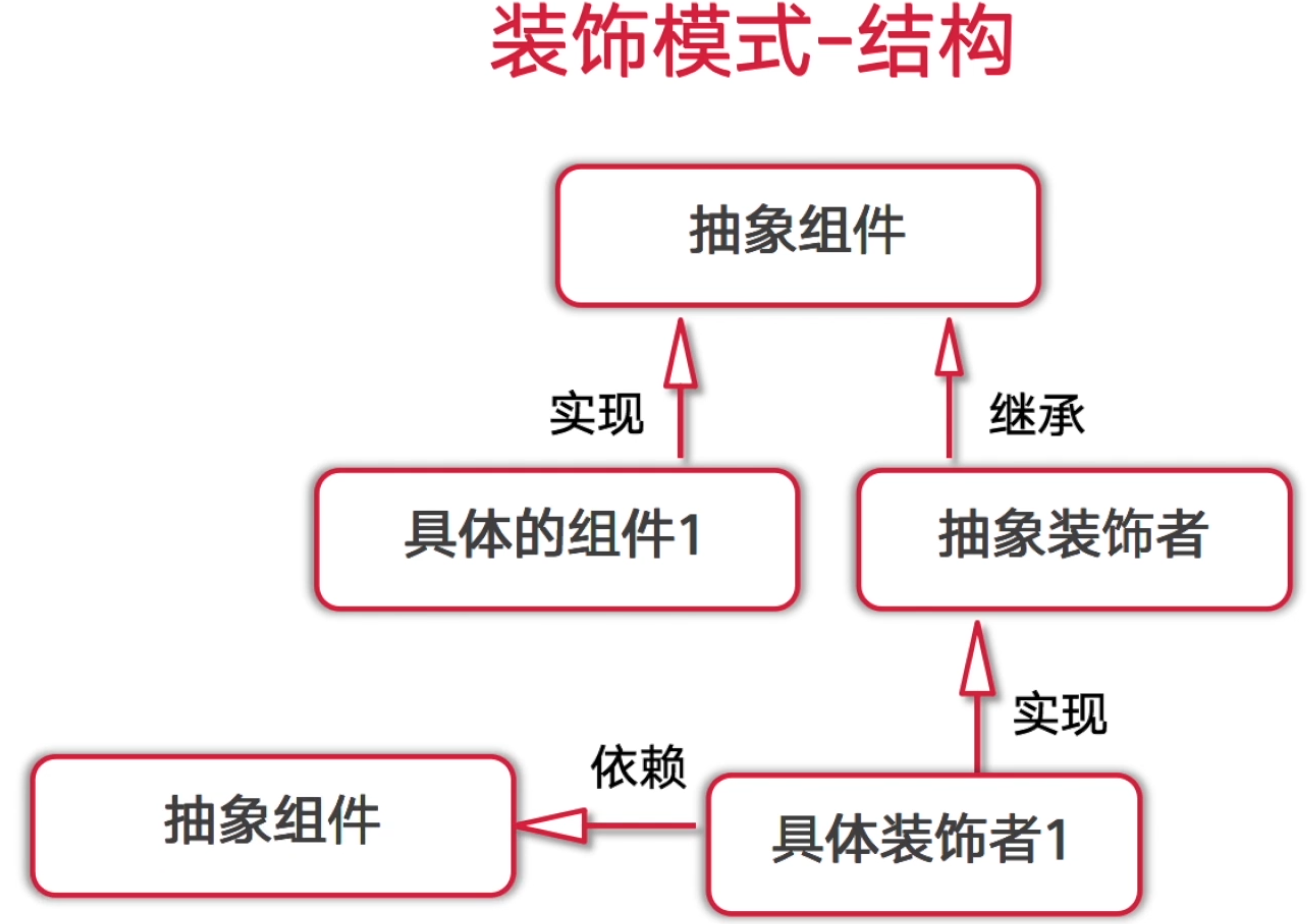
二. 装饰模式
装饰模式属于一种结构型的模式。
特点:
1. 是一种动态的往一个类里添加新的行为的设计模式。
2. 装饰模式就功能而言比生成子类的方式更加的灵活,这样可以给单个对象而不是整个类添加一些功能。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号