python os 模块介绍
"""
重命名文件
os.rename(src,dst)
os.rename('123.txt','124.txt')
删除文件
os.remove(path)
os.remove('123.txt')
创建目录
os.mkdir()
创建多级目录
os.makedirs()
删除目录
os.rmdir()
删除多级目录
os.removedirs()
获取当前目录
os.getcwd()
修改所在目录
os.chdir()
判断文件是否存在
os.path.exists()
判断是否为文件
os.path.isfile()
判断是否为目录
os.path.isdir()
获取绝对路径
os.path.abspath()
判断是否为绝对路径
os.path.isabs()
获取路径的最后部分
os.path.basename()
获取父级路径
os.path.dirname()
获取文件夹内的子文件(重要)
os.listdir()
"""
import os
# os.rename("log.txt","log.properties")
# os.remove("log.properties")
# open("log.txt","w")
# os.mkdir("abc")
# os.rmdir("abc")
# os.makedirs("a/b/c/d")
# os.removedirs("a/b/c/d")
# os.chdir("../")
# print(os.getcwd())
# file_name = "abc.jpeg"
# if os.path.exists(file_name):
# if os.path.isdir(file_name):
# print("删除文件夹成功")
# os.rmdir(file_name)
# elif os.path.isfile(file_name):
# print("删除文件成功")
# os.remove(file_name)
# else:
# print("文件不存在")
path = os.getcwd()
for f in os.listdir(path):
if f.endswith(".py"):
print(f)
os.walk方法,主要用来遍历一个目录内各个子目录和子文件。
os.walk(top, topdown=True, onerror=None, followlinks=False)
可以得到一个三元tupple(dirpath, dirnames, filenames),
第一个为起始路径,第二个为起始路径下的文件夹,第三个是起始路径下的文件。
dirpath
是一个string,代表目录的路径,
dirnames
是一个list,包含了dirpath下所有子目录的名字。
filenames
是一个list,包含了非目录文件的名字。
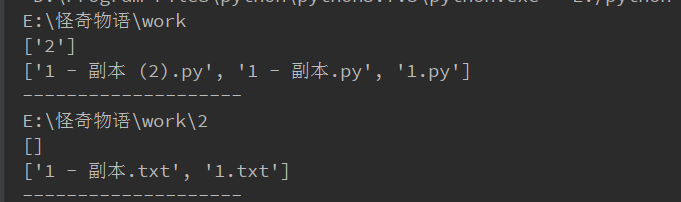
for (path, dirs, files) in os.walk(r"E:\怪奇物语\work"):
print(path) # 路径名
print(dirs) # 包含的文件夹名
print(files) # 包含的文件
print("--"*10)
以文件的默认编码打开此文件
with open("your_file", 'rb') as fp:
file_data = fp.read()
result = chardet.detect(file_data)
file_content = file_data.decode(encoding=result['encoding'])
几个案例
# 1.封装自定一个函数,可以将Iterable对象中的所有数据写到目标文件file中,
# 如果Iterable中存储的不是字符串,转换为字符串处理
def write_lines(file, Iterable):
with open(file, mode="a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for i in Iterable:
if isinstance(i, str):
f.write(i + '\n')
else:
f.write(str(i) + "\n")
# write_lines("1.txt",[1,2,3,4,5,6,"abcde"])
# 2.自定义一个函数,可以实现文件的复制(先读取目标文件,然后写入新文件)
# 比如:def copyfile(file) 将file复制一份,被复制出来的文件名为file_副本.后缀
def copyfile(file):
filetup = file.rpartition(".")
new_name = str(filetup[0]) + "_副本" + str(filetup[1] + filetup[2])
if os.path.exists(file):
with open(file, mode="r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
with open(new_name, mode="w", encoding="utf-8") as f1:
content = f.read(1024)
while content:
f1.write(content)
content = f.read(1024)
else:
print("file not exists")
# copyfile("digui.py")
# 3.打印某个文件夹内所有的的文件名
def print_all_file(file_path):
file_list = os.listdir(file_path)
for f in file_list:
f = file_path + "\\" + f
if os.path.isfile(f):
print(f)
elif os.path.isdir(f):
print_all_file(f)
# print_all_file(r"E:\python workspace\day13")
# 4.尝试将一个文件夹内所有的.py文件名前都添加上你的名字做前缀(注意文件先备份)
# 例如:test01.py -> xxx_test01.py
def add_prefix(file_path, prefix):
file_list = os.listdir(file_path)
for f in file_list:
f = file_path + "\\" + f
if os.path.isfile(f):
basename = os.path.basename(f)
dirname = os.path.dirname(f)
# print(dirname+"\\"+prefix+basename)
os.rename(f, dirname + "\\" + prefix + basename)
elif os.path.isdir(f):
add_prefix(f, prefix)
# add_prefix(r"E:\python workspace\day13","songdan_")
# 5.封装一个函数,可以实现类似操作系统的模糊查询功能(输入一个关键字,可以展示目标文件夹中包含关键字的所有文件)
import chardet
def find_file_contains_key(f,key):
if key in f:
print(f"包含{key}的文件名为:{f}:")
with open(f, mode="rb") as fp:
file_data = fp.read()
result = chardet.detect(file_data)
file_content = file_data.decode(encoding=result['encoding'])
now_fname = ""
for line in file_content:
line = line.strip()
if key in line:
if now_fname == "":
now_fname = f.name
print(f"包含内容为{key}的文件名为:{f.name}:")
print(f"\t\t内容为:{line}")
def show_file_by_word(file_path, key):
file_list = os.listdir(file_path)
for f in file_list:
f = file_path + "\\" + f
# 文件,查询里面是否包含关键字
if os.path.isfile(f) and f.endswith(".py"):
find_file_contains_key(f,key)
# 文件夹,找出里面的文件
elif os.path.isdir(f):
show_file_by_word(f, key)
show_file_by_word(r"E:\python workspace\day13", "songdan")
# 6.统计某个文件夹内所有.py文件中的代码行数
count = 0
def count_file_words(file_path):
file_list = os.listdir(file_path)
global count
for f in file_list:
f = file_path + "\\" + f
if os.path.isfile(f) and f.endswith(".py"):
with open(f, mode="r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if "#" not in line and len(line) > 0:
count += 1
# 文件夹,找出里面的文件
elif os.path.isdir(f):
count_file_words(f)
return count
# count_file_words(r"E:\python workspace\day13\test")
print(count)
更多案例参见:https://github.com/geekcomputers/Python/tree/master/

