hdu4027
Can you answer these queries?
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65768/65768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2757 Accepted Submission(s): 657
Problem Description
A lot of battleships of evil are arranged in a line before the battle. Our commander decides to use our secret weapon to eliminate the battleships. Each of the battleships can be marked a value of endurance. For every attack of our secret weapon, it could decrease the endurance of a consecutive part of battleships by make their endurance to the square root of it original value of endurance. During the series of attack of our secret weapon, the commander wants to evaluate the effect of the weapon, so he asks you for help.
You are asked to answer the queries that the sum of the endurance of a consecutive part of the battleship line.
Notice that the square root operation should be rounded down to integer.Input
The input contains several test cases, terminated by EOF.
For each test case, the first line contains a single integer N, denoting there are N battleships of evil in a line. (1 <= N <= 100000)
The second line contains N integers Ei, indicating the endurance value of each battleship from the beginning of the line to the end. You can assume that the sum of all endurance value is less than 263.
The next line contains an integer M, denoting the number of actions and queries. (1 <= M <= 100000)
For the following M lines, each line contains three integers T, X and Y. The T=0 denoting the action of the secret weapon, which will decrease the endurance value of the battleships between the X-th and Y-th battleship, inclusive. The T=1 denoting the query of the commander which ask for the sum of the endurance value of the battleship between X-th and Y-th, inclusive.Output
For each test case, print the case number at the first line. Then print one line for each query. And remember follow a blank line after each test case.
Sample Input
10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 5 0 1 10 1 1 10 1 1 5 0 5 8 1 4 8
Sample Output
Case #1: 19 7 6
Source
The 36th ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shanghai Site —— Online Contest
读完题目,首先感觉是一道线段树,在具体实现的时候碰到了一点小麻烦:找不到
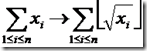 的快速转换方法,这就意味着对于每一次的Attack Command,需要直接对[L,R]区间的每个数进行操作xi=[(xi)^0.5],由于没有仔细观察数据特性,导致当时觉得线段树由于这种限制,当时不敢写了。
的快速转换方法,这就意味着对于每一次的Attack Command,需要直接对[L,R]区间的每个数进行操作xi=[(xi)^0.5],由于没有仔细观察数据特性,导致当时觉得线段树由于这种限制,当时不敢写了。
其实观察一下就可以发现,由于xi<=2^63-1,所以对于任意的xi,至多执行7次的Attack Command,这个xi就不会再变化,而是始终保持xi=1;
由此想出本题算法: 将整个大的区间[1,N]划分成很多互不相交的区间段(线段树构树),对于每个区间段,记录一个值:numcmd1,表示这个区间段被执行Attack Command的次数,初始时所有区间的numcmd1=0。对于每次的Attack Command,如果发现被执行区间的numcmd1的次数<7,那么直接对这个区间的每一个数实施xi=[(xi)^0.5]操作;否则, 不对这个区间执行操作; 同时,为了应对本题的Querry Command,还需要在每个区间上记录一个sum值,
其中sum=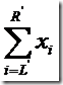 (L’,R’是区间的左右端点),每次执行完Attack Command,直接自底向上的用左右子区间的sum值更新父亲区间的sum值;
(L’,R’是区间的左右端点),每次执行完Attack Command,直接自底向上的用左右子区间的sum值更新父亲区间的sum值;
剩下的就是线段树的一些 构树,延迟标记下移 等细节的考虑,直接贴代码:
1: #include<iostream>
2: #include<cstdio>
3: #include<cmath>
4:
5: using namespace std;
6:
7: #define nsize 200000
8: #define Lim 8
9: #define uproot(root){t[root].sum=t[root<<1].sum+t[(root<<1)+1].sum;}
10: typedef long long bint;
11: struct sgtree
12: {
13: int l,r;
14: bint sum;
15: int numcmd1;
16: };
17: sgtree t[nsize*3];
18: bint a[nsize];
19: void build(int root,int l,int r)
20: {
21: t[root].l=l,t[root].r=r,t[root].numcmd1=0;
22: if (t[root].l==t[root].r) {t[root].sum=a[t[root].l];return;}
23: int mid=(l+r)>>1;
24: build(root<<1,l,mid),build((root<<1)+1,mid+1,r);
25: uproot(root);
26: }
27:
28: void upinterval(int root)
29: {
30: ++t[root].numcmd1;
31: if (t[root].l==t[root].r){t[root].sum=(bint)sqrt((double)t[root].sum); return;}
32: upinterval(root<<1),upinterval((root<<1)+1);
33: uproot(root);
34: }
35:
36: void docmd1(int root,int l,int r)
37: {
38: if (t[root].numcmd1>=Lim) return;
39: if (t[root].l==l && t[root].r==r) {upinterval(root);return;}
40: int mid=(t[root].l+t[root].r)>>1;
41: if (r<=mid) docmd1(root<<1,l,r);
42: else if (l>mid) docmd1((root<<1)+1,l,r);
43: else docmd1(root<<1,l,mid),docmd1((root<<1)+1,mid+1,r);
44: uproot(root);
45: }
46:
47:
48:
49: bint docmd2(int root,int l,int r)
50: {
51: if (t[root].numcmd1>=Lim) return r-l+1;
52: if (t[root].l==l&&t[root].r==r) return t[root].sum;
53: int mid=(t[root].l+t[root].r)>>1;
54: if (r<=mid) return docmd2(root<<1,l,r);
55: else if (l>mid) return docmd2((root<<1)+1,l,r);
56: else return docmd2(root<<1,l,mid)+docmd2((root<<1)+1,mid+1,r);
57: }
58: int main()
59: {
60: int n,m,i,cmd,x,y,numcase=0;
61: while (scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
62: {
63: ++numcase;
64: printf("Case #%d:\n",numcase);
65: for (i=1;i<=n;++i) scanf("%I64d",&a[i]);
66: build(1,1,n);
67: scanf("%d",&m);
68: for (i=1;i<=m;++i)
69: {
70: scanf("%d%d%d",&cmd,&x,&y);
71: if (x>y) swap(x,y);
72: if (cmd==0) docmd1(1,x,y);
73: else printf("%I64d\n",docmd2(1,x,y));
74: }
75: putchar('\n');
76: }
77: return 0;
78: }
