高级装配—条件化的Bean
条件化的Bean:
通过活动的profile,我们可以获得不同的Bean。Spring 4提供了一个更通用的基于条件的Bean的创建方式,即使用@Conditional注解。
@Conditional根据满足某个特定的条件创建一个特定的Bean。比如,当某一个jar包在一个类路径下时,自动配置一个或者多个Bean。或者只有一个Bean创建时,才会创建另一个Bean。总的来说,就是根据特定条件来控制Bean的创建行为,这样我们可以利用这个特性进行一些自动配置。
下面的示例将以不同的操作系统作为条件,我们将通过实现Condition接口,并重写其matches方法来构造判断条件。如在Windows系统下运行程序输出dir,Linux下输出ls。
一、判断条件定义
1、判定Windows的条件:
package com.home.Cont; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata; //编写Windows的判断类 public class WindowsCondition implements Condition { @Override public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { return context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name").contains("Windows"); } }
2、判定Linux的条件
package com.home.Cont; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata; //编写Linux的判断类 public class LinuxCondition implements Condition { @Override public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { return context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name").contains("Linux"); } }
二、不同系统下的Bean
1、接口
package com.home.Cont; //不同系统命令的接口 public interface ListService { public String showListCmd(); } 2、Windows下所要创建
2、Windows下所要创建的Bean
package com.home.Cont; //window下的命令 public class WindowsListService implements ListService { @Override public String showListCmd() { return "dir"; } }
3、Linux下所要创建的Bean
package com.home.Cont; //Linux下的命令 public class LinuxListService implements ListService { @Override public String showListCmd() { return "ls"; } }
三、配置类
package com.home.Cont; import org.springframework.context.annotation.*; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages="com.home.Cont") public class ConditionConfig { @Bean @Conditional(LinuxCondition.class)// 使用@Conditional注解,符合Linux条件就实例化LinuxListService public ListService linuxListService() { return new LinuxListService(); } @Bean @Conditional(WindowsCondition.class)// 使用@Conditional注解,符合Windows条件就实例化WindowsListService public ListService windowsListService() { return new WindowsListService(); } }
package com.home.Cont; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class SpringConditionalTest { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConditionConfig.class); @Test public void contextTest() { ListService listService = context.getBean(ListService.class); System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name") + "系统下的列表命令为:" + listService.showListCmd());; } @After public void closeContext() { context.close(); } }
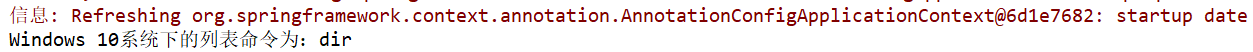



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号