高级装配—配置profile bean
配置profile bean
1.@profile注解是spring提供的一个用来标明当前运行环境的注解。
我们正常开发的过程中经常遇到的问题是,开发环境是一套环境,qa测试是一套环境,线上部署又是一套环境。这样从开发到测试再到部署,会对程序中的配置修改多次,尤其是从qa到上线这个环节,让qa的也不敢保证改了哪个配置之后能不能在线上运行。
为了解决上面的问题,我们一般会使用一种方法,就是配置文件,然后通过不同的环境读取不同的配置文件,从而在不同的场景中跑我们的程序。
那么,spring中的@profile注解的作用就体现在这里。在spring使用DI来依赖注入的时候,能够根据当前制定的运行环境来注入相应的bean。最常见的就是使用不同的DataSource了。
下面详细的介绍一下,如何通过spring的@profile注解实现上面的功能。
创建一个Maven项目,其中的配置如下:
pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.home</groupId> <artifactId>ProfileTest</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <name>ProfileTest Maven Webapp</name> <!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --> <url>http://www.example.com</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target> <springframework.version>4.3.7.RELEASE</springframework.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-test --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId> <version>RELEASE</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>ProfileTest</finalName> <pluginManagement><!-- lock down plugins versions to avoid using Maven defaults (may be moved to parent pom) --> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.0.0</version> </plugin> <!-- see http://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/default-bindings.html#Plugin_bindings_for_war_packaging --> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.0.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.7.0</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.20.1</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.2.0</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.5.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.8.2</version> </plugin> </plugins> </pluginManagement> </build> </project>
App:
package com.hom.demo; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * Hello world! // */ @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.hom.demo"}) public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(com.hom.demo.App.class); Person p = context.getBean(Person.class); p.speak(); } }
接口MoveFactor:
package com.hom.demo; public interface MoveFactor { void speak(); }
Chines:
package com.hom.demo; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Configuration @Profile(value = "dev") @Component public class Chinese implements MoveFactor { @Override public void speak() { System.out.println("我是中国人"); } }
English:
package com.hom.demo; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Profile("qa") public class English implements MoveFactor{ @Override public void speak() { System.out.println("i am an English"); } }
German:
package com.hom.demo; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Profile("prod") public class German implements MoveFactor{ @Override public void speak() { System.out.println("i am a German"); } }
package com.hom.demo; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Person { @Autowired private MoveFactor moveFactor; public void speak(){ moveFactor.speak(); } }
SpringTest:
package com.hom.demo; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = App.class) @ActiveProfiles("dev") public class SpringTest { @Autowired Person p; @Test public void testProfile(){ p.speak(); } }
当修改@ActiveProfile中的值时,输出的内容也会随之改变。
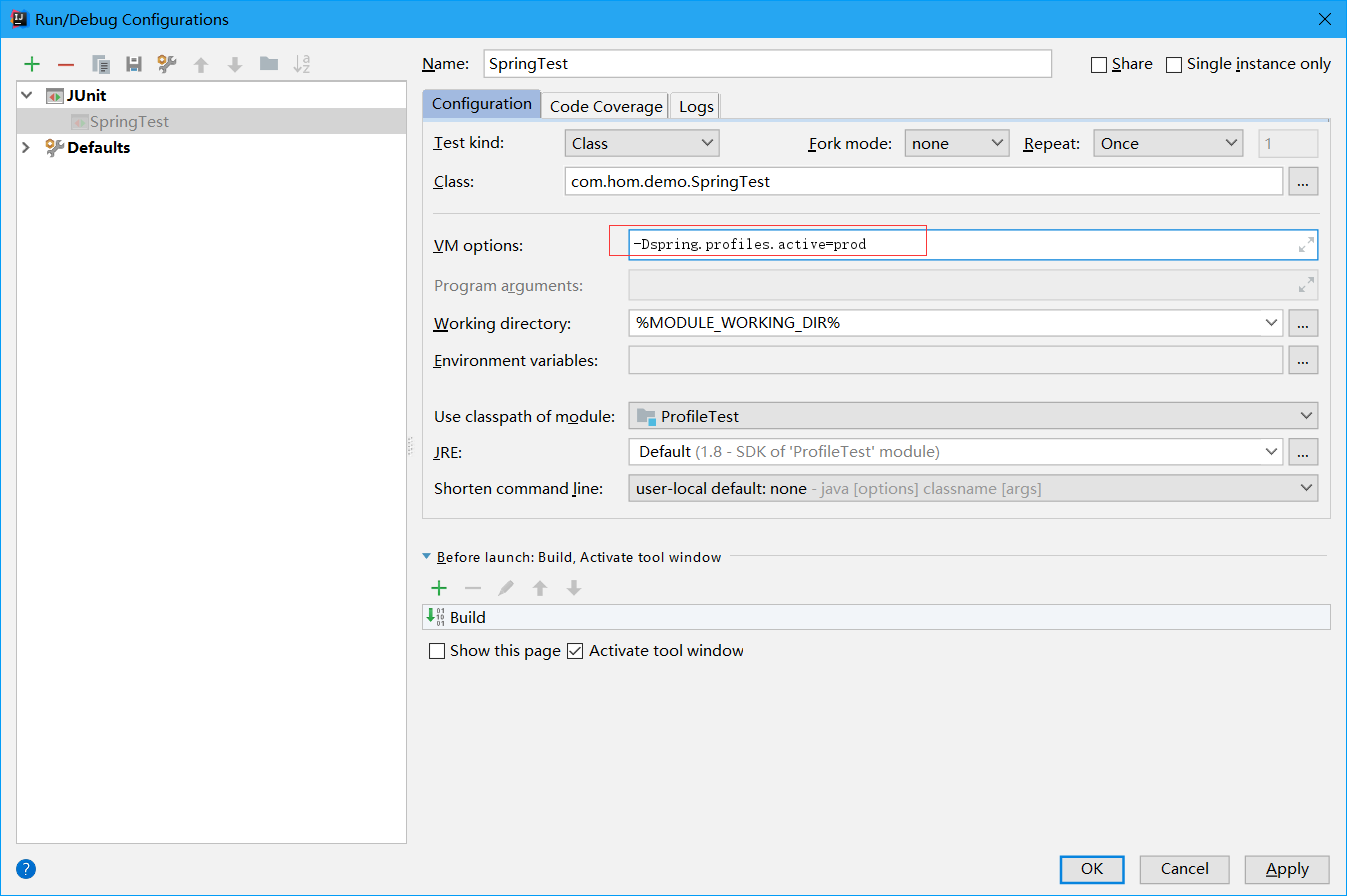
如果使用的是main函数进行真正的开发、测试和上线时,我们需要设置一下运行参数:
-Dspring.profiles.active=prod
XML中配置profile
application.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd" profile="dev"> <bean id="chinese" class="com.hom.demo.Chinese"></bean> </beans>
我们还可以在<beans>中嵌套定义<beans>元素,而不是为没个环境都创建一个profile.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd" > <beans profile="dev"> <!--这里可以指定需要的profile名--> <bean id="chinese" class="com.hom.demo.Chinese"></bean> </beans> <beans profile="qa"> <bean id="english" class="com.hom.demo.English"></bean> </beans> </beans>
3.激活profile
Spring在确定那个profile处于激活状态时,需要依赖两个独立的属性:
spring.Profile.active(激活的Profile)
spring.Profile.default(默认的Profile)
这里有多种方式来设置这两个属性:
- 作为DispathServlet的初始参数
- 作为Web应用的上下文参数
- 作为JNDI条目
- 作为环境变量
- 作为JVM的系统属性
- 在集成测试类上,使用@ActiveProfile注解设置
我所喜欢的一种方式是使用DispatcherServlet的参数将spring.rpofiles.default设置开发环境的Profile,我会在Servlet上下文中配置,如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" version="3.0" id="WebApp_1525601902125">
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLoacation</param-name>
<param-value>application.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--为上下文设置默认的profile-->
<context-param>
<param-name>spring.rpofiles.default</param-name>
<param-value>dev</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--为Servlet设置默认的profile-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>spring.rpofiles.default</param-name>
<param-value>dev</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Spring提供了@ActiveProfile注解设置激活状态



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号