Sentinel笔记-熔断降级与系统自适应限流
先来一张官网图
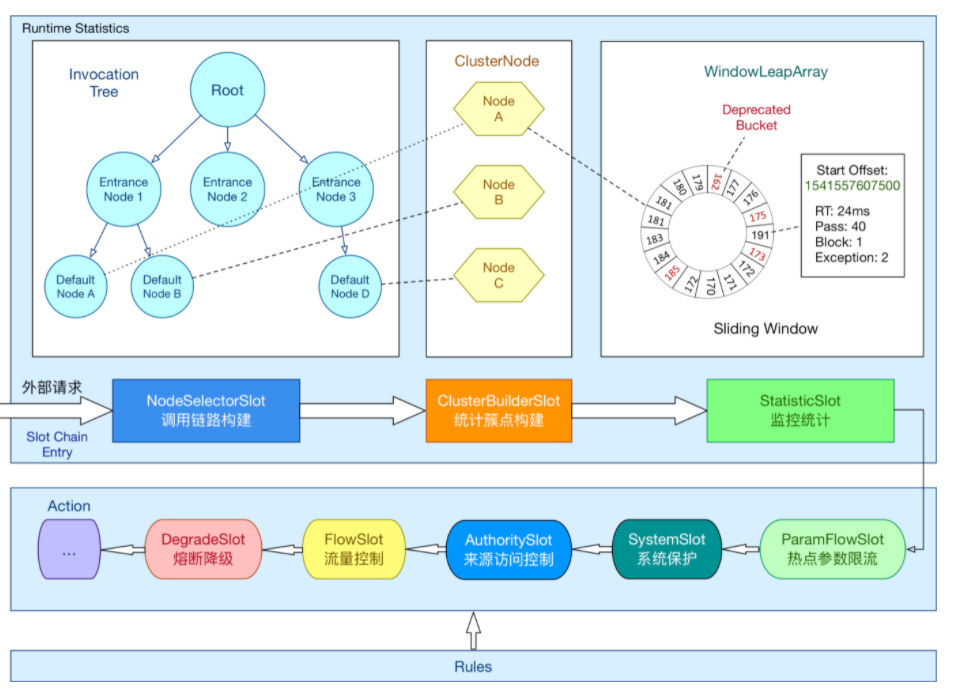
熔断策略
-
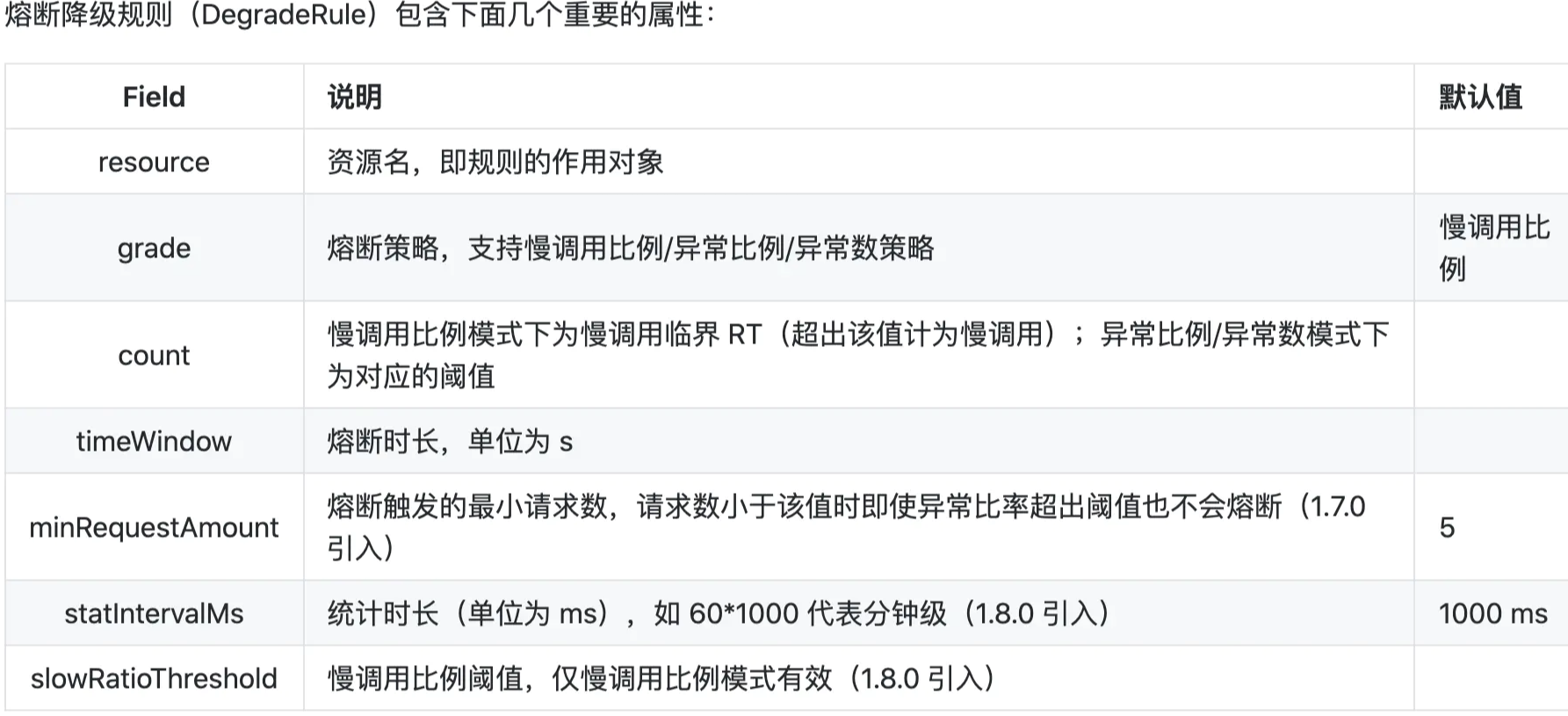
慢调用比例 (SLOW_REQUEST_RATIO):选择以慢调用比例作为阈值,需要设置允许的慢调用 RT(即最大的响应时间),请求的响应时间大于该值则统计为慢调用。当单位统计时长(statIntervalMs)内请求数目大于设置的最小请求数目,并且慢调用的比例大于阈值,则接下来的熔断时长内请求会自动被熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求响应时间小于设置的慢调用 RT 则结束熔断,若大于设置的慢调用 RT 则会再次被熔断。
-
异常比例 (ERROR_RATIO):当单位统计时长(statIntervalMs)内请求数目大于设置的最小请求数目,并且异常的比例大于阈值,则接下来的熔断时长内请求会自动被熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求成功完成(没有错误)则结束熔断,否则会再次被熔断。异常比率的阈值范围是 [0.0, 1.0],代表 0% - 100%。
-
异常数 (ERROR_COUNT):当单位统计时长内的异常数目超过阈值之后会自动进行熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求成功完成(没有错误)则结束熔断,否则会再次被熔断。
熔断状态,
- 熔断有三种状态,分别为OPEN、HALF_OPEN、CLOSED。
- OPEN:表示熔断开启,拒绝所有请求
- HALF_OPEN:探测恢复状态,如果接下来一个请求通过则结束熔断,否则继续熔断
- CLOSED:表示熔断关闭,请求顺利通过
规则构建
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager#newCircuitBreakerFrom
public final class DegradeRuleManager { //静态变量包含 resource信息 //(resource -> Breaker) private static volatile Map<String, List<CircuitBreaker>> circuitBreakers = new HashMap<>(); //(resource -> Breaker) private static volatile Map<String, Set<DegradeRule>> ruleMap = new HashMap<>(); private static CircuitBreaker newCircuitBreakerFrom(/*@Valid*/ DegradeRule rule) { switch (rule.getGrade()) { case RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT: return new ResponseTimeCircuitBreaker(rule); case RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO: case RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_COUNT: return new ExceptionCircuitBreaker(rule); default: return null; } } ////////// }
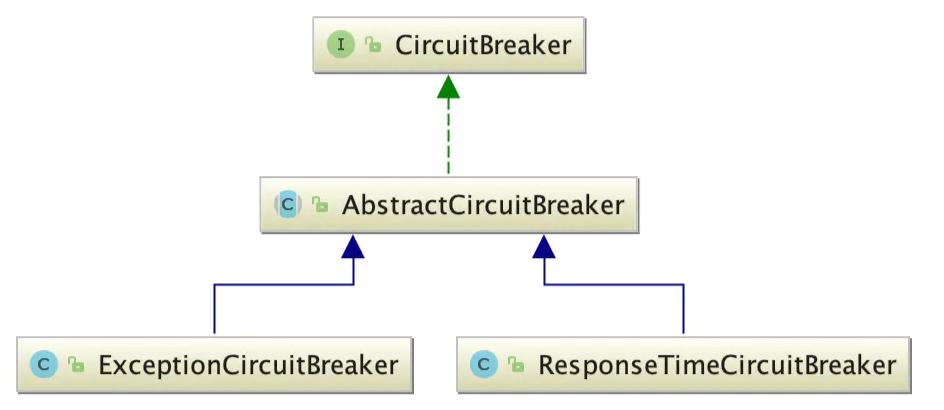
熔断拦截器主要包含ResponseTimeCircuitBreaker和ExceptionCircuitBreaker。
public class ExceptionCircuitBreaker extends AbstractCircuitBreaker { private final int strategy; private final int minRequestAmount; private final double threshold; private final LeapArray<SimpleErrorCounter> stat; @Override public void onRequestComplete(Context context) { Entry entry = context.getCurEntry(); if (entry == null) { return; } Throwable error = entry.getError(); SimpleErrorCounter counter = stat.currentWindow().value(); if (error != null) { counter.getErrorCount().add(1); } counter.getTotalCount().add(1); handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(error); } private void handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(Throwable error) { if (currentState.get() == State.OPEN) { return; } if (currentState.get() == State.HALF_OPEN) { // In detecting request if (error == null) { fromHalfOpenToClose(); } else { fromHalfOpenToOpen(1.0d); } return; } List<SimpleErrorCounter> counters = stat.values(); long errCount = 0; long totalCount = 0; for (SimpleErrorCounter counter : counters) { errCount += counter.errorCount.sum(); totalCount += counter.totalCount.sum(); } if (totalCount < minRequestAmount) { return; } double curCount = errCount; if (strategy == DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO) { // Use errorRatio curCount = errCount * 1.0d / totalCount; } if (curCount > threshold) { transformToOpen(curCount); } } }
引用资料: https://www.jianshu.com/p/500d461d2391
SystemSlot
是实现系统自适应限流的切入点。DegradeSlot 在 ProcessorSlotChain 链表中被放在 FlowSlot 的后面,作为限流的兜底解决方案,而 SystemSlot 在 ProcessorSlotChain 链表中被放在 FlowSlot 的前面,强制优先考虑系统目前的情况能否处理当前请求,让系统尽可能跑在最大吞吐量的同时保证系统的稳定性。
系统自适应限流规则针对所有流量类型为 IN 的资源生效,因此不需要配置规则的资源名称。SystemRule 定义的字段如下:
public class SystemRule extends AbstractRule { private double highestSystemLoad = -1; private double highestCpuUsage = -1; private double qps = -1; private long avgRt = -1; private long maxThread = -1; }
- qps:按 QPS 限流的阈值,默认 -1,大于 0 才生效。
- avgRt:按平均耗时的限流阈值,默认 -1,大于 0 才生效。
- maxThread:最大并行占用的线程数阈值,默认 -1,大于 0 才生效。
- highestCpuUsage:按 CPU 使用率限流的阈值,取值[0,1]之间,默认 -1,大于等于 0.0 才生效。
- highestSystemLoad:按系统负载限流的阈值,默认 -1,大于 0.0 才生效。
如果配置了多个 SystemRule,则每个配置项只取最小值。例如三个 SystemRule 都配置了 qps,则取这三个规则中最小的 qps 作为限流阈值,这在调用 SystemRuleManager#loadRules 方法加载规则时完成。
public static void loadSystemConf(SystemRule rule) { // 是否开启系统自适应限流判断功能 boolean checkStatus = false; // highestSystemLoad if (rule.getHighestSystemLoad() >= 0) { // 多个规则都配置则取最小值 highestSystemLoad = Math.min(highestSystemLoad, rule.getHighestSystemLoad()); highestSystemLoadIsSet = true; // 开启系统自适应限流检查功能 checkStatus = true; } // highestCpuUsage if (rule.getHighestCpuUsage() >= 0) { if (rule.getHighestCpuUsage() > 1) {} // [0,1) else { // 多个规则都配置则取最小值 highestCpuUsage = Math.min(highestCpuUsage, rule.getHighestCpuUsage()); highestCpuUsageIsSet = true; checkStatus = true; } } // avgRt if (rule.getAvgRt() >= 0) { // 多个规则都配置则取最小值 maxRt = Math.min(maxRt, rule.getAvgRt()); maxRtIsSet = true; checkStatus = true; } // maxThread if (rule.getMaxThread() >= 0) { // 多个规则都配置则取最小值 maxThread = Math.min(maxThread, rule.getMaxThread()); maxThreadIsSet = true; checkStatus = true; } // qps if (rule.getQps() >= 0) { // 多个规则都配置则取最小值 qps = Math.min(qps, rule.getQps()); qpsIsSet = true; checkStatus = true; } checkSystemStatus.set(checkStatus); }
SystemRuleManager#checkSystem 方法从全局的资源指标数据统计节点 Constans.ENTRY_NODE 读取当前时间窗口的指标数据,判断总的 QPS、平均耗时这些指标数据是否达到阈值,或者总占用的线程数是否达到阈值,如果达到阈值则抛出 Block 异常(SystemBlockException)。除此之外,checkSystem 方法还实现了根据系统当前 Load 和 CPU 使用率限流。
SystemRuleManager#checkSystem 方法源码如下:
public static void checkSystem(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) throws BlockException { if (resourceWrapper == null) { return; } // 如果有配置 SystemRule,则 checkSystemStatus 为 true if (!checkSystemStatus.get()) { return; } // 只限流类型为 IN 的流量 if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() != EntryType.IN) { return; } // qps 限流 double currentQps = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0.0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.successQps(); if (currentQps > qps) { throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "qps"); } // 占用线程数限流 int currentThread = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.curThreadNum(); if (currentThread > maxThread) { throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "thread"); } // 平均耗时限流 double rt = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.avgRt(); if (rt > maxRt) { throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "rt"); } // 系统平均负载限流 if (highestSystemLoadIsSet && getCurrentSystemAvgLoad() > highestSystemLoad) { if (!checkBbr(currentThread)) { throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "load"); } } // cpu 使用率限流 if (highestCpuUsageIsSet && getCurrentCpuUsage() > highestCpuUsage) { throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "cpu"); } }
获取系统负载和 CPU 使用率
Sentinel 通过定时任务每秒钟使用 OperatingSystemMXBean API 获取这两个指标数据的值,代码如下:
@Override public void run() { try { OperatingSystemMXBean osBean = ManagementFactory .getPlatformMXBean(OperatingSystemMXBean.class); // getSystemLoadAverage currentLoad = osBean.getSystemLoadAverage(); // getSystemCpuLoad currentCpuUsage = osBean.getSystemCpuLoad(); if (currentLoad > SystemRuleManager.getSystemLoadThreshold()) { writeSystemStatusLog(); } } catch (Throwable e) { RecordLog.warn("[SystemStatusListener] Failed to get system metrics from JMX", e); } }
详细参考: http://learn.lianglianglee.com/专栏/深入理解%20Sentinel(完)/13%20熔断降级与系统自适应限流.md


