sentinel笔记 NodeSelectorSlot,ClusterBuilderSlot
NodeSelectorSlot
NodeSelectorSlot 负责为资源的首次访问创建 DefaultNode,以及维护 Context.curNode 和调用树,
一次调用链路上出现多次调用SphU#entry,则每次调用生成的CEntry最终会变成双向链表,存储在Context中。
NodeSelectorSlot 被放在 ProcessorSlotChain 链表的第一个位置,这是因为后续的 ProcessorSlot 都需要依赖这个 ProcessorSlot。
public class NodeSelectorSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<Object> { // Context 的 name -> 资源的 DefaultNode private volatile Map<String, DefaultNode> map = new HashMap<>(10); // 入口方法 @Override public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable { // 使用 Context 的名称作为 key 缓存资源的 DefaultNode DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName()); if (node == null) { synchronized (this) { node = map.get(context.getName()); if (node == null) { // 为资源创建 DefaultNode node = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null); // 替换 map HashMap<String, DefaultNode> cacheMap = new HashMap<>(map.size()); cacheMap.putAll(map); cacheMap.put(context.getName(), node); map = cacheMap; // 绑定调用树 ((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node); } } } // 替换 Context 的 curNode 为当前 DefaultNode context.setCurNode(node); fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args); } // 出口方法什么也不做 @Override public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) { fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args); } }
NodeSelectorSlot#map的作用:
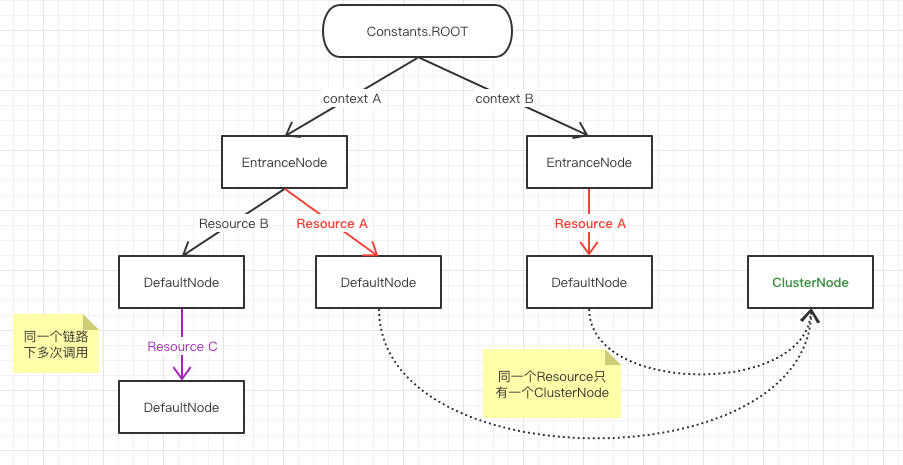
一个资源对应一个slotchain,一个slotchain下记录不同的context创建的DefaultNode.
Sentinel 会为同一资源 ID 创建多少个 DefaultNode 取决于有多少个调用链使用其作为入口资源,直白点就是同一资源存在多少个 DefaultNode 取决于 Context.name 有多少种不同取值,这就是为什么说一个资源可能有多个 DefaultNode 的原因。
举个例子,
对同一支付接口,我们需要使用 Spring MVC 暴露给前端访问,同时也可能会使用 Dubbo 暴露给其它内部服务调用。Sentinel 的 Web MVC 适配器在调用链路入口创建名为“sentinel_spring_web_context”的 Context,与 Sentinel 的 Dubbo 适配器调用 ContextUtil#enter 方法创建的 Context 名称不同。针对这种情况,我们可以实现只限制 Spring MVC 进来的流量,也就是限制前端发起接口调用的 QPS、并行占用的线程数等。
spring-webmvc默认拦截使用的context是由类com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.spring.webmvc.AbstractSentinelInterceptor来实现的,默认值是sentinel_spring_web_context 。
context+resource确认唯一的DeafultNode。
一个Resouce有且只有一个ClusterNode,一个 ClusterNode 负责统计一个资源的全局指标数据。
一个Resouce有且只有一个ProcessorSlotChain, 每个ProcessorSlotChain包含一个Map, 存储本resource下,context与DefaultNode的关系。
每个StatisticsNode还有Map,包含Node的origin信息,用来对不同来源的Node做区分统计。
小结:
- 一个调用链路上只会创建一个 Context,在调用链路的入口创建(一个调用链路上第一个被 Sentinel 保护的资源)。
- 一个 Context 名称只创建一个 EntranceNode,也是在调用链路的入口创建,调用 Context#enter 方法时创建。
- 与方法调用的入栈出栈一样,一个线程上调用多少次 SphU#entry 方法就会创建多少个 CtEntry,前一个 CtEntry 作为当前 CtEntry 的父节点,当前 CtEntry 作为前一个 CtEntry 的子节点,构成一个双向链表。Context.curEntry 保存的是当前的 CtEntry,在调用当前的 CtEntry#exit 方法时,由当前 CtEntry 将 Context.curEntry 还原为当前 CtEntry 的父节点 CtEntry。
- 一个调用链路上,如果多次调用 SphU#entry 方法传入的资源名称都相同,那么只会创建一个 DefaultNode,如果资源名称不同,会为每个资源名称创建一个 DefaultNode,当前 DefaultNode 会作为调用链路上的前一个 DefaultNode 的子节点。
- StatisticSlot 负责记录请求是否被放行、请求是否被拒绝、请求是否处理异常、处理请求的耗时等指标数据,在 StatisticSlot 调用 DefaultNode 用于记录某项指标数据的方法时,DefaultNode 也会调用 ClusterNode 的相对应方法,完成两份指标数据的收集。
- DefaultNode 统计当前资源的各项指标数据的维度是同一个 Context(名称相同),而 ClusterNode 统计当前资源各项指标数据的维度是全局。
node关系表
ClusterNode 构造器:ClusterBuilderSlot
ClusterNode 出现的背景
在一个资源的 ProcessorSlotChain 中,NodeSelectorSlot 负责为资源创建 DefaultNode,这个 DefaultNode 仅限同名的 Context 使用。所以一个资源可能会存在多个 DefaultNode,那么想要获取一个资源的总的 QPS 就必须要遍历这些 DefaultNode。为了性能考虑,Sentinel 会为每个资源创建一个全局唯一的 ClusterNode,用于统计资源的全局并行占用线程数、QPS、异常总数等指标数据。
public class ClusterBuilderSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> { // 资源 -> ClusterNode private static volatile Map<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> clusterNodeMap = new HashMap<>(); private static final Object lock = new Object(); // 非静态,一个资源对应一个 ProcessorSlotChain,所以一个资源共用一个 ClusterNode private volatile ClusterNode clusterNode = null; @Override public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable { if (clusterNode == null) { synchronized (lock) { if (clusterNode == null) { // 创建 ClusterNode clusterNode = new ClusterNode(resourceWrapper.getName(), resourceWrapper.getResourceType()); // 添加到缓存 HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(Math.max(clusterNodeMap.size(), 16)); newMap.putAll(clusterNodeMap); newMap.put(node.getId(), clusterNode); clusterNodeMap = newMap; } } } // node 为 NodeSelectorSlot 传递过来的 DefaultNode node.setClusterNode(clusterNode); // 如果 origin 不为空,则为远程创建一个 StatisticNode if (!"".equals(context.getOrigin())) { Node originNode = node.getClusterNode().getOrCreateOriginNode(context.getOrigin()); context.getCurEntry().setOriginNode(originNode); } fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args); } @Override public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) { fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args); } } // ClusterNode#getOrCreateOriginNode //origin 表示来源应用的名称 public Node getOrCreateOriginNode(String origin) { StatisticNode statisticNode = originCountMap.get(origin); if (statisticNode == null) { lock.lock(); try { statisticNode = originCountMap.get(origin); if (statisticNode == null) { // The node is absent, create a new node for the origin. statisticNode = new StatisticNode(); HashMap<String, StatisticNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(originCountMap.size() + 1); newMap.putAll(originCountMap); newMap.put(origin, statisticNode); originCountMap = newMap; } } finally { lock.unlock(); } } return statisticNode; }
备注:
ClusterNode 有一个 Map 类型的字段用来缓存 origin 与 StatisticNode 的映射,如果上游服务在调用当前服务的接口传递 origin 字段过来,那么 ClusterBuilderSlot 就会为 ClusterNode 创建一个 StatisticNode,用来统计当前资源被远程服务调用的指标数据。
例如,当 origin 表示来源应用的名称时,对应的 StatisticNode 统计的就是针对该调用来源的指标数据,可用来查看哪个服务访问这个接口最频繁,由此可实现按调用来源限流。
资源指标数据统计:StatisticSlot
StatisticSlot 才是实现资源各项指标数据统计的 ProcessorSlot,它与 NodeSelectorSlot、ClusterBuilderSlot 组成了资源指标数据统计流水线,分工明确。
首先 NodeSelectorSlot 为资源创建 DefaultNode,将 DefaultNode 向下传递,ClusterBuilderSlot 负责给资源的 DefaultNode 加工,添加 ClusterNode 这个零部件,再将 DefaultNode 向下传递给 StatisticSlot。
源码比较简单,
public class StatisticSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> { @Override public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable { try {// 这里先调用其他Slot的方法,然后由StatisticsSlot做统计数据。 fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args); // 增加线程数,pass个数 node.increaseThreadNum(); node.addPassRequest(count); //如果Origin不为空,则处理OriginNode统计信息 if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) { context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum(); context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count); } //如果流量类型为 IN,则将资源全局唯一的 ClusterNode 的并行占用线程数、当前时间窗口被放行的请求数都增加 1 if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) { // Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics. Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum(); Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count); } // 处理自定义扩展回调 for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) { handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args); } } catch (PriorityWaitException ex) { //当捕获到 PriorityWaitException 异常时,说明当前请求已经被休眠了一会了,但请求还是允许通过的, //只自增当前资源并行占用的线程数 node.increaseThreadNum(); if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) { context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum(); } if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) { Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum(); } for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) { handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args); } } catch (BlockException e) { //BlockException 异常只在需要拒绝请求时抛出, 此处记录下本异常. context.getCurEntry().setBlockError(e); // 记录Block个数, 线程数-1 node.increaseBlockQps(count); if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) { context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseBlockQps(count); } //如果流量类型为 IN,增加全局block个数 if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) { // Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics. Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseBlockQps(count); } // 处理自定义扩展回调 for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) { handler.onBlocked(e, context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args); } throw e; } catch (Throwable e) { // Unexpected internal error, set error to current entry. context.getCurEntry().setError(e); throw e; } } @Override public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) { Node node = context.getCurNode(); if (context.getCurEntry().getBlockError() == null) { // Calculate response time (use completeStatTime as the time of completion). long completeStatTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(); context.getCurEntry().setCompleteTimestamp(completeStatTime); long rt = completeStatTime - context.getCurEntry().getCreateTimestamp(); Throwable error = context.getCurEntry().getError(); // Record response time and success count. recordCompleteFor(node, count, rt, error); //处理OriginNode数据 recordCompleteFor(context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode(), count, rt, error); if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) { recordCompleteFor(Constants.ENTRY_NODE, count, rt, error); } } // Handle exit event with registered exit callback handlers. // 处理自定义扩展回调 Collection<ProcessorSlotExitCallback> exitCallbacks = StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getExitCallbacks(); for (ProcessorSlotExitCallback handler : exitCallbacks) { handler.onExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args); } fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count); } private void recordCompleteFor(Node node, int batchCount, long rt, Throwable error) { if (node == null) { return; } node.addRtAndSuccess(rt, batchCount); node.decreaseThreadNum(); if (error != null && !(error instanceof BlockException)) { node.increaseExceptionQps(batchCount); } } }
注意点:
1. StatisticsSlot是在所有其他Slot执行完之后再做统计信息
2. entry操作时只统计线程个数,Pass个数,被熔断时统计Block个数
3. exit正常退出时才统计 RT, Sucess个数,减少线程个数。
参照站点: http://learn.lianglianglee.com/%E4%B8%93%E6%A0%8F/%E6%B7%B1%E5%85%A5%E7%90%86%E8%A7%A3%20Sentinel%EF%BC%88%E5%AE%8C%EF%BC%89/08%20%E8%B5%84%E6%BA%90%E6%8C%87%E6%A0%87%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%9F%E8%AE%A1%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E5%85%A8%E8%A7%A3%E6%9E%90%EF%BC%88%E4%B8%8A%EF%BC%89.md



