Eureka源码解析(三)
Eureka Server收到请求之后的处理
Eureka Server端如何对请求过来的服务实例数据进行了存储的?
请求入口在: com.netflix.eureka.resources.ApplicationResource.addInstance() 。
这里可以发现,这里所提供的REST服务,采用的是jersey来实现的。Jersey是基于JAX-RS标准,提供REST的实现的支持。
ApplicationResource.addInstance()
当EurekaClient调用register方法发起注册时,会调用ApplicationResource.addInstance方法。
服务注册就是发送一个 POST 请求带上当前实例信息到类 ApplicationResource 的 addInstance方法进行服务注册
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info,
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
//...
DataCenterInfo dataCenterInfo = info.getDataCenterInfo();
if (dataCenterInfo instanceof UniqueIdentifier) {
String dataCenterInfoId = ((UniqueIdentifier) dataCenterInfo).getId();
if (isBlank(dataCenterInfoId)) {
boolean experimental = "true".equalsIgnoreCase(serverConfig.getExperimental("registration.validation.dataCenterInfoId"));
if (experimental) {
String entity = "DataCenterInfo of type " + dataCenterInfo.getClass() + " must contain a valid id";
return Response.status(400).entity(entity).build();
} else if (dataCenterInfo instanceof AmazonInfo) {
AmazonInfo amazonInfo = (AmazonInfo) dataCenterInfo;
String effectiveId = amazonInfo.get(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId);
if (effectiveId == null) {
amazonInfo.getMetadata().put(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId.getName(), info.getId());
}
} else {
logger.warn("Registering DataCenterInfo of type {} without an appropriate id", dataCenterInfo.getClass());
}
}
}
registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));
return Response.status(204).build(); // 204 to be backwards compatible
}
PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.register
我们先来看PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl的类关系图,从类关系图可以看出,PeerAwareInstanceRegistry的最顶层接口为LeaseManager与LookupService,
- 其中LookupService定义了最基本的发现示例的行为
- LeaseManager定义了处理客户端注册,续约,注销等操作
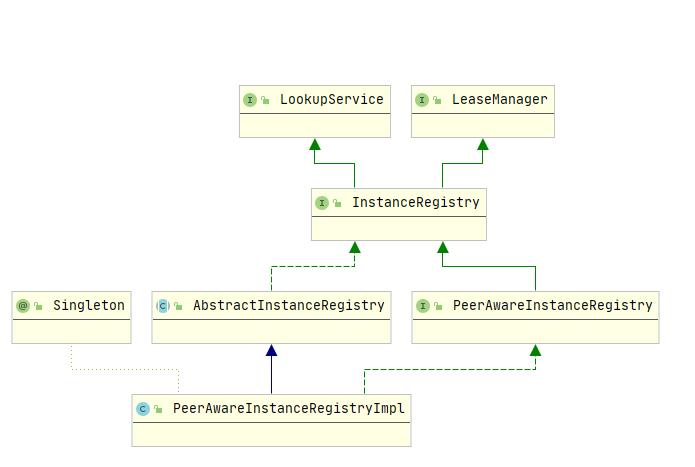
在 addInstance 方法中,最终调用的是 PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.register 方法。
- leaseDuration 表示租约过期时间,默认是90s,也就是当服务端超过90s没有收到客户端的心跳,则主动剔除该节点
- 调用super.register发起节点注册
- 将信息复制到Eureka Server集群中的其他机器上,同步的实现也很简单,就是获得集群中的所有节点,然后逐个发起注册
@Override
public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS;
if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) {
//如果客户端有自己定义心跳超时时间,则采用客户端的时间
leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs();
}
//节点注册
super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);
//复制到Eureka Server集群中的其他节点
replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);
}
AbstractInstanceRegistry.register
简单来说,Eureka-Server的服务注册,实际上是将客户端传递过来的实例数据保存到Eureka-Server中的ConcurrentHashMap中。
public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
try {
read.lock();
//从registry中获得当前实例信息,根据appName
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName());
//增加注册次数到监控信息中
REGISTER.increment(isReplication);
//如果当前appName是第一次注册,则初始化一个ConcurrentHashMap
if (gMap == null) {
final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>();
gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);
if (gMap == null) {
gMap = gNewMap;
}
}
//从gMap中查询已经存在的Lease信息,Lease中文翻译为租约,实际上它把服务提供者的实例信息包装成了一个lease,里面提供了对于改服务实例的租约管理
Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId());
// 当instance已经存在是,和客户端的instance的信息做比较,时间最新的那个,为有效instance信息
if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) {
Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp();
Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp();
logger.debug("Existing lease found (existing={}, provided={}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);
// this is a > instead of a >= because if the timestamps are equal, we still take the remote transmitted
// InstanceInfo instead of the server local copy.
if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) {
logger.warn("There is an existing lease and the existing lease's dirty timestamp {} is greater" +
" than the one that is being registered {}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);
logger.warn("Using the existing instanceInfo instead of the new instanceInfo as the registrant");
registrant = existingLease.getHolder();
}
} else {
//当lease不存在时,进入到这段代码
synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) {
// Since the client wants to register it, increase the number of clients sending renews
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews + 1;
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
}
}
logger.debug("No previous lease information found; it is new registration");
}
//构建一个lease
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);
if (existingLease != null) {
//当原来存在Lease的信息时,设置serviceUpTimestamp, 保证服务启动的时间一直是第一次注册的那个
lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp());
}
gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease);
//添加到最近注册的队列中
recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(
System.currentTimeMillis(),
registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")"));
// 检查实例状态是否发生变化,如果是并且存在,则覆盖原来的状态
if (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) {
logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the "
+ "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId());
if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) {
logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId());
overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus());
}
}
InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId());
if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) {
logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap);
registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap);
}
// Set the status based on the overridden status rules
InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication);
registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);
//得到instanceStatus,判断是否是UP状态,
if (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) {
lease.serviceUp();
}
// 设置注册类型为添加
registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED);
// 租约变更记录队列,记录了实例的每次变化, 用于注册信息的增量获取
recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease));
registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();
// 让缓存失效
invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress());
logger.info("Registered instance {}/{} with status {} (replication={})",
registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getId(), registrant.getStatus(), isReplication);
} finally {
read.unlock();
}
}
总结
至此,服务注册在客户端和服务端的处理过程做了一个详细的分析,实际上在Eureka Server端,会把客户端的地址信息保存到ConcurrentHashMap中存储。并且服务提供者和注册中心之间,会建立一个心跳检测机制,用于监控服务提供者的健康状态。



